Petunia.
Family Solanaceae > Subfamily Petunioideae.
Plants of the World Online (Kew) accepts 17 species while other sources have up to 40.
Mostly from South America two species are naturalised in Australia.
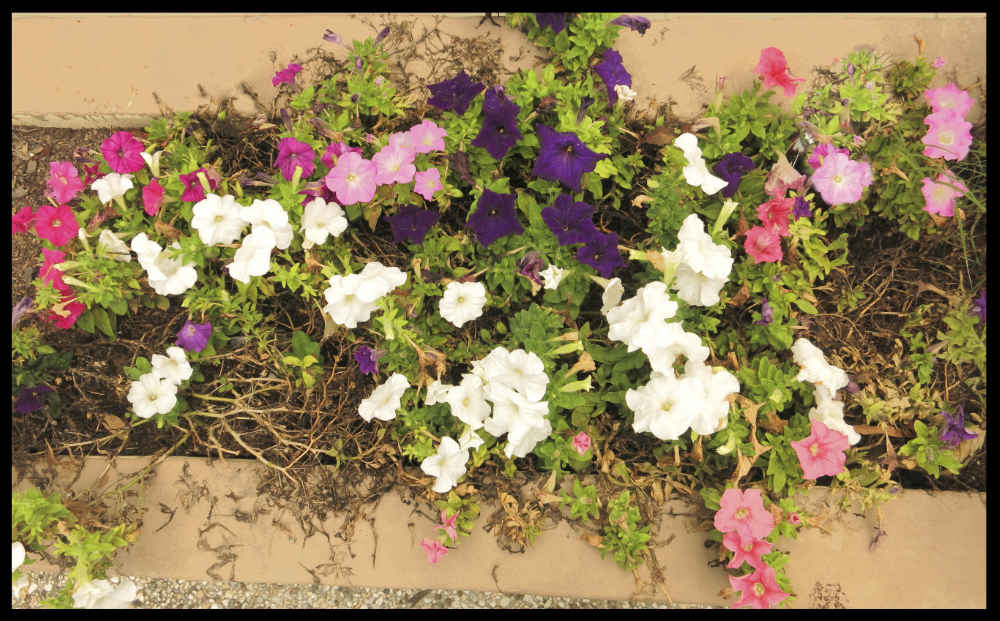
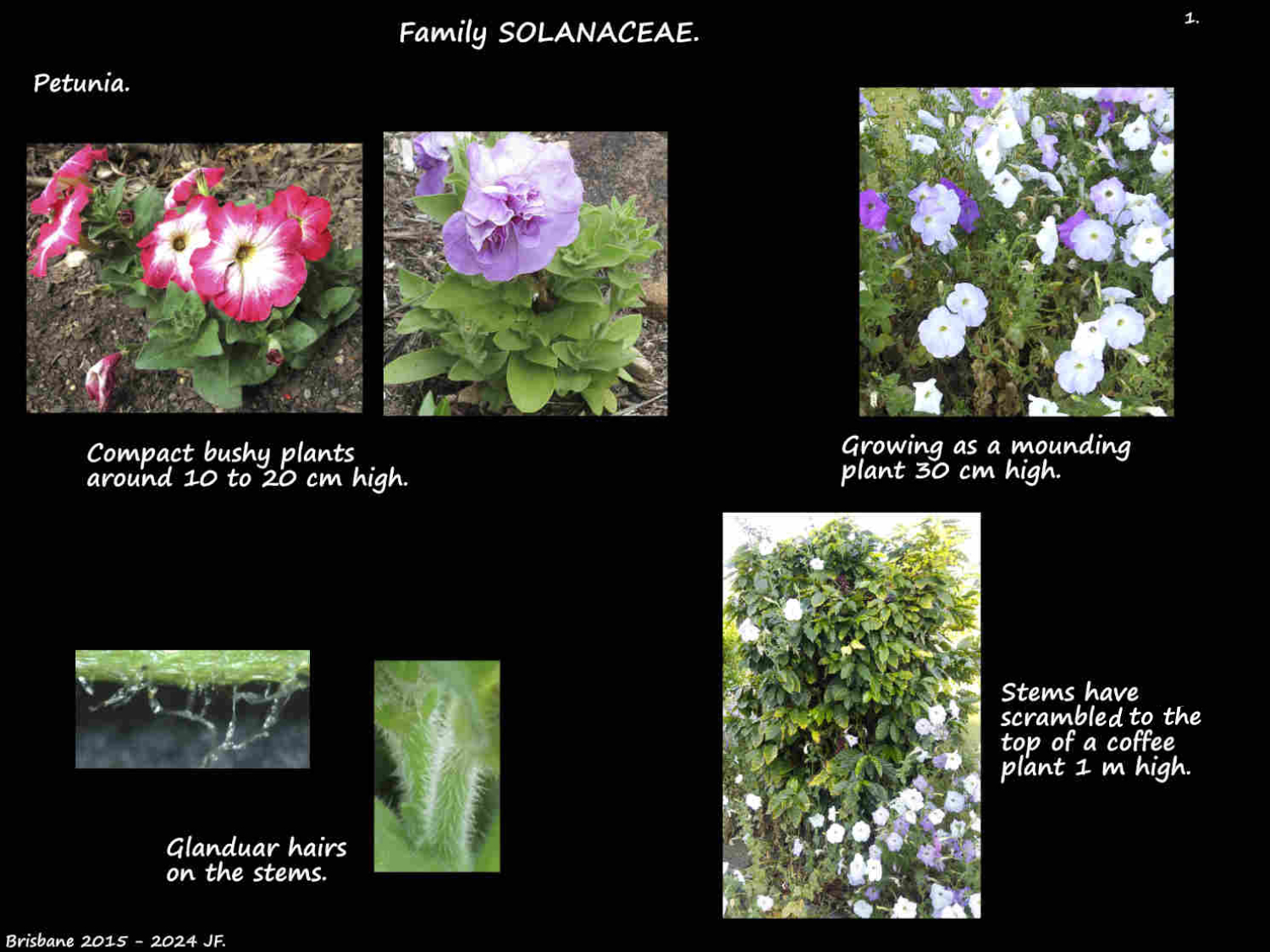
Most are erect, sprawling or trailing herbs.
Often around 25 to 35 cm high they can be up to 60 to 80 cm and nearly 1 m wide.
Parts have glandular hairs secreting a sticky substance.
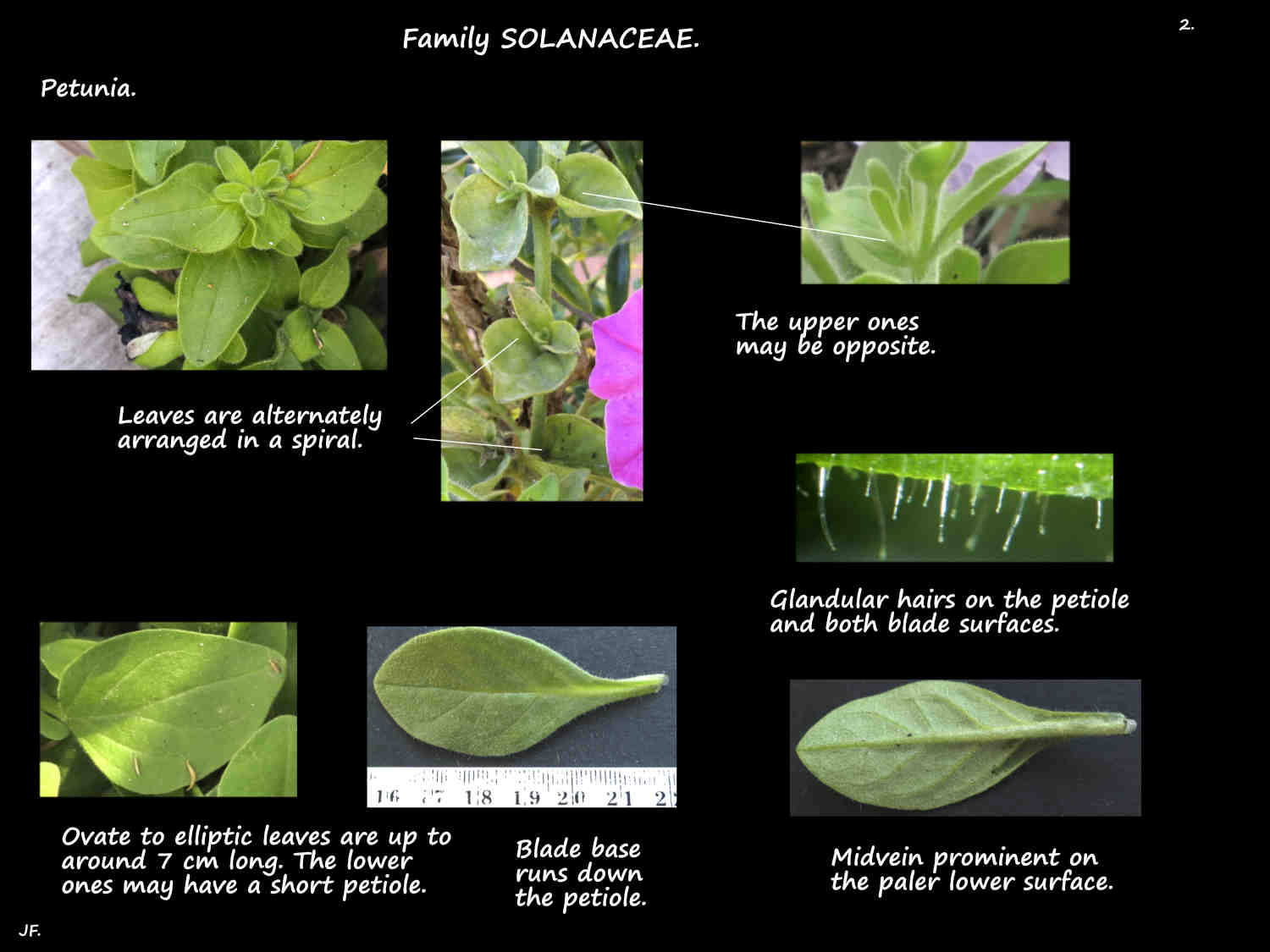
Leaves are alternately arranged in a spiral with the upper ones sometimes being opposite.
Up to 7 cm long they have a short or no petiole.
The base of the ovate to elliptic blade tapers and may run down the petiole.
Secretions from the glandular hairs on the leaves make them sticky.
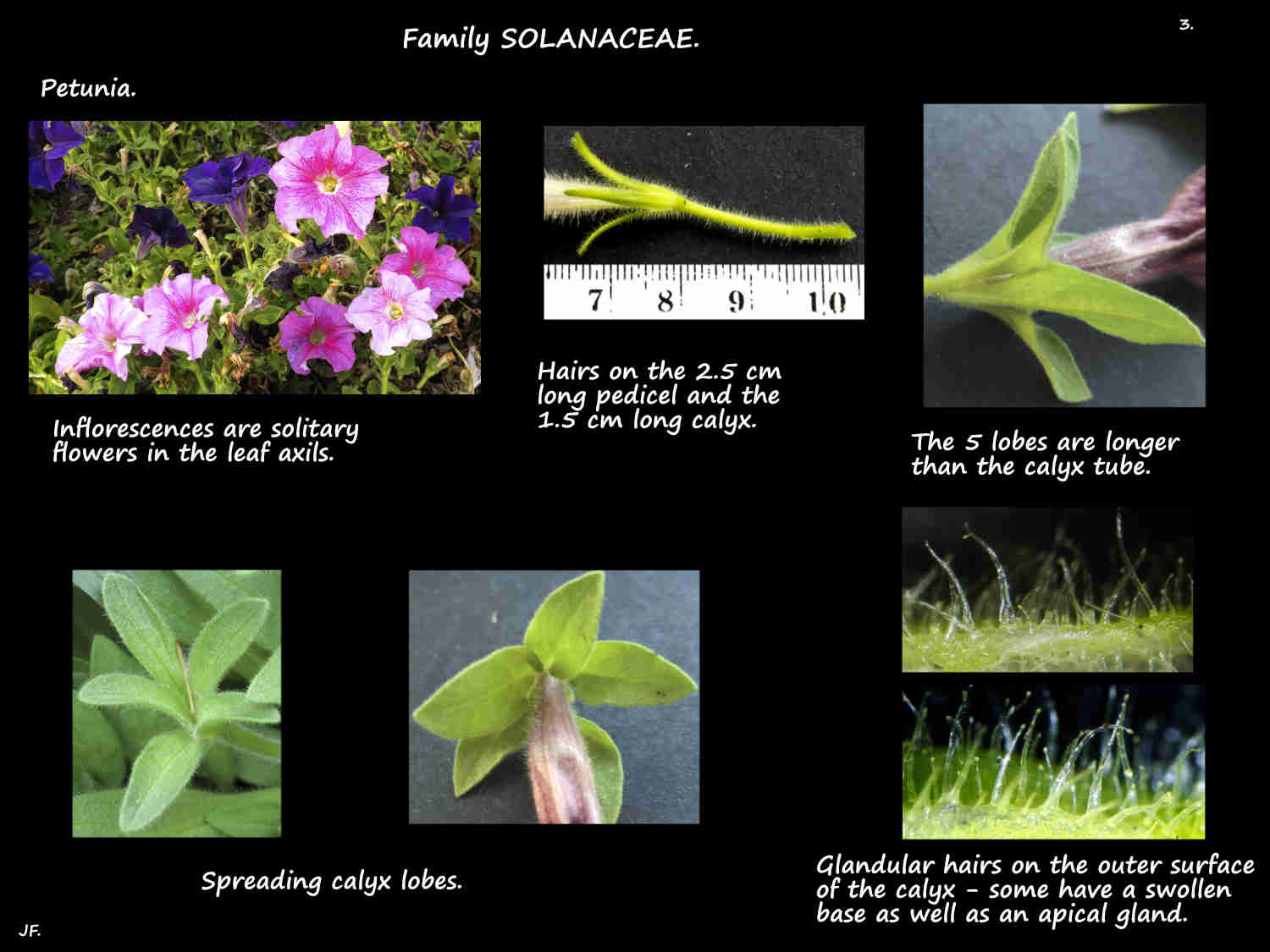
Inflorescences are a solitary flower, over 2 cm long in the leaf axils.
There is usually a pair of leaf-like bracts at the base of the pedicels (flower stalks).
The bell or funnel-shaped calyx, up to around 2 cm long has 5 spreading lobes with their bases shortly fused.
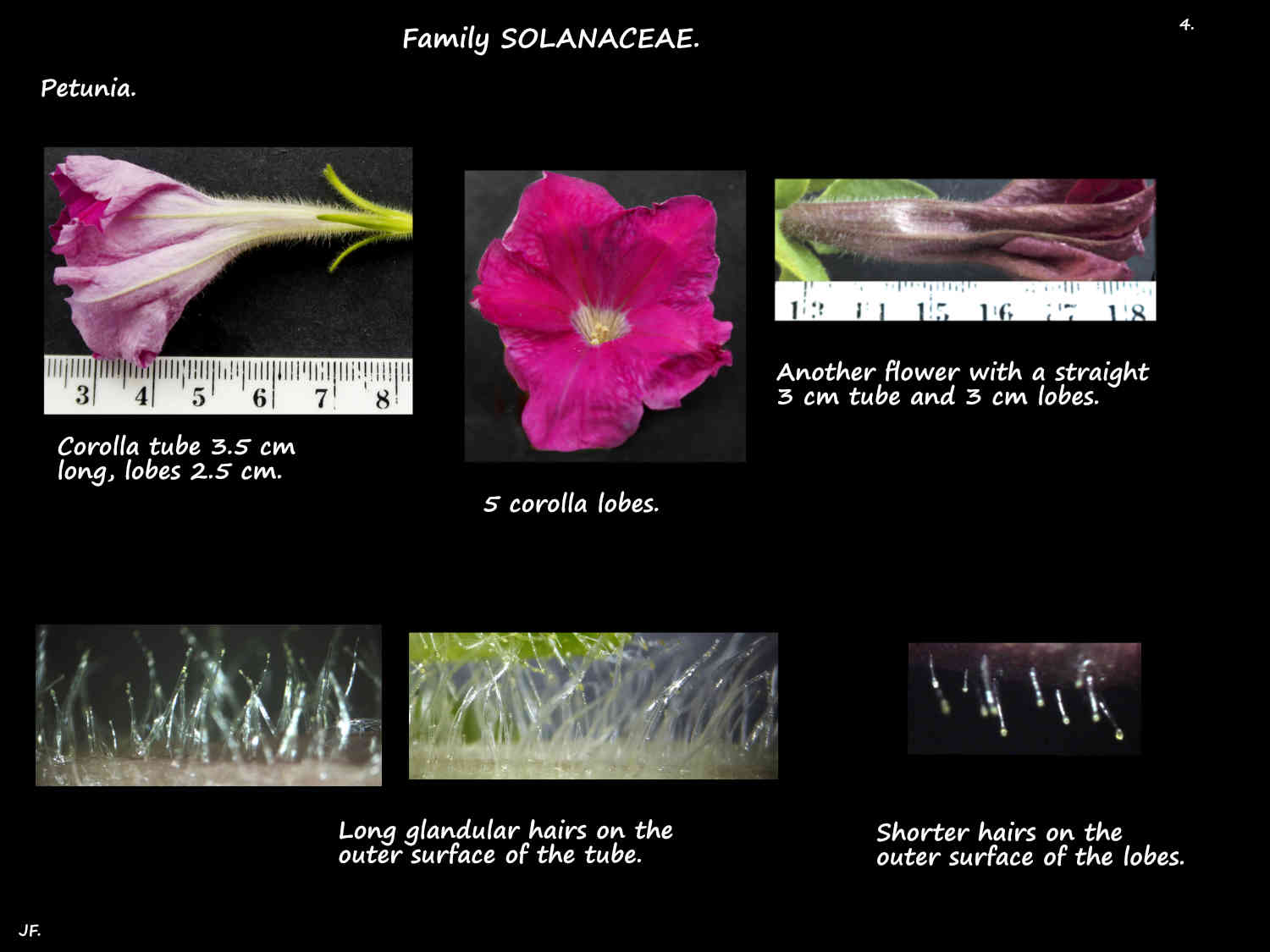
The usually funnel-shaped corolla has a long mainly straight tube with 5 shorter lobes of equal length.
The tube is up to around 4.5 cm long and the flowers 6 cm across.
Including cultivars they come in a wide range of colours.
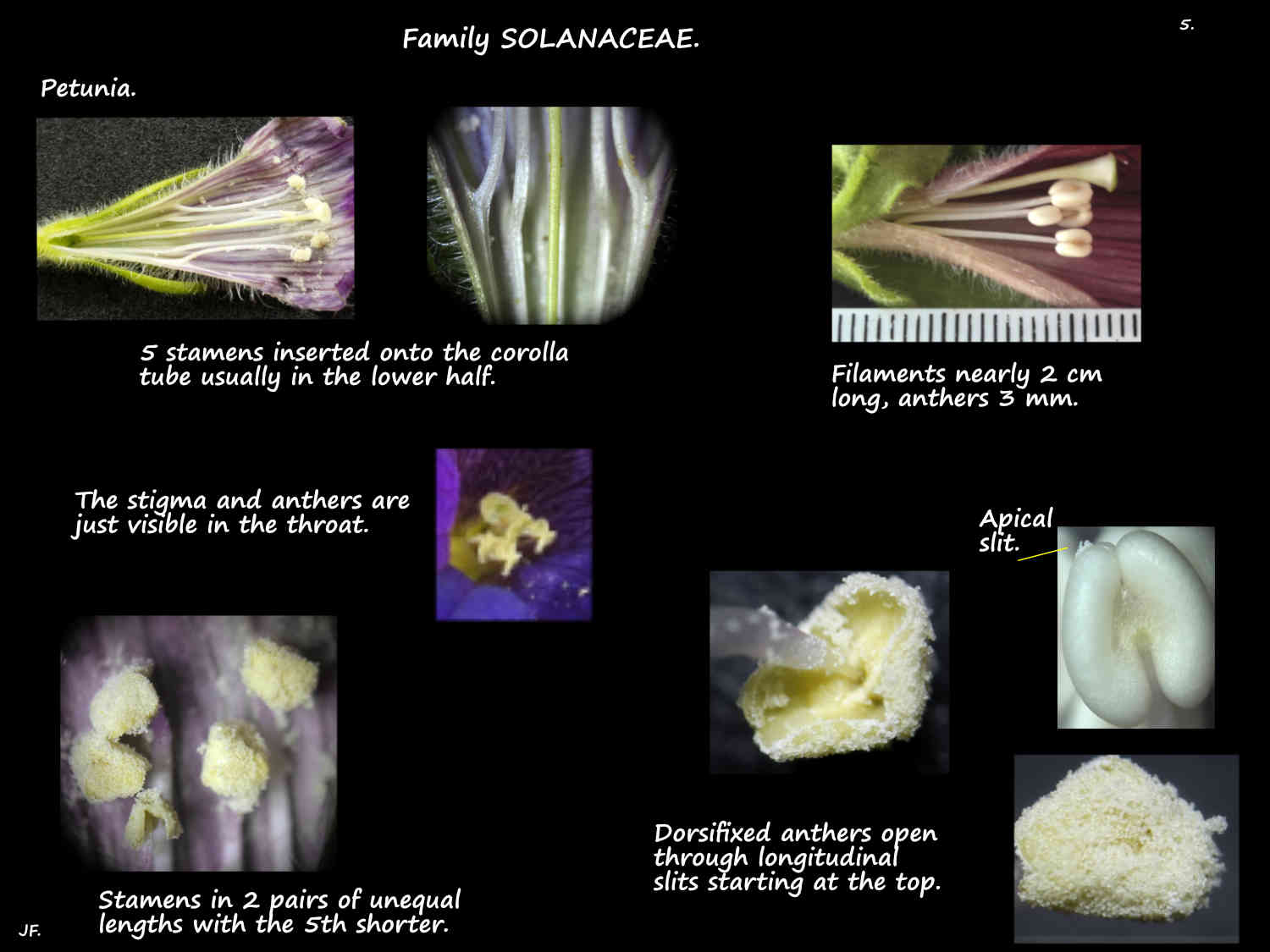
There are 5 stamens inserted onto the corolla tube usually in the lower half.
They can all be equal or in 2 pairs of unequal length with the fifth longer or shorter.
The dorsifixed anthers have 2 pollen sacs that open, often from the top, through longitudinal slits.
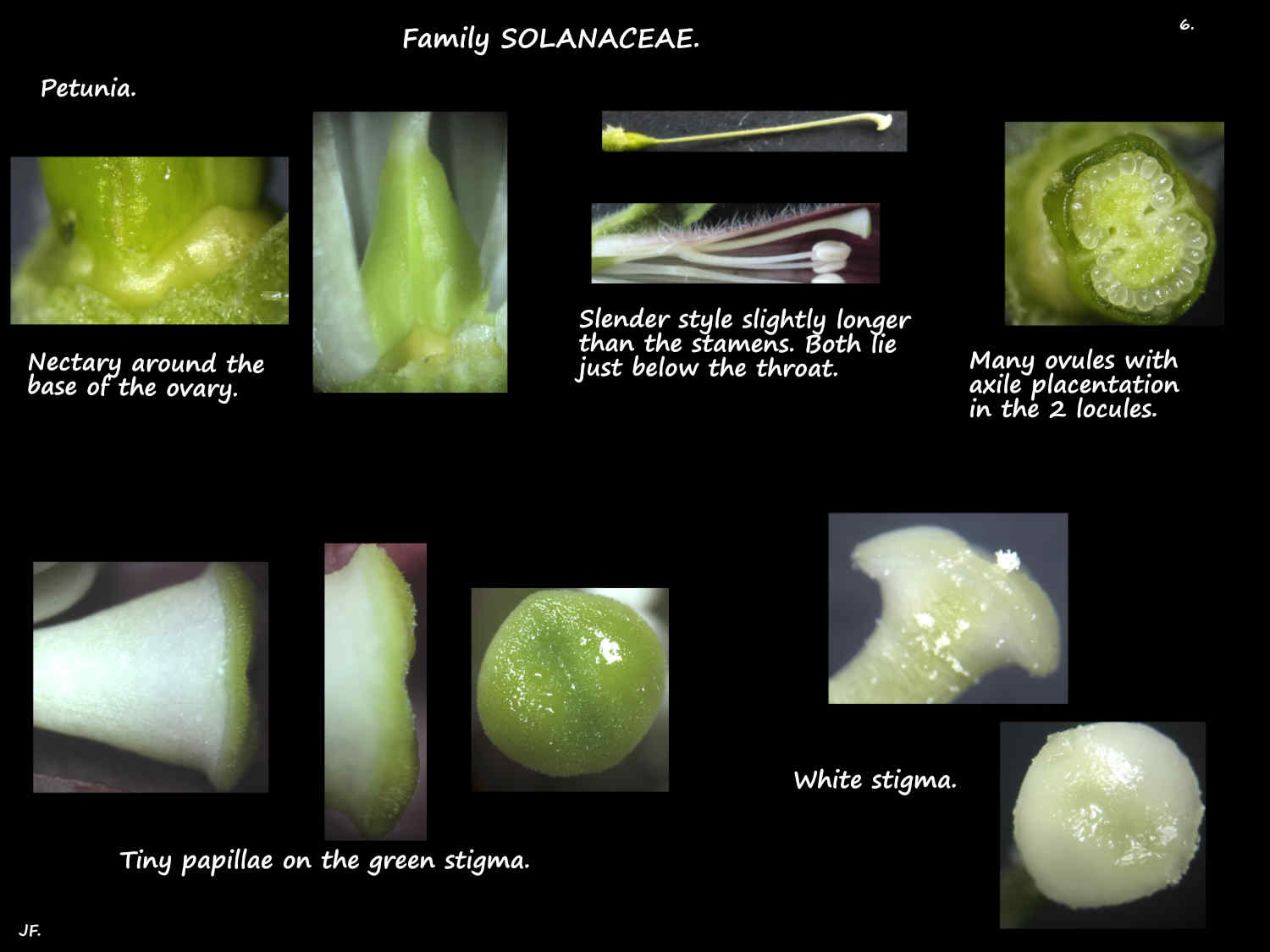
The annular or slightly lobed nectary disc is fused to the base of the ovary.
The superior ovary has 2 locules each with numerous ovules.
The slender style has a small variously shaped stigma that lies in the throat.
The fruit are an ovoid septicidal capsule around 1 cm long.
The calyx remains attached.
There are numerous seeds, 0.5 mm long in each of the 2 chambers.
(See also Calibrachoa under Solanaceae).
J.F.