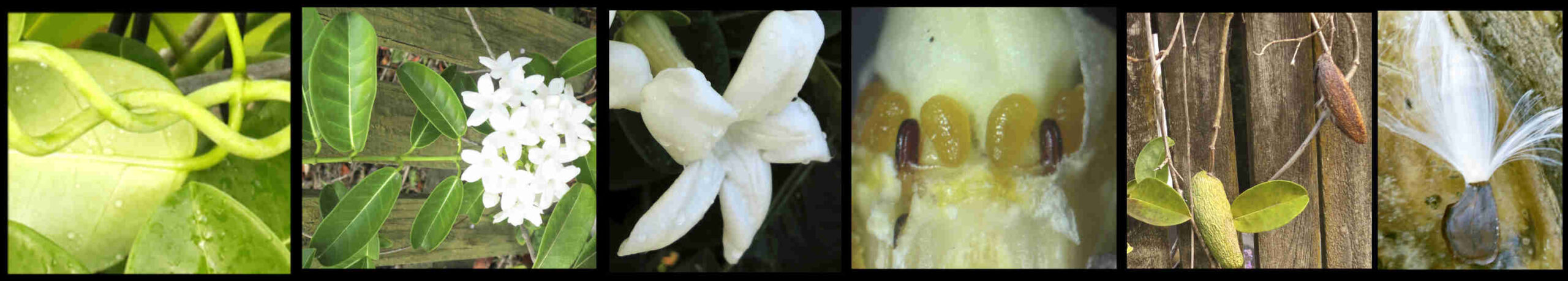
Stephanotis floribunda
Family Apocynaceae > Subfamily Asclepiadoideae > Tribe Marsdenieae.
Madagascar jasmine was known for a period as Marsdenia floribunda.
It is a commonly cultivated plant.
The woody vines (lianas) have twining stems up to around 6 m long.
The little branched stems and the leaves have a milky latex.
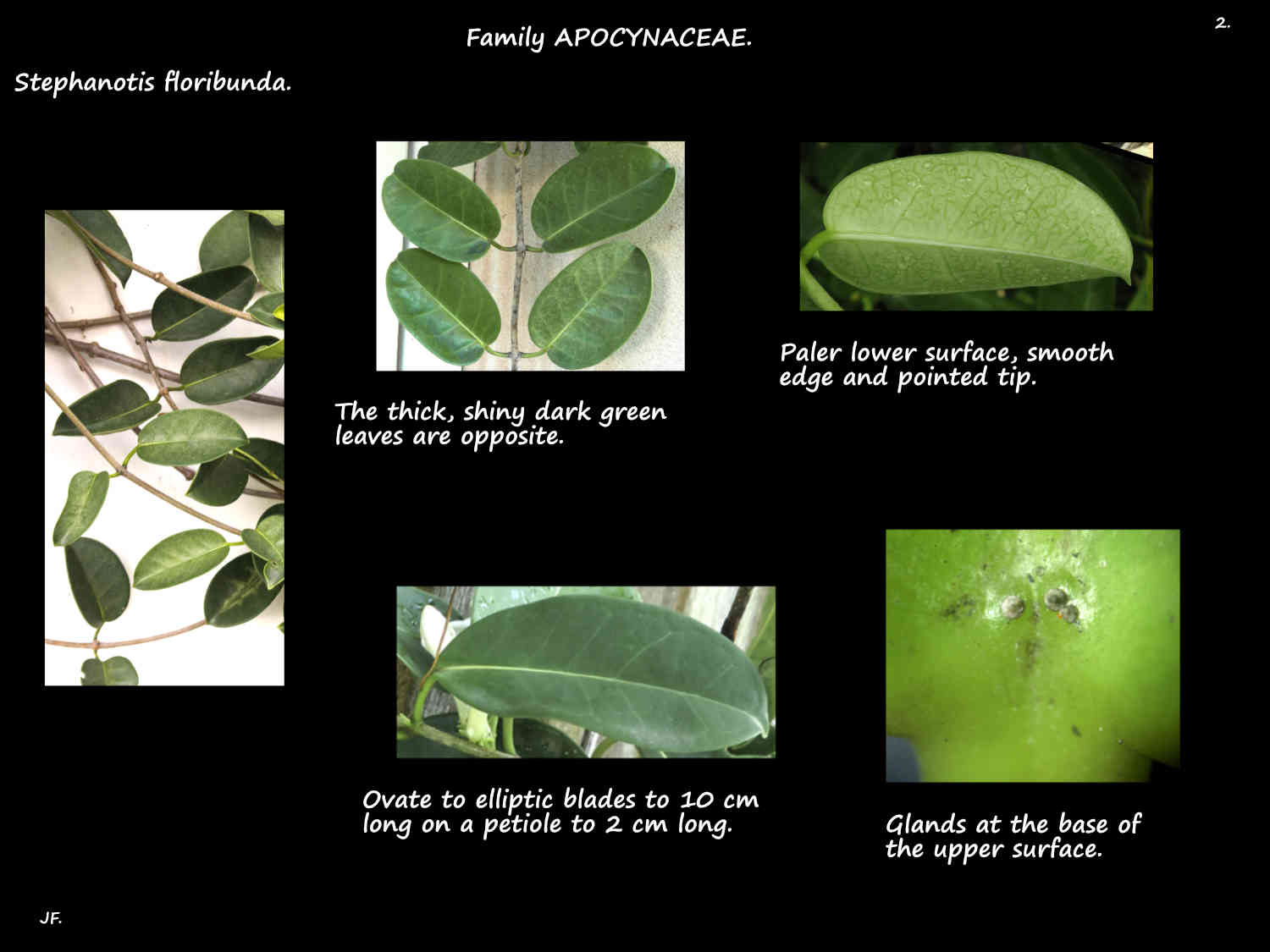
The simple dark green leaves, on a petiole up to 2 cm long are opposite.
The ovate to elliptic blade is up to 10 cm long and 6 cm wide.
They have a mucro (small abrupt point) at the tip, a rounded base and a smooth edge.
There are no hairs but the base of the upper blade surface has small glands.
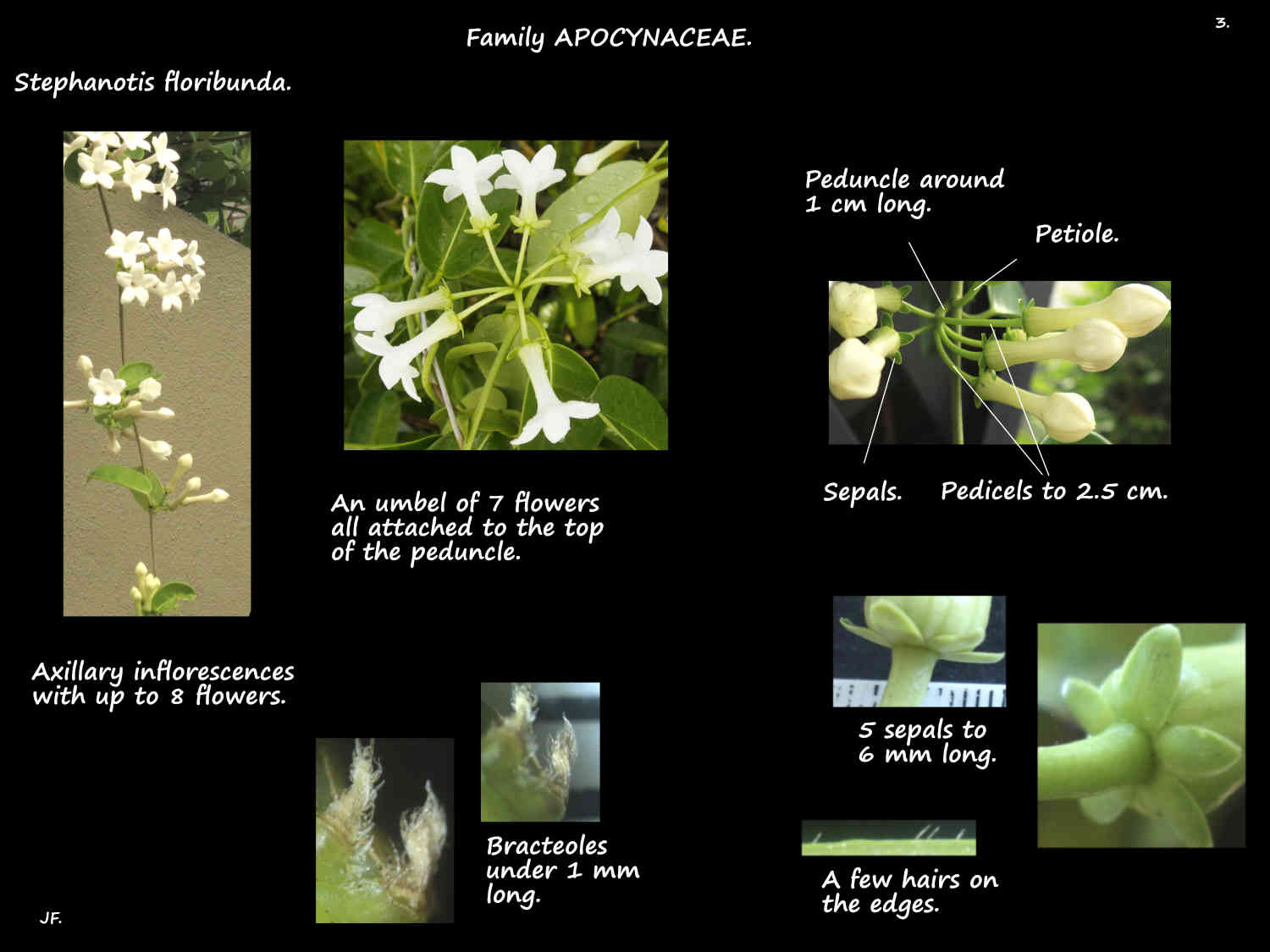
Axillary inflorescences are a cluster of up to around 8 flowers in an umbel.
In an umbel all the flower stalks (pedicels) are attached to the top of the peduncle.
The peduncles are around 1 cm long and the pedicels 2.5 cm.
There are small bracteoles at base of the pedicels.
The highly scented flowers appear on new growth.
The calyx has 5 free green sepals around 6 mm long.
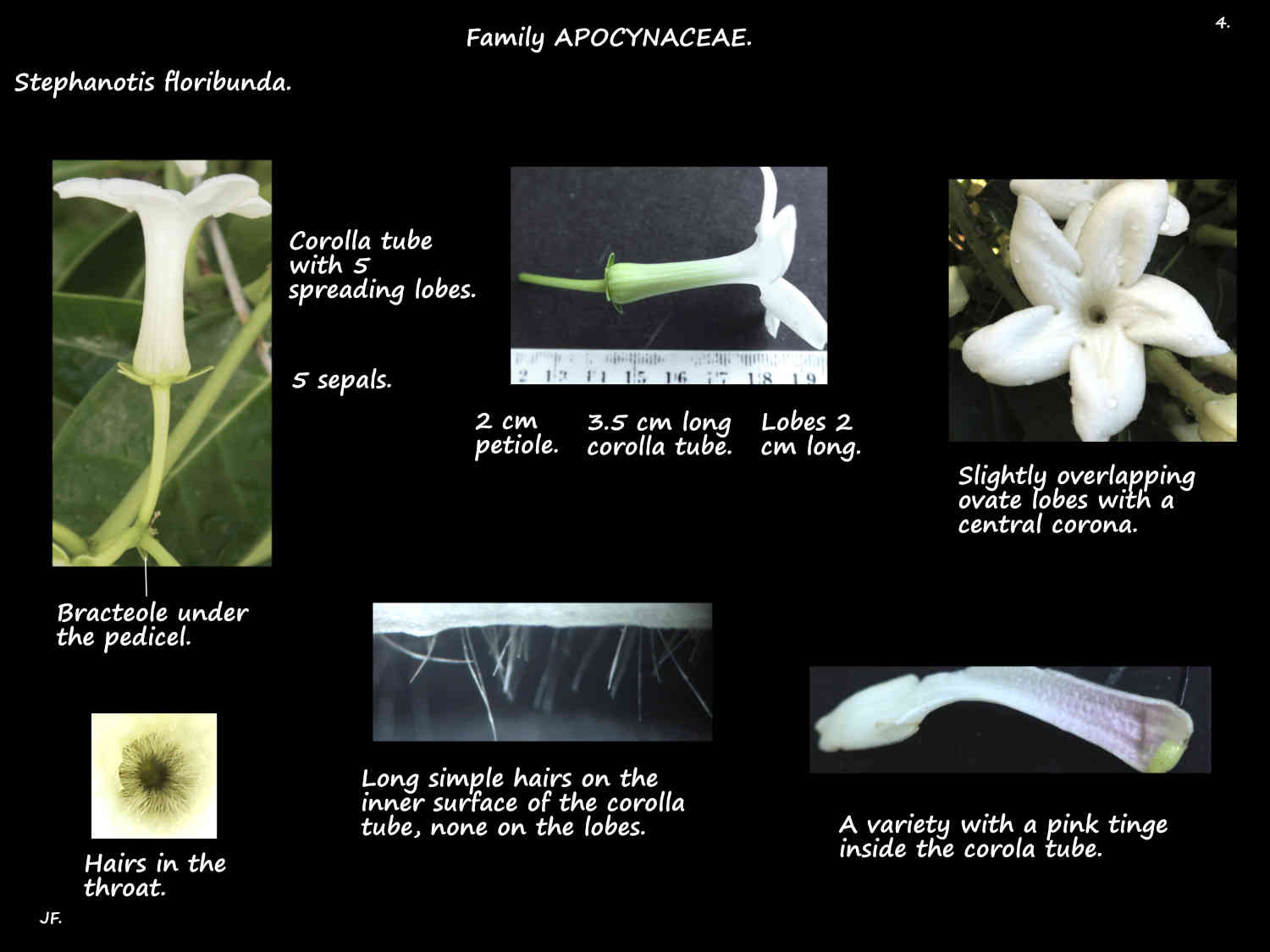
The funnel-shaped corolla is up to 3 cm long.
It has a tubular base with 5 spreading ovate lobes around 1 cm long.
They are white then become cream as they age.
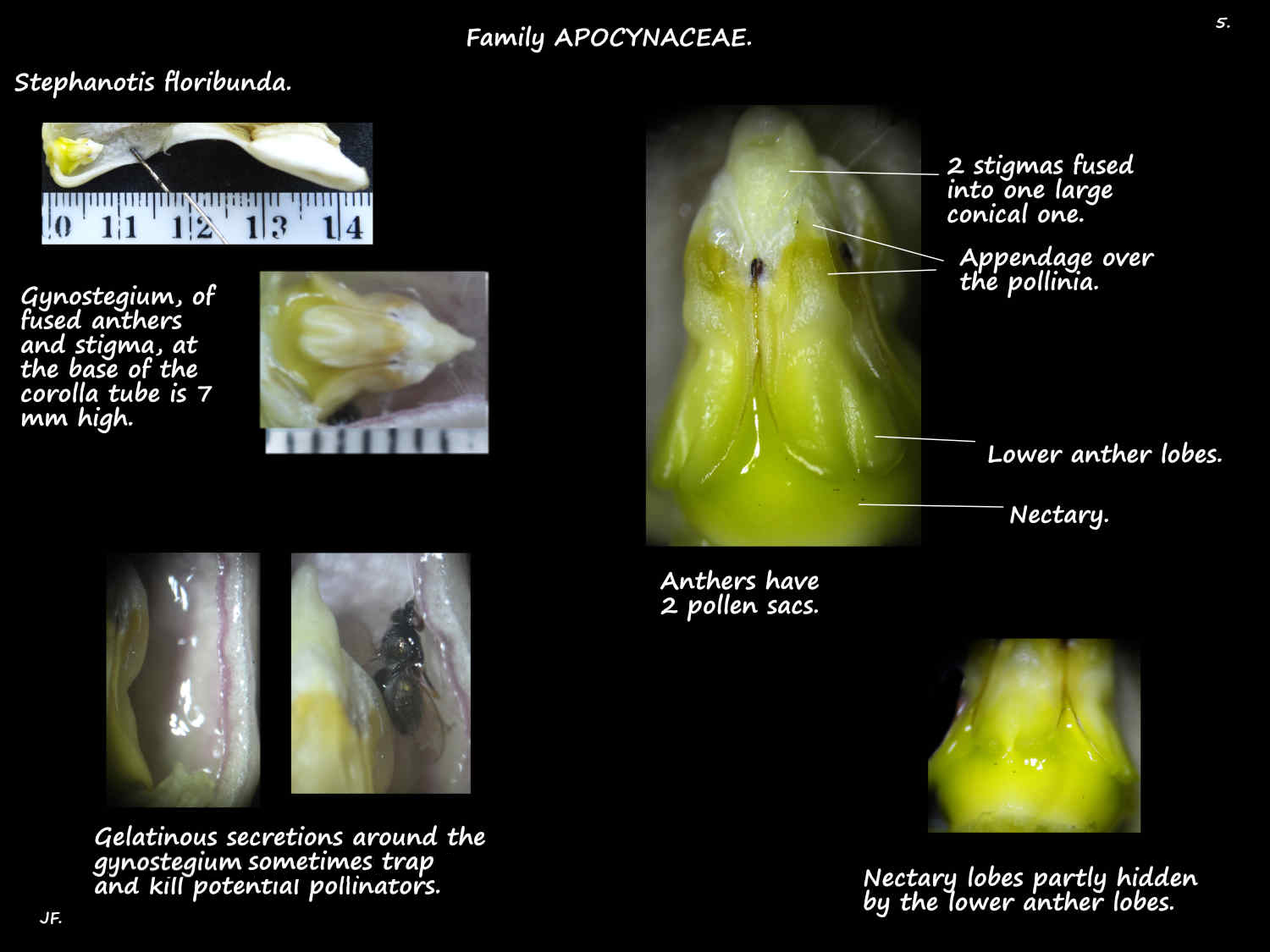
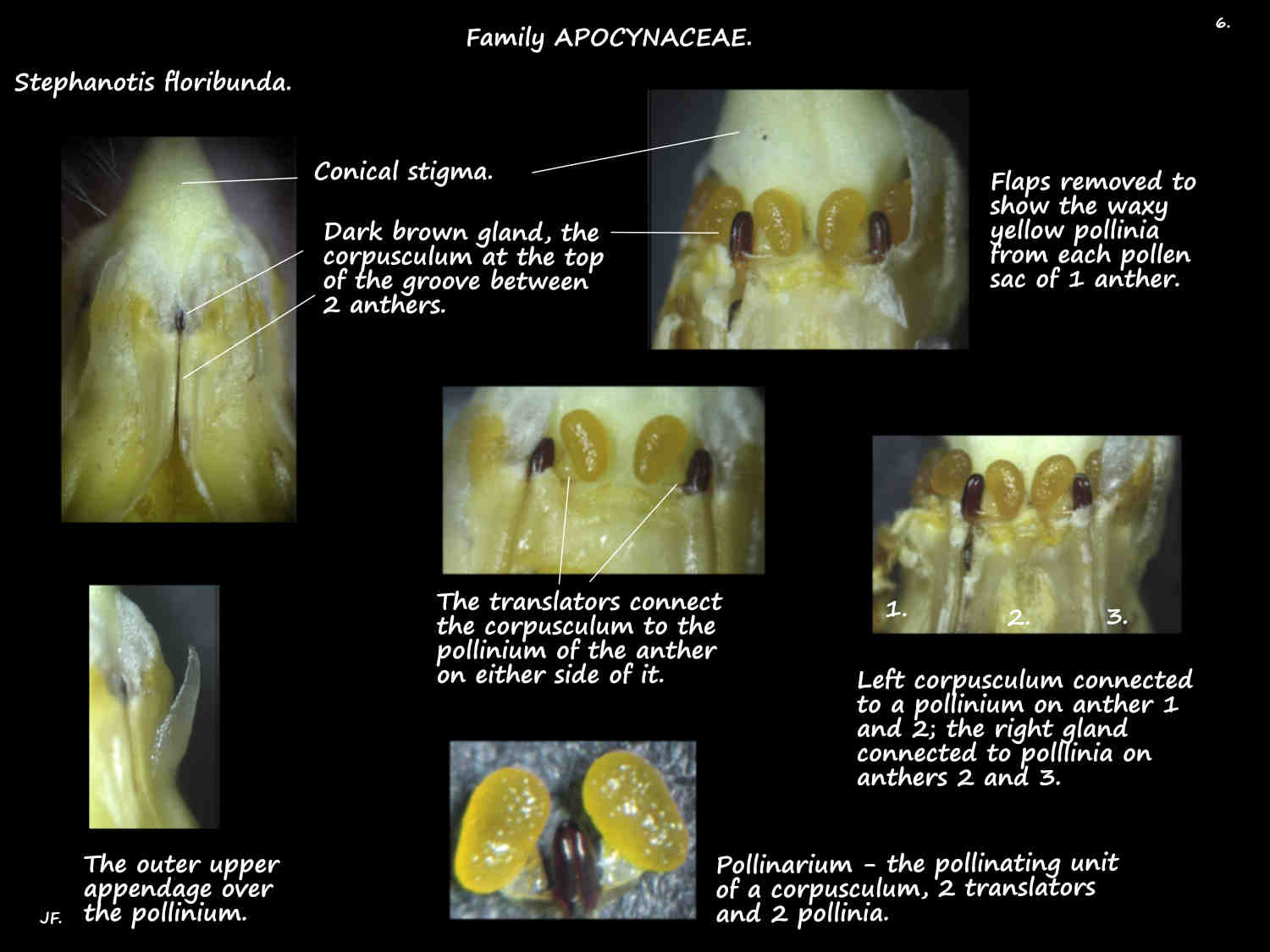
The characteristic feature is the structure of the anthers and stigma.
Each stamen has 2 pollen sacs or thecae.
The anthers are fused to the conical stigma to form a small gynostegium at the base of the corolla tube.
On each theca the pollen is fused in a waxy ball or pollinium.
The small cap-like structures over the pollinia on each anther are covered by a flap.
At the top of the groove between the upper lobes of adjacent anthers is a small brown bi-lobed gland called a corpusculum.
The corpusculum is connected to the pollinium on either side by a narrow thread or translator (retinaculum) to form a structure called a pollinarium.
Pollinators get tangled in the pollinarium and carry it to another flower.
(The Orchidaceae is the only other family to have a similar pollinating structure).
The nectaries are partly hidden under the lower lobes of the anthers.
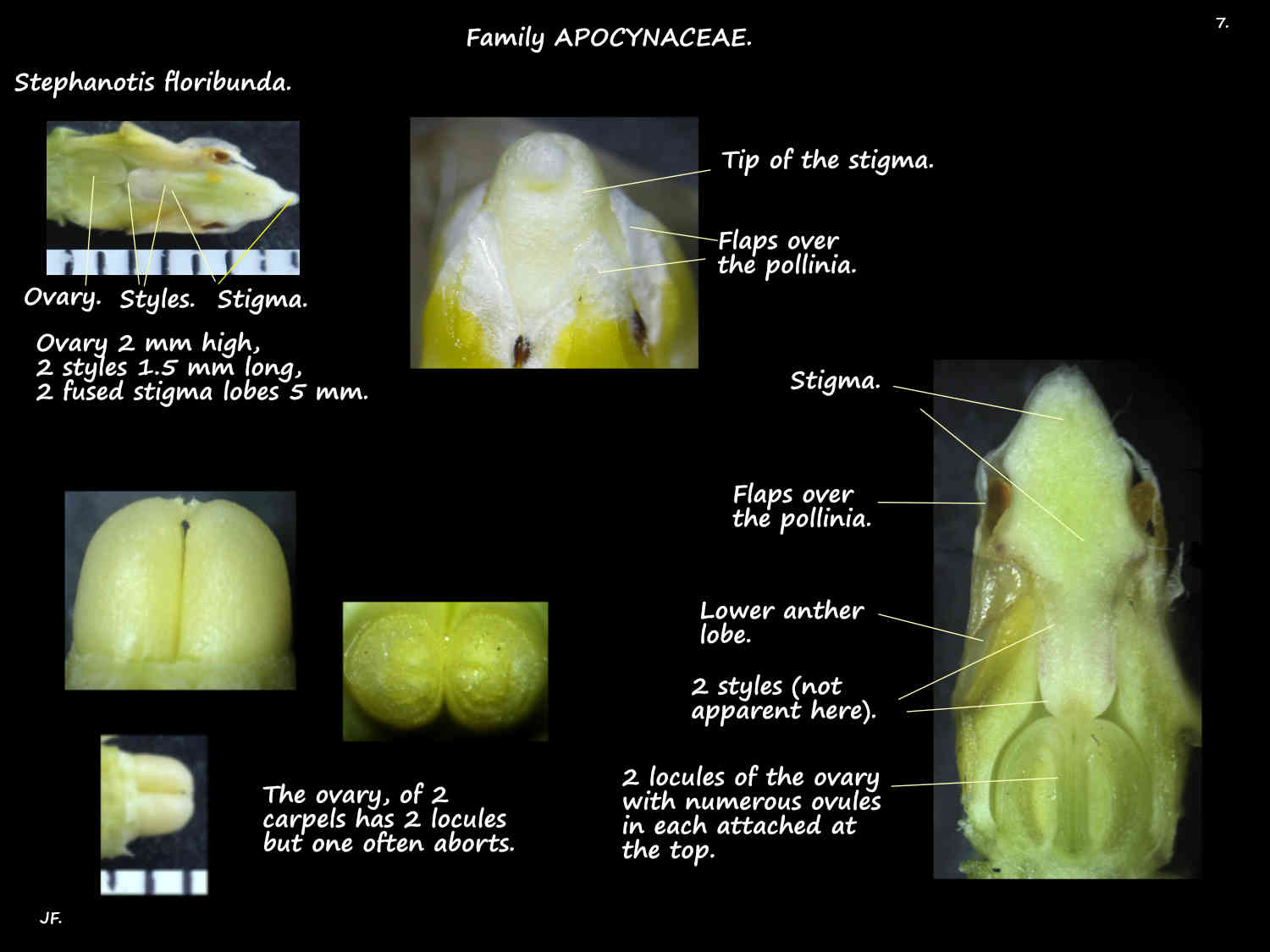
The superior ovary has 2 locules with numerous ovules.
There are 2 short styles and one large stigma.
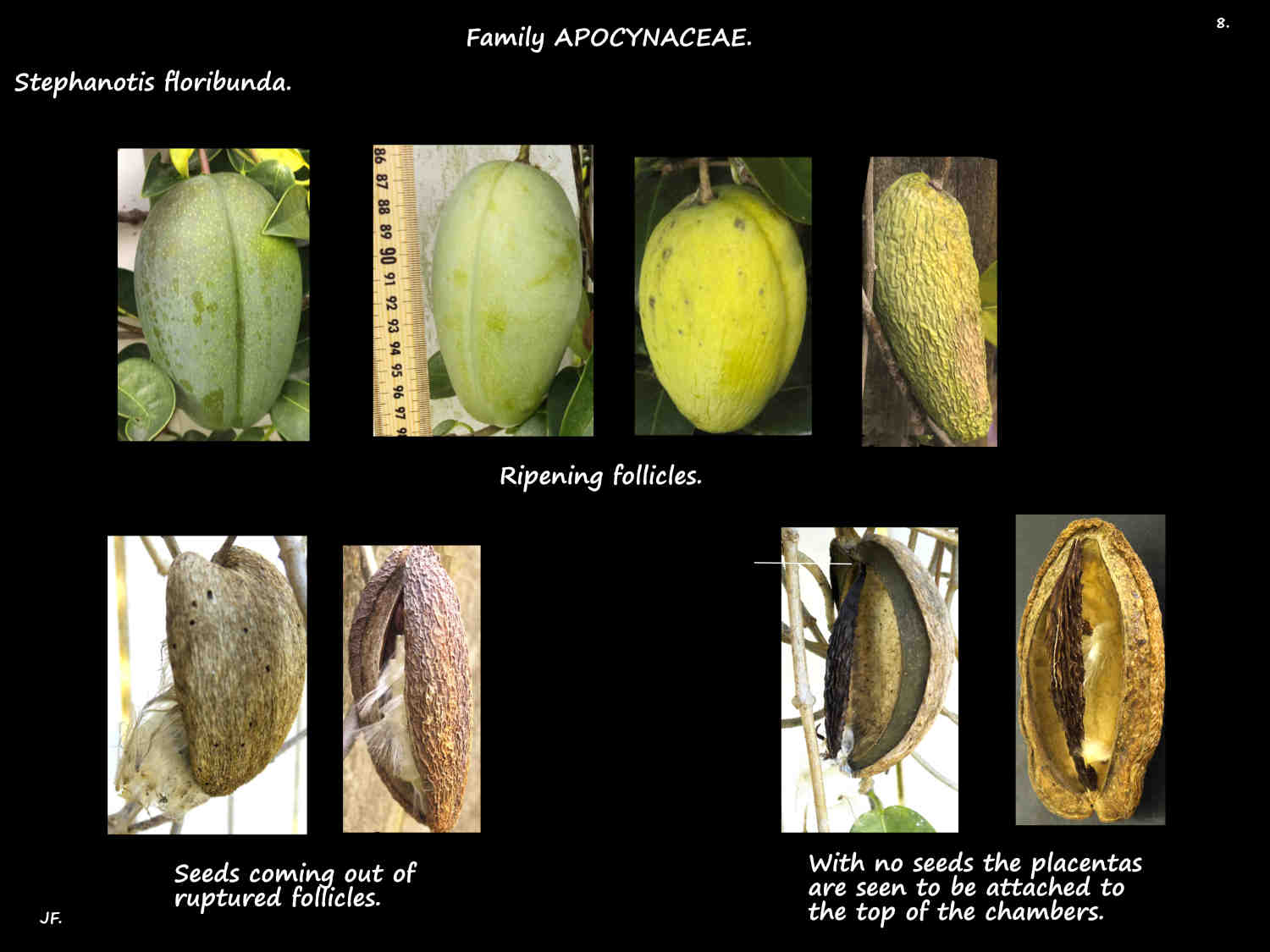
The fruit are follicles with one developing from each locule.
There may only be 1 follicle if one locule does nor develop.
The ovoid follicles, up to 10 cm long take months to mature.
Mature brown follicles open to release numerous seeds with a plume of silky hairs on one end.
There are a few cultivars including one with pink tinted petals and another with variegated leaves.
J.F.