Gazania.
Family Asteraceae > Subfamily Vernonioideae > Tribe Arctotideae > Subtribe Gorteriinae.
Mabberley and most others accept 16 species and Plants of the World Online 19.
Excluding spelling variations World Flora Online recognises 22 species.
Native to Southern Africa two species, G. linearis and G. rigens are naturalised in Australia.
Plants can be invasive and are a declared weed in some areas.
Species, and the many cultivars are common garden plants.
Because they hybridise so easily it can sometimes be difficult to distinguish them.
Almost all species are perennial herbs with a few annuals and small subshrubs.
They form clumps and with new plants growing along the rhizomes can cover large areas.
They can form dense mats up to around 30 cm high on the ground while others are trailing.
Parts have a lot of milky latex.
The alternate leaves, with or without a petiole are crowded at the base and rarely on a stem.
Up to 20 or 30 cm long they are mostly spoon-shaped or oblanceolate with some almost linear.
The green blue-green or silvery blades can be entire or lobed.
Unlobed leaves have a pointed tip and there are occasionally small spines on the edge.
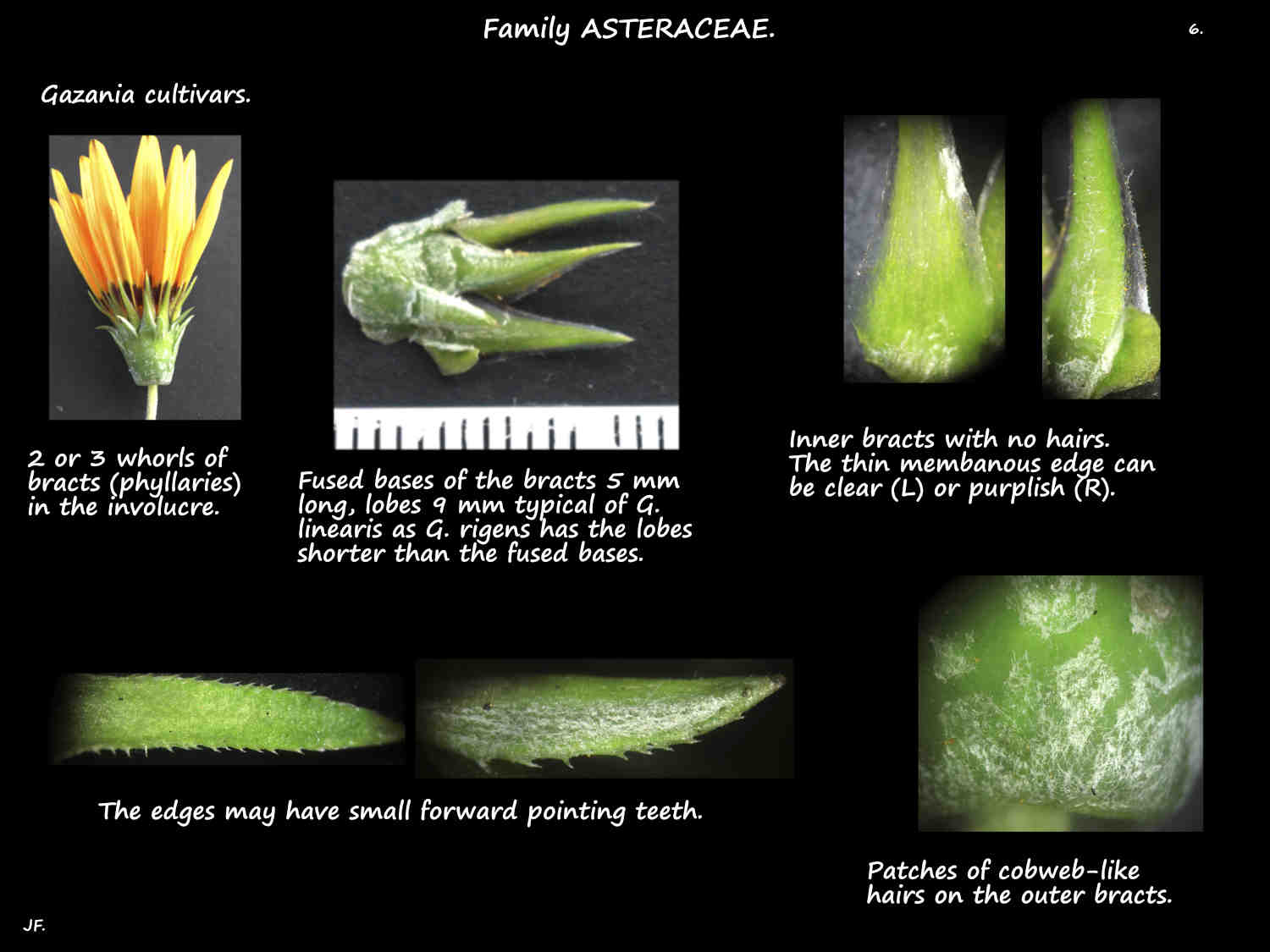
The upper surface may have no hairs or a few long cobweb-like ones.
The lower surface is white due to the dense long matted hairs.
Old dead leaves may fall off or persist.
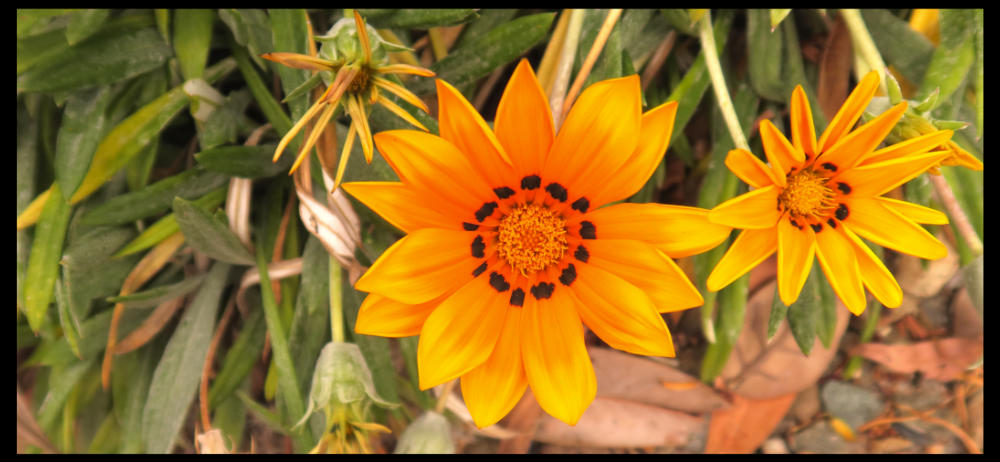
The solitary flower heads or capitula are on a stalk or peduncle up to 20 or 30 cm long.
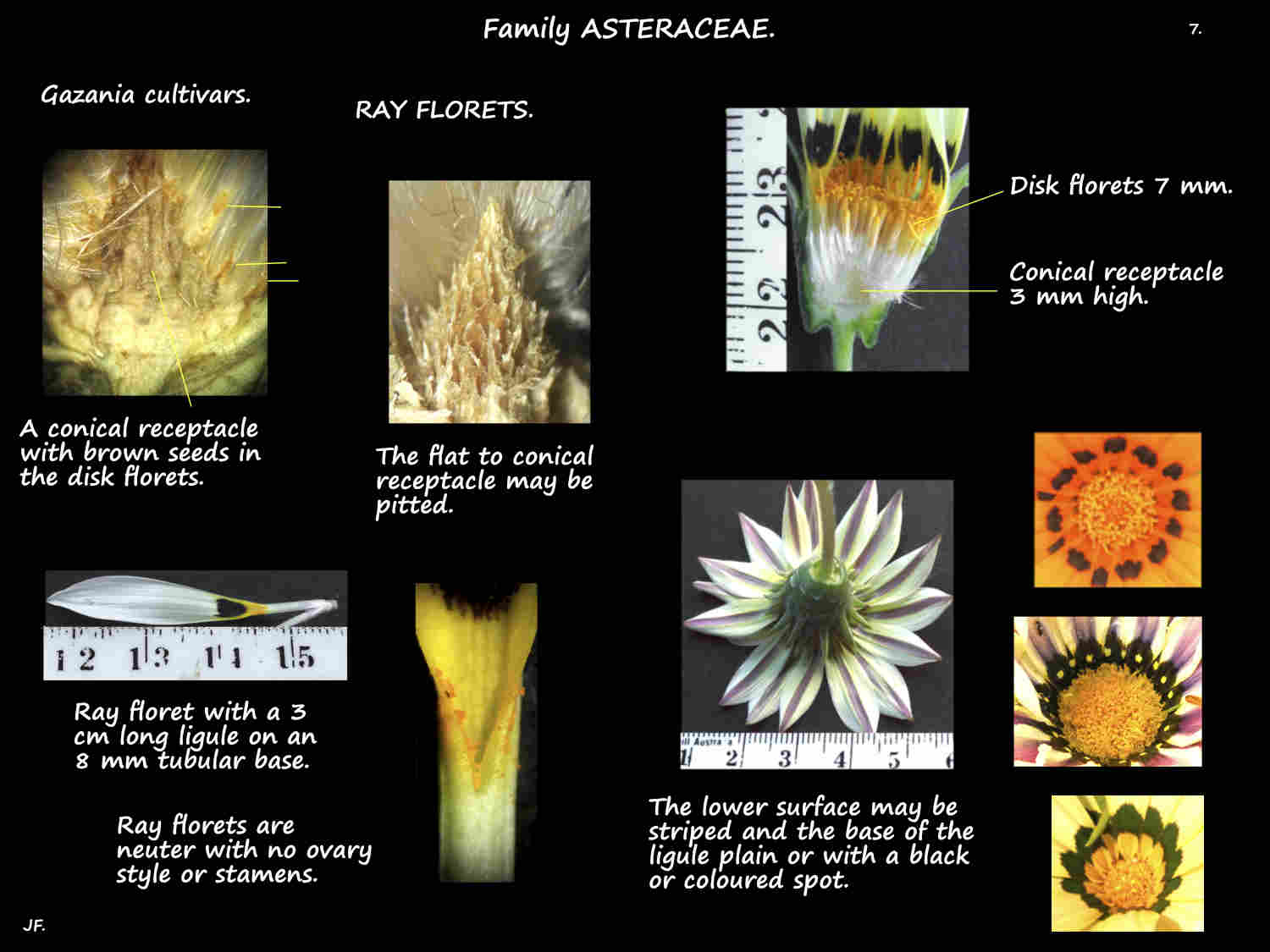
The bell-shaped heads, up to 12 cm across have both ray and disk florets.
The involucre at the base of the head has 2 to 3 (4) rows of overlapping bracts or phyllaries.
They are joined at the base forming a cup that covers the base of the florets.
The green bract lobes, longer or shorter than the cup are lance-shaped with thin margins.
The flat to convex receptacle holding the florets has no scales (paleae).
The single row of ray florets at the edge of the head have no sexual parts.
The corolla tube has a large ligule with 4 small lobes at the tip.
The mostly yellow, orange or sometimes reddish upper surface may have a dark area at the base
with or without a white dot on it.
The lower or outer surface sometimes has a green or reddish stripe.
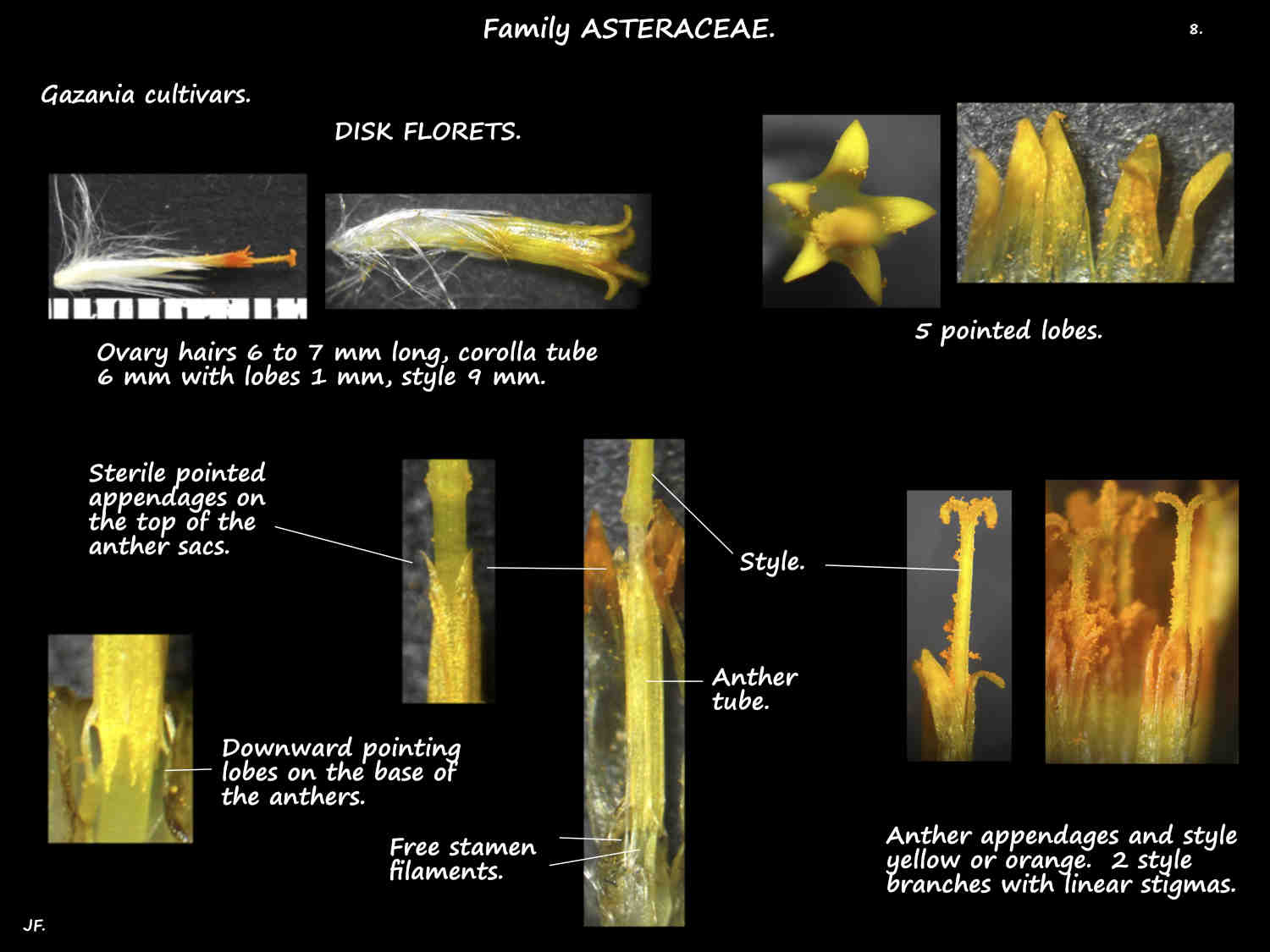
The numerous yellow disk florets have a tubular base with 5 short pointed lobes.
Disk florets are bisexual with the outer ones being fertile and the inner ones sterile or functionally male.
The anthers of the 5 stamens are fused into a tube except for the downward pointing lower lobes and the tip appendage.
The inferior ovary has a thin style with hairs just below the 2 style branches.
In sterile disk flowers the style does not divide at the top.
The cypselae (commonly called achenes) have the other flower parts still attached.
The seeds are narrowly obovoid to obconical with or without faint ribs.
They are surrounded by the long silky hairs on the wall of the ovary.
The pappus, at the top of the ovary and external to the corolla has 2 rows of scales shorter or as long as the hairs on the ovary.
The around 8 thin narrow pappus scales can be difficult to see among the ovary hairs.
Gazania cultivars.
Species seen here are G. linearis and the trailing or clumping varieties of G. rigens.
As well as shades of yellow and orange cultivars come in many colours including red, pink, maroon, burgundy,
copper and cream either with or without the dark basal spot.
There are also some doubles with more rows of ray florets.
J.F.