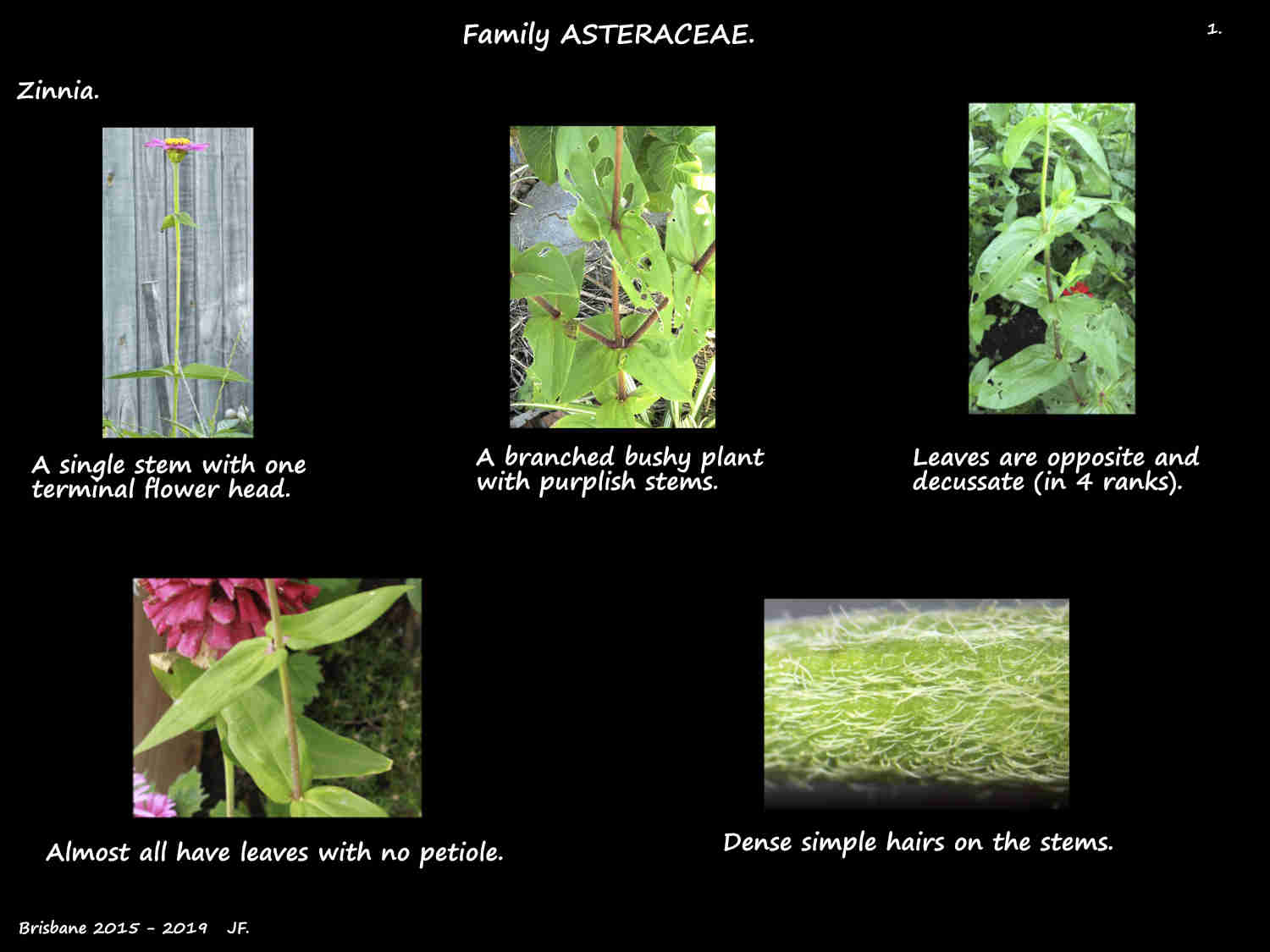
Zinnia.
Family Asteraceae > Subfamily Asteroideae > Tribe Heliantheae > Subtribe Zinniinae.
The 23 (17 to 25) species of Zinnias are native to North and South America especially Mexico.
They are annual or perennial herbs or small shrubs.
The erect or occasionally prostrate plants are from 10 cm to 1 m high.
Growing from a taproot the stems can be circular or angled and smooth or finely ribbed.
There are hairs on the green or sometimes purplish stems.
The simple opposite (subopposite) leaves occasionally have a short petiole.
Most have leaf bases that are joined around the stem.
The mid to light green leaves are lance-shaped linear oblong or ovate.
There are 1, 3 or 5 nerves from the round or wedge-shaped base.
There are hairs and usually scattered glands.
The solitary terminal flower heads are on a hollow peduncle that can be smooth or slightly ribbed.
It may be wider at the top where there are usually some hairs.
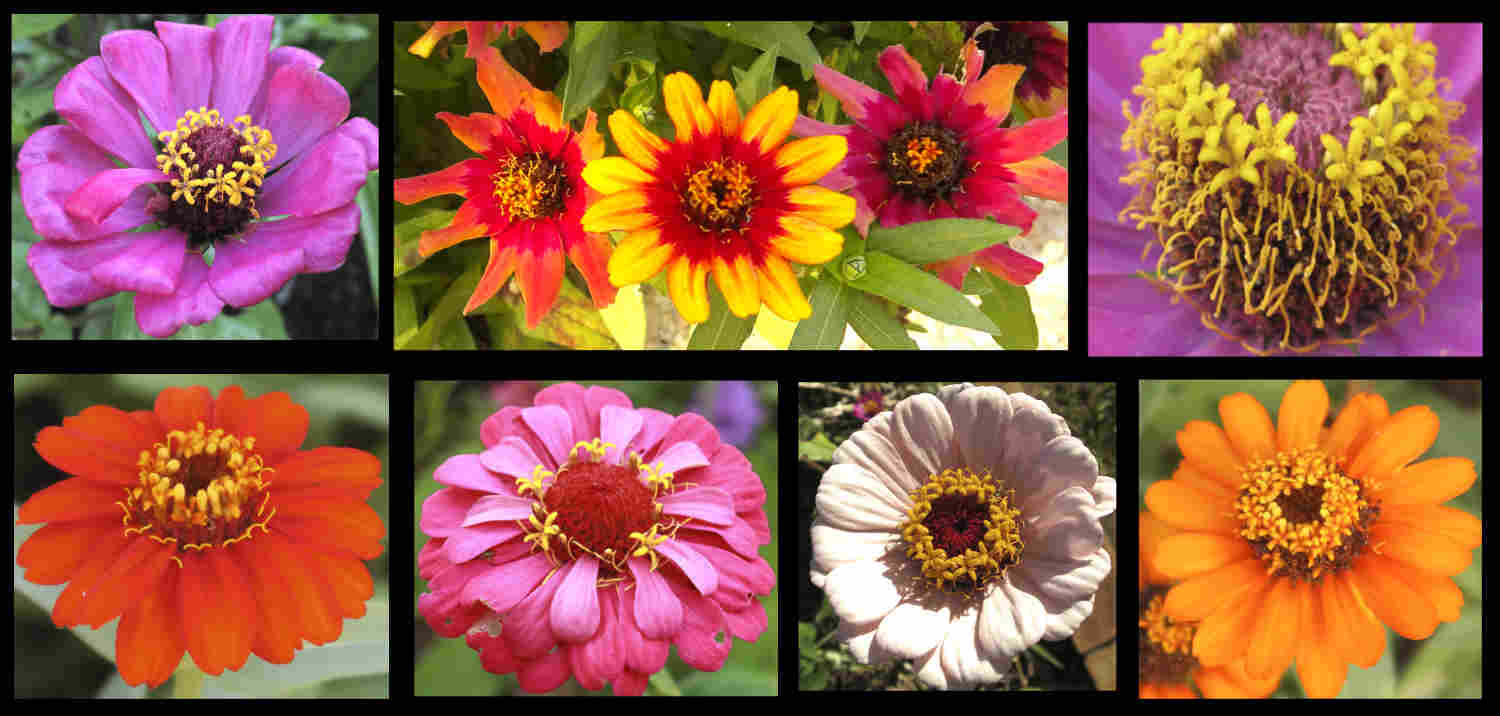
Almost all species have both ray and disk florets in the heads.
The basal involucre has 3 or more whorls of overlapping bracts or phyllaries.
Of different sizes they are oblong to obovate and usually with a rounded tip.
The often darker coloured tips are finely incised or have fine hairs.
The receptacle holding the florets is convex, cone-shaped or cylindrical.
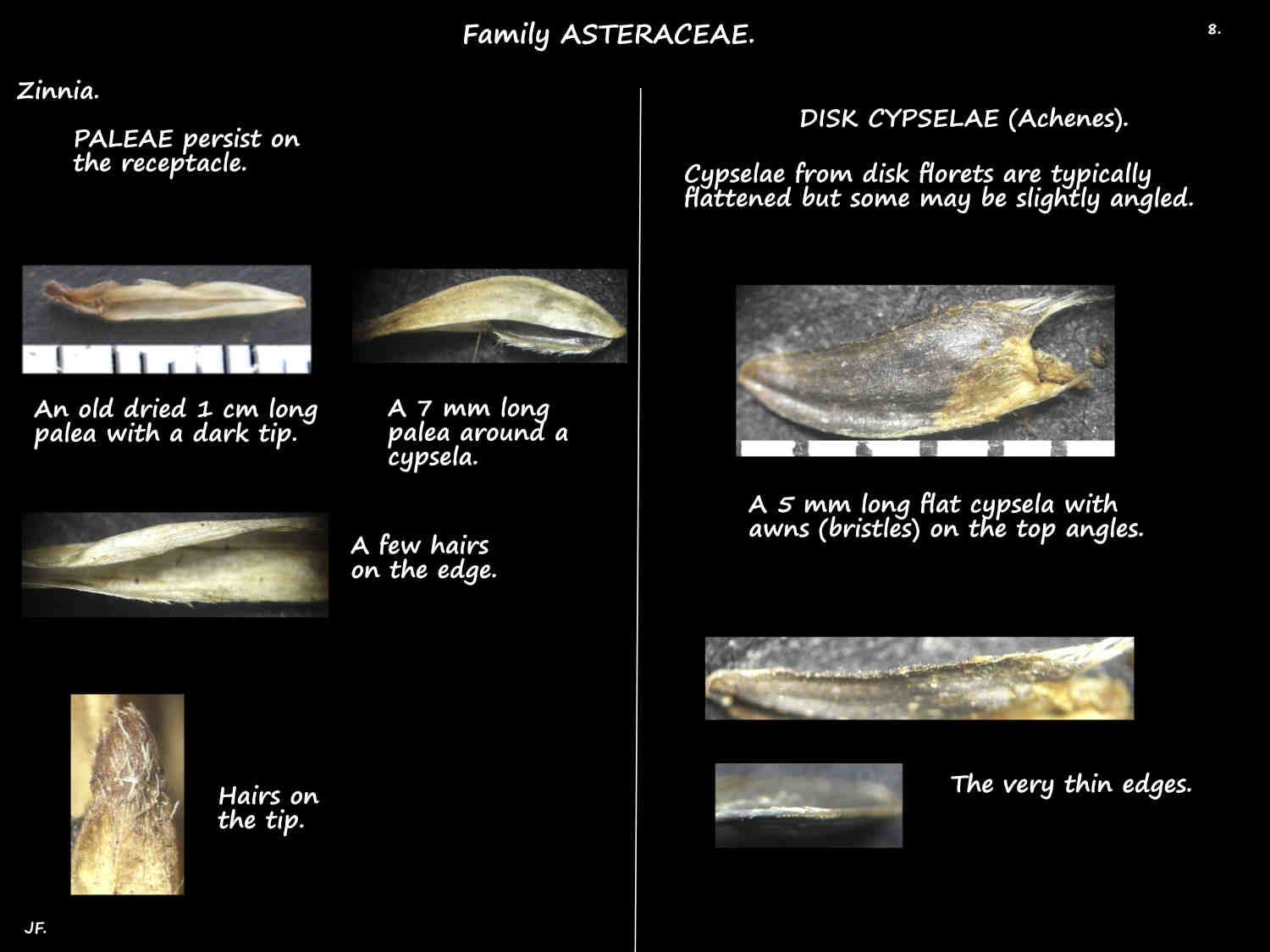
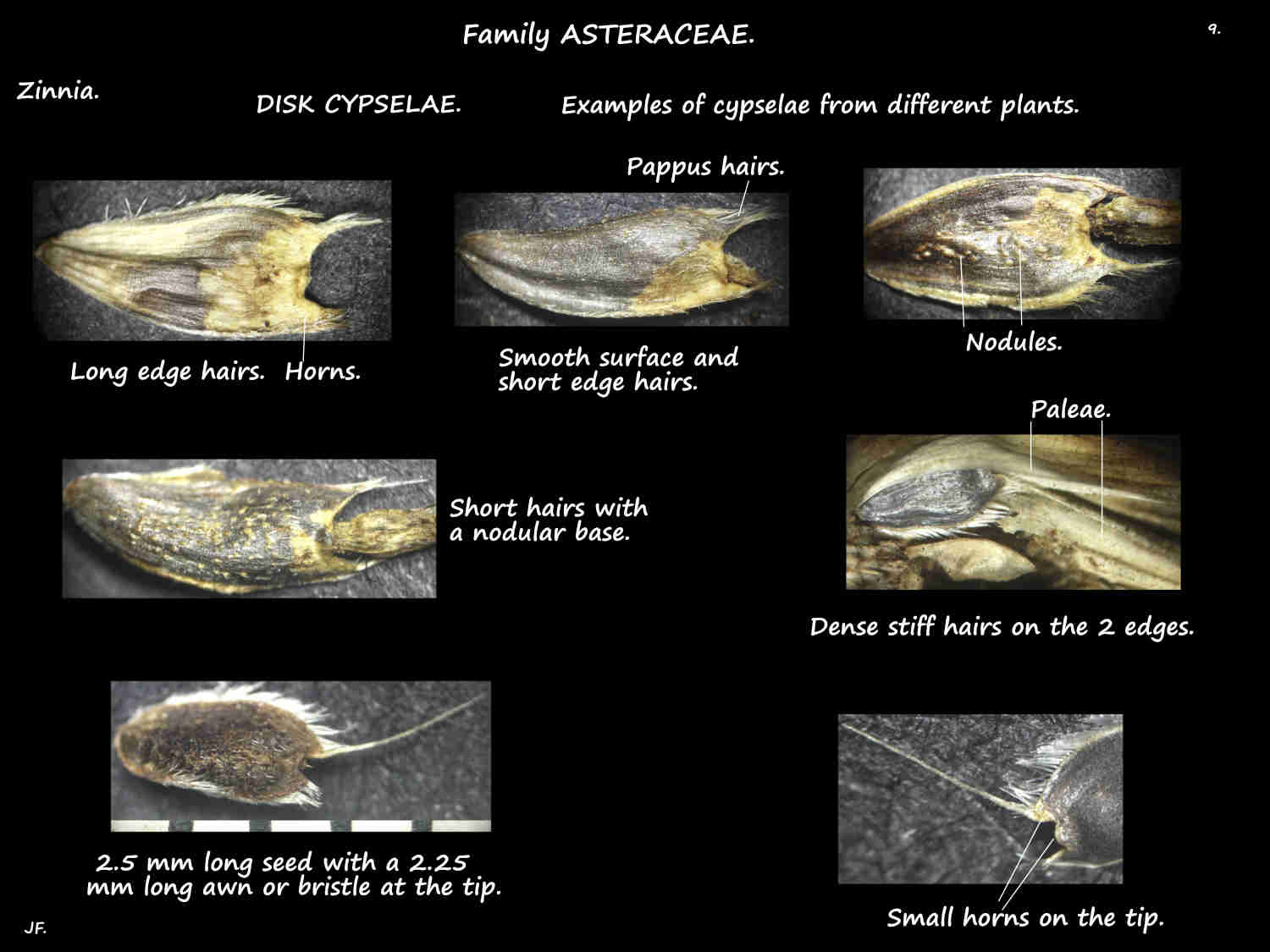
The persistent yellow red or purplish scales or paleae (the chaff) on the receptacle have a fringed tip.
There are one or more rows of fertile female ray florets around the edge of the head.
The obovate ligule, with 1 to 3 small lobes may or may not be on a tubular base.
Ray florets come in a wide range of colours including red, white, yellow and purple.
They have an inferior, smooth or hairy ovary and a style with 2 linear stigma lobes.
The usually yellow or reddish bisexual disk florets have a tubular base with 5 pointed lobes.
The corolla tube may be wider at the base or the same width throughout.
One of the lobes is usually larger and all lobes may have dense hairs on the inner surface.
The 5 stamen filaments are inserted onto the base of the corolla tube.
The loosely joined anthers have apical appendages and may have downward pointing basal lobes.
The inferior ovary has 1 style with 2 flattened branches with the linear stigmas.
The fruit are cypselae often incorrectly called achenes which come from a superior ovary.
Cypselae vary between the species and can be from 4 to 10 mm long.
Those from ray florets are distinctly 3-angled while disk cypselae are typically flattened although some may be slightly angled.
The surface can be smooth, nodular or hairy and there may be a beak or horns.
Hairs may be all over or mainly along the edges or angles.
There may have no pappus or one or two awns or bristles at the top.
Species available in Australia include Zinnia elegans, Zinnia grandiflora, Zinnia haageana,
Zinnia marylandica and Zinnia peruviana although most garden zinnias are cultivars of these.
J.F.