Lotus purpureus.
In Family Fabaceae > Subfamily Faboideae the Asparagus or Winged pea is native to the Mediterranean area.
It has a number of synonyms including Lotus arborescens, Tetragonolobus purpurea, Tetragonolobus purpureus, Lotus tetragonolobus, and Tetragonolobus tetragonolobuss.
It is seen confused with the Winged bean Psophocarpus tetragonolobus.
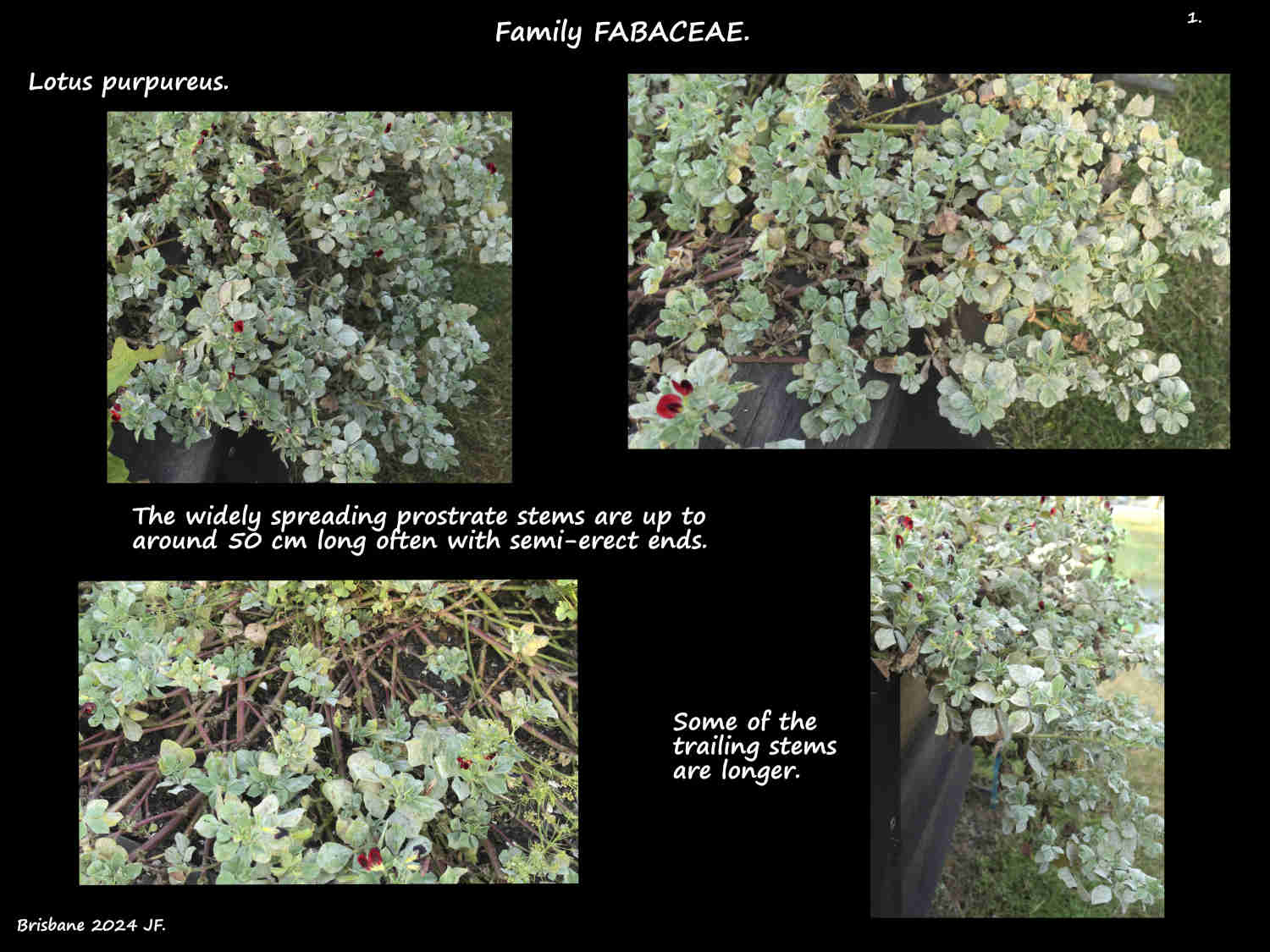
They are annual or perennial herbs or very small slightly woody shrublets.
The fleshy mainly prostrate stems are up to around 50 cm long with their erect tips to around 15 cm.
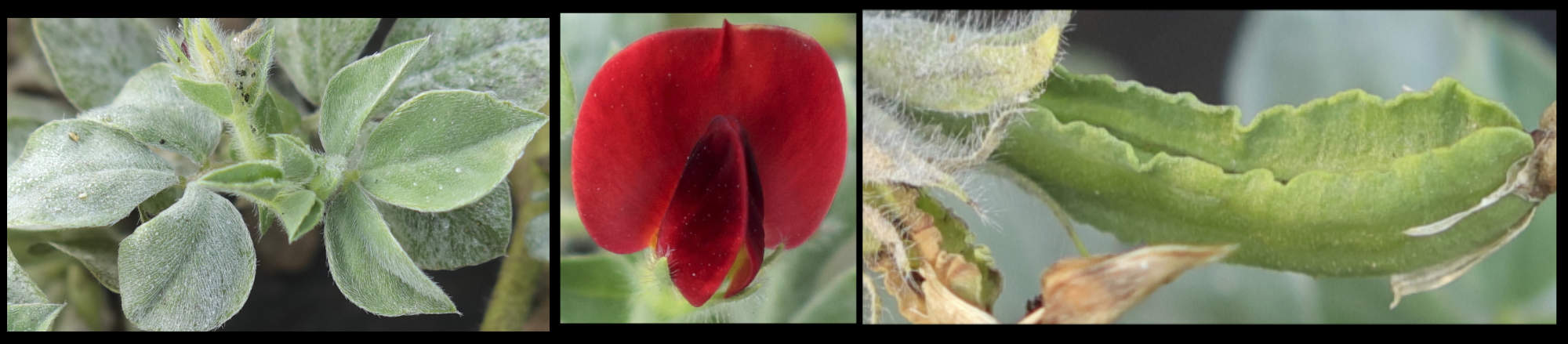
There are dense hairs on young round stems and less on the older ridged stems.
Leaves have no petiole or a very short one under 1 cm long.
Leaves have 5 leaflets on a midrib or rachis up to around 2 cm long.
The 5 leaflets are on petiolules so short they are sometimes described as having none.
That of the terminal leaflet is slightly longer.
The upper 3 leaflets are ovate or diamond-shaped.
The around 1.5 to 2 cm long by 1.5 cm wide leaflets have a wedge-shaped base and a pointed tip.
The bottom pair are much smaller and resemble stipules.
They can be so minute the leaves appear to be tri-foliate.
There are long simple hairs on all parts.
Axillary inflorescences are an umbel with 2 (1) flowers at the tip of a short stalk (peduncle).
Flowers, around 2 cm long are typically on a very short pedicel.
Sometimes they are directly attached to the stem (sessile).
At the peduncle base are 1 to 3 small leaves that are often called bracts.
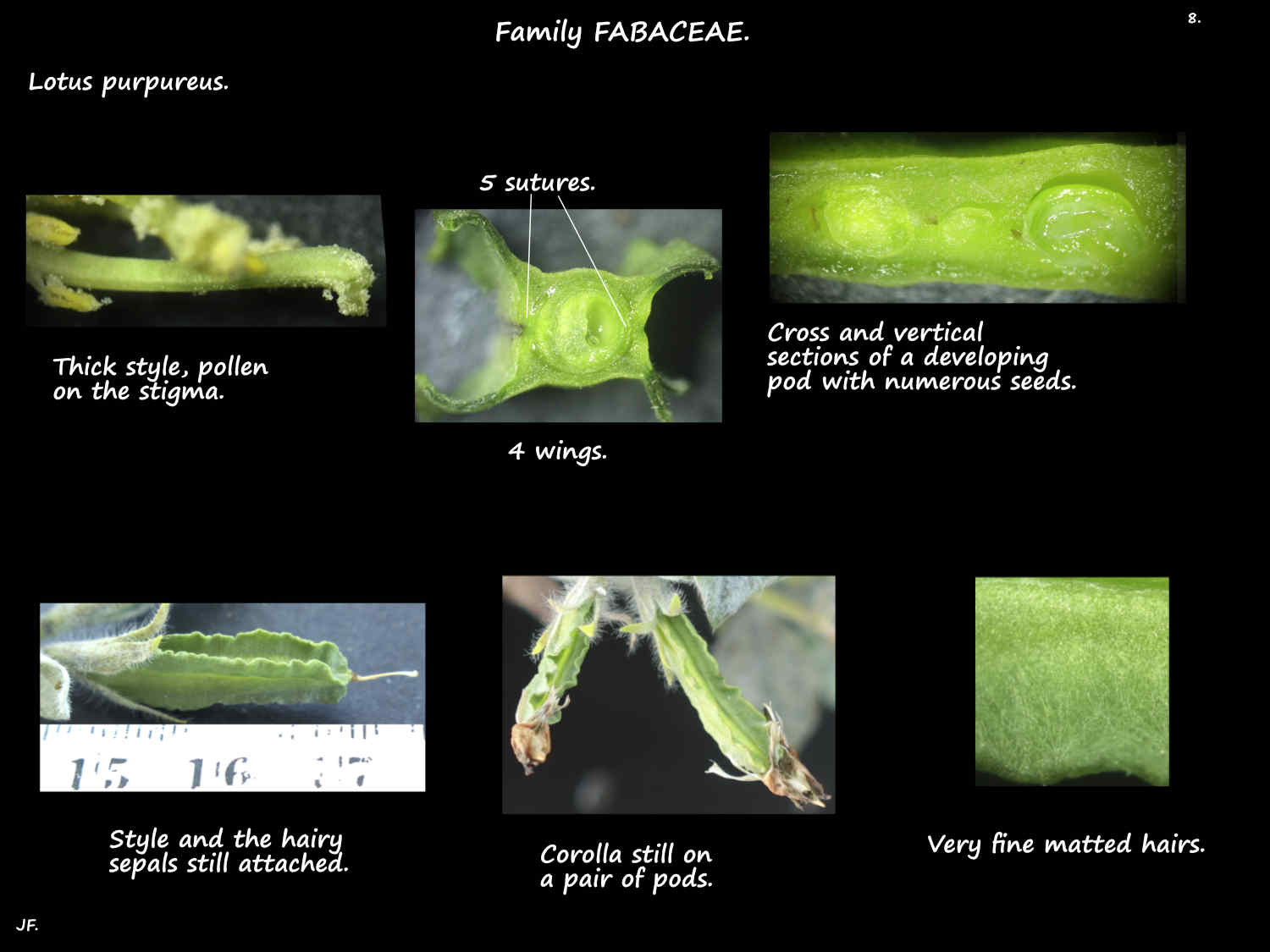
The narrow calyx has a tubular base with typically 5 slightly flaring lobes.
The tube is 2 to 3 mm long and the longest lobes around 6 or 7 mm.
The lobes are unequal often with the upper 2 being partly fused.
The lower lobe may be longer and rarely the calyx has 2 lips.
The lobes may have purple markings and there are long simple hairs.
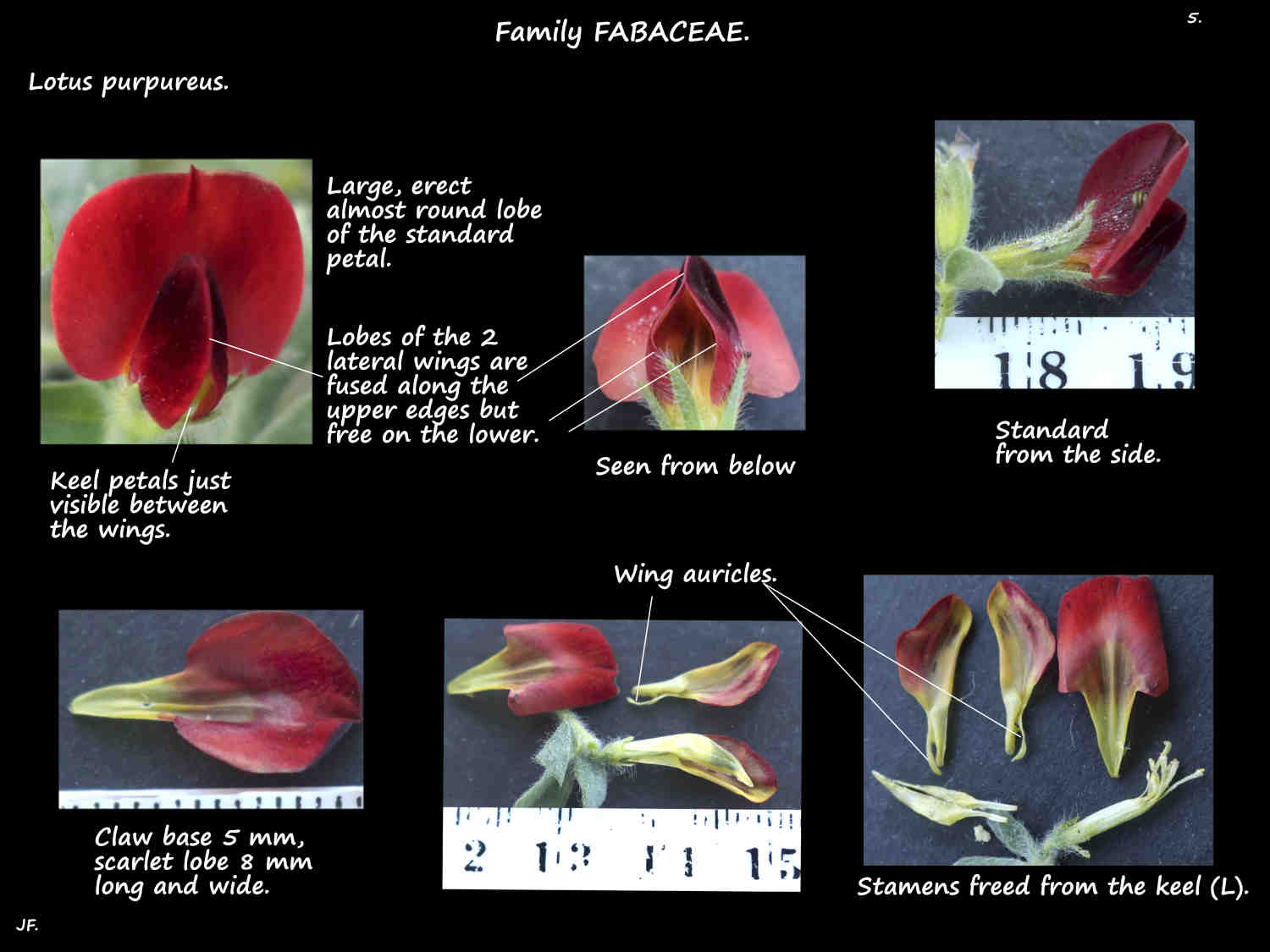
Flowers have the 5 petals typical of the pea family.
The largest petal is the erect standard that can be nearly 3 cm long.
It has a narrow greenish wedge-shaped base and a bright red lobe.
The lobe is bent up at almost 90 degrees to the base.
The base has thick rolled in edges and the lobe is obovate to almost round with a pointed tip.
There are no hairs.
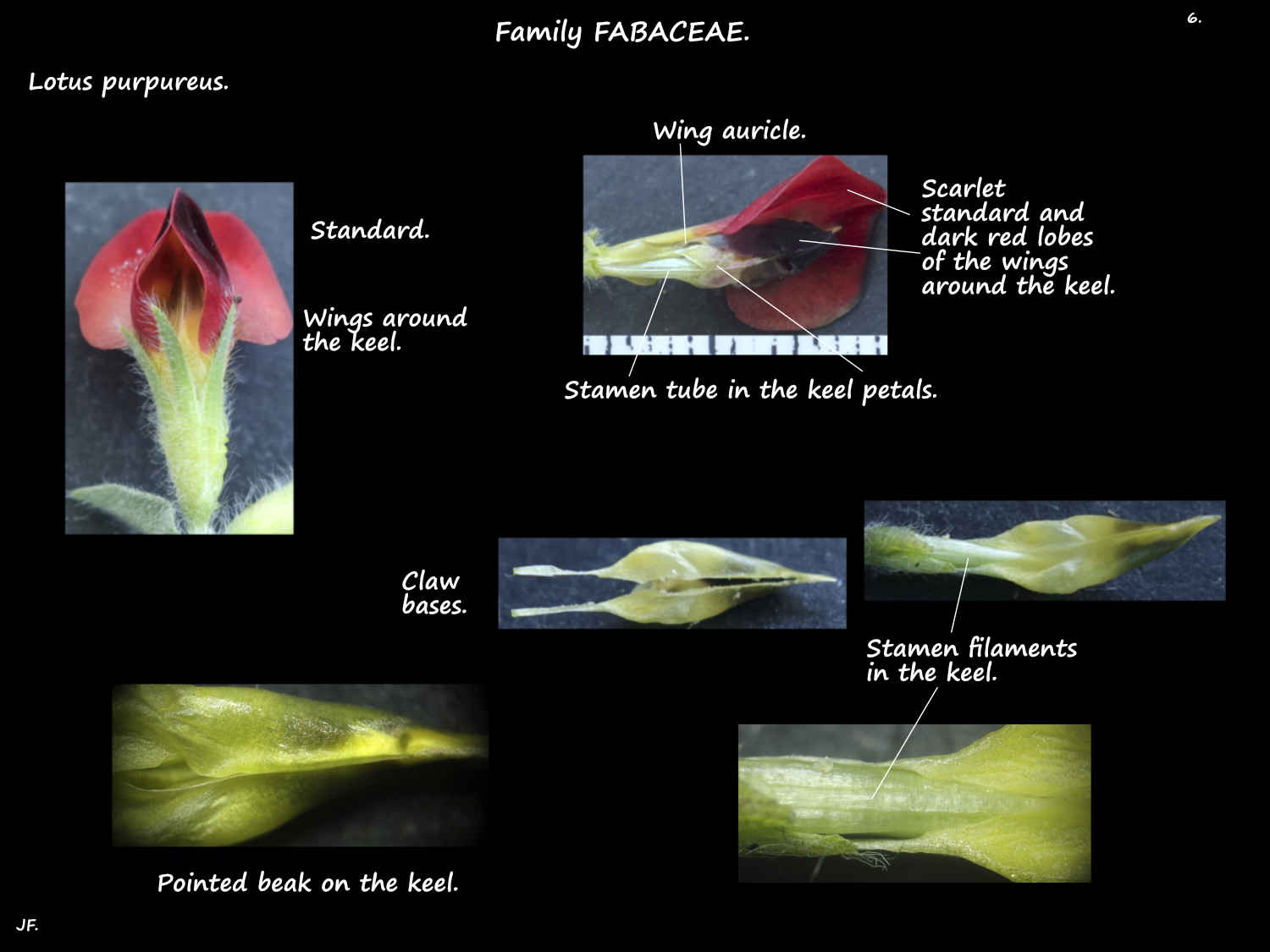
The 2 side petals are the wings with greenish claw bases.
The bright red oblong lobes pouch outwards around the keel.
The upper edges of the vertical lobes are fused while the lower edges are free.
There is a narrow appendage or auricle from the base of the lobes.
The 2 smallest petals are the downward curved keel petals.
The claw bases are greenish and the outwards pouching lobes a mix of red and green.
They bases are free but the lobe edges are fused.
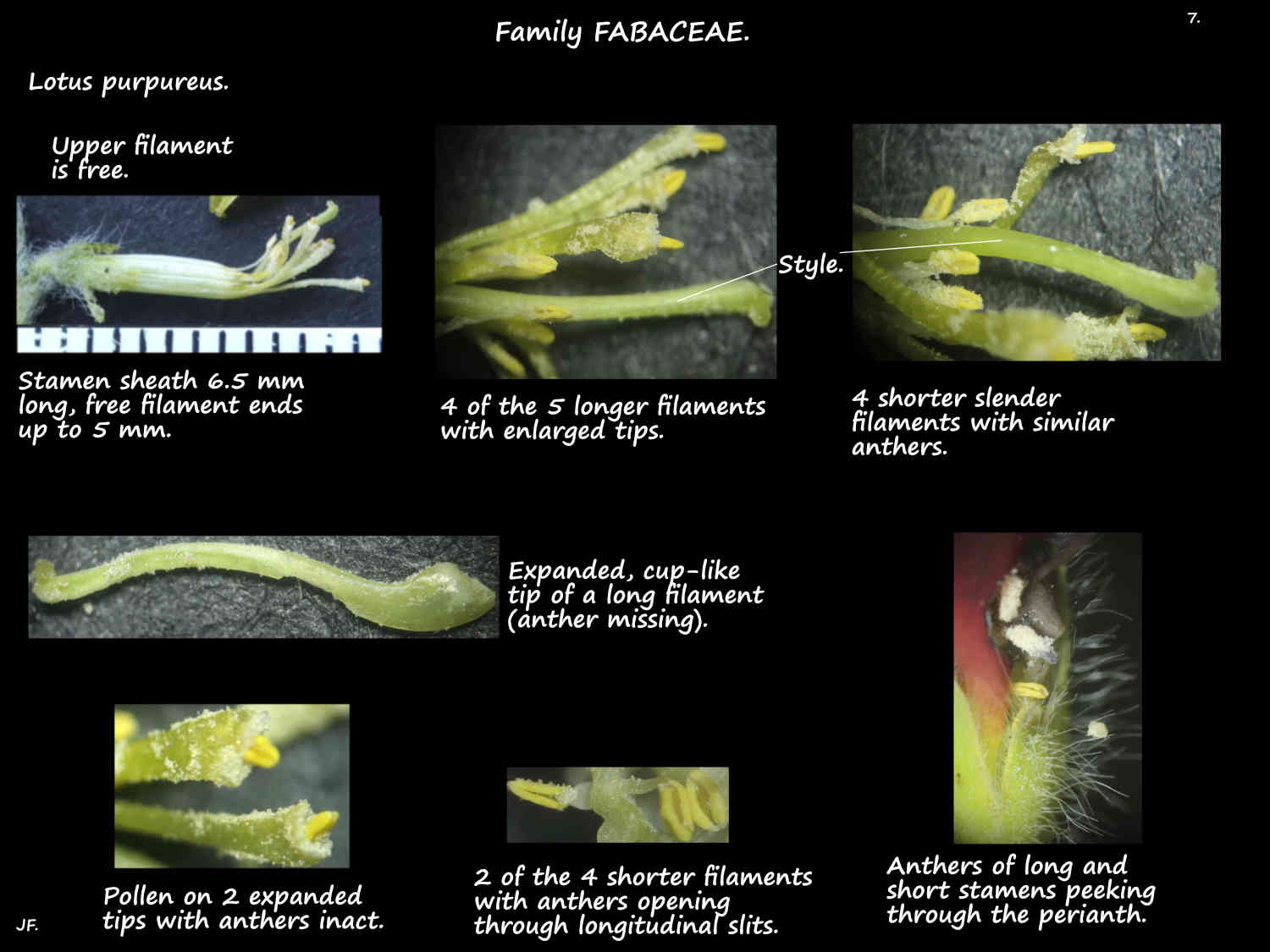
The 10 stamens are enclosed by the keel petals.
The upper stamen is free.
Filaments of the other 9 are fused into a tube for most of their length.
The free ends of the filaments are in 2 groups with similar anthers.
Five of the filaments are thicker and have tips that widen into a cup-like structure around the anther.
The free filament ends holding the other 4 anthers are usually slender.
The hairy superior ovary, with numerous ovules may be on a short stalk.
The fruit are a cylindrical legume or pod around 6 cm long and 8 mm thick.
There are 4 wavy wings with two on either side of the 2 sutures.
There are usually septae between the seeds.
Pods split into 2 sections (valves) that usually twist.
J.F.