Medicosma.
Family Rutaceae > Subfamily Zanthoxyloideae.
Plants of the World Online recognises 25 species from New Guinea, New Caledonia and Australia.
In Australia they are found in coastal areas of Queensland and New South Wales.
The 6 endemic to Australia are Medicosma cunninghamii, Medicosma fareana, Medicosma glandulosa, Medicosma obovata, Medicosma riparia and Medicosma sessiliflora.
Some are very similar with differentiation coming down the leaf shape and the angle of the veins.
They are shrubs around 2 m high or small trees to 10 m.
New twigs and leaves may have scattered stellate hairs.
Other parts can have simple, stellate or bundled hairs.
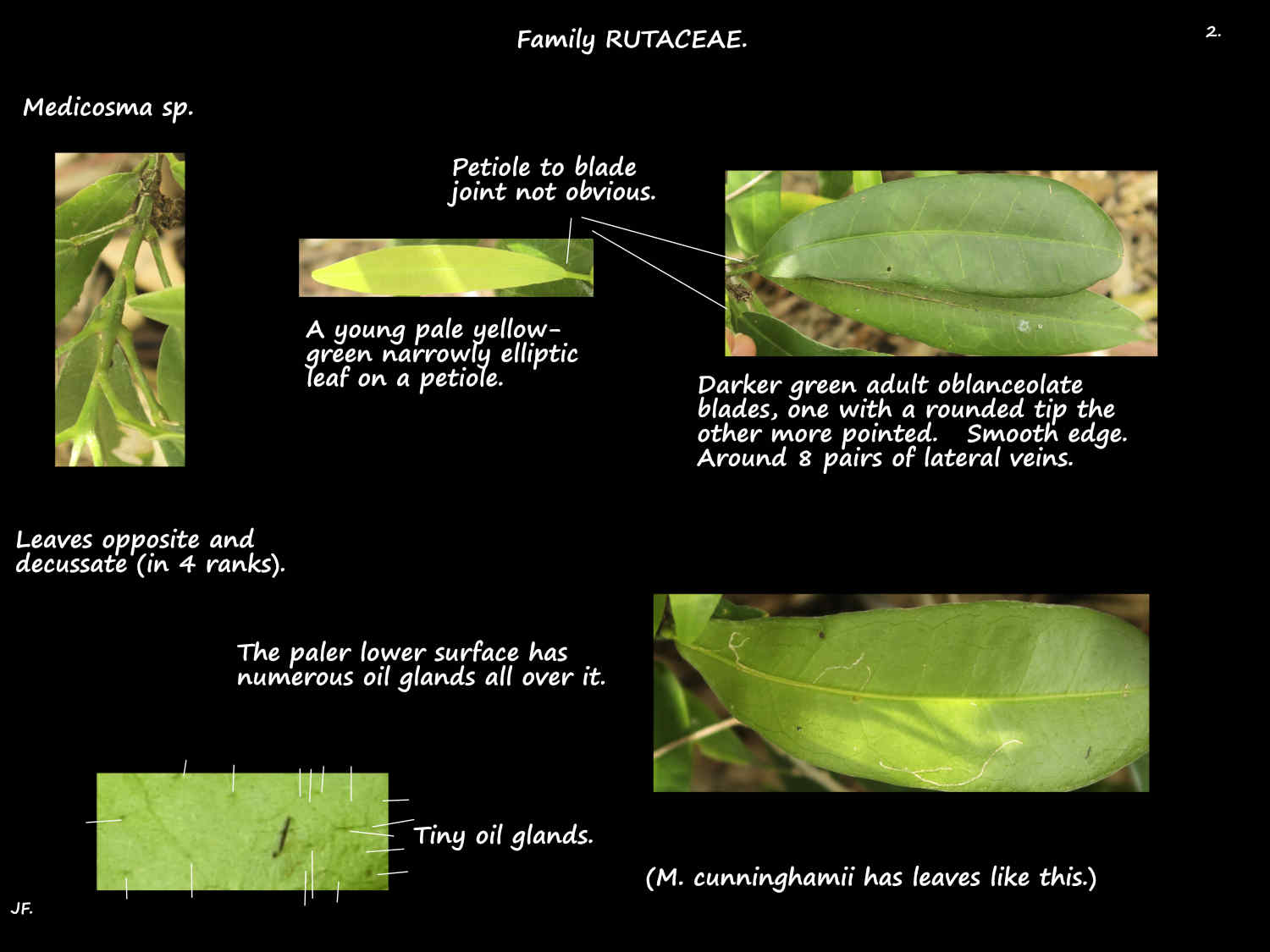
Leaves are typically opposite but may be sub-opposite or alternate.
They are on a petiole up to around 2 cm long.
There may be a slight swelling at the junction with the blade.
The simple (occasionally trifoliate) blades are from 4 to around 23 cm long.
The obovate, elliptic or oblanceolate blades are 2 to 7 cm wide.
Dark green leaves have a smooth edge, a blunt or pointed tip and a wedge-shaped or rounded base.
Oil glands are present as numerous tiny dots or 2 or 3 circular glands on the lower surface.
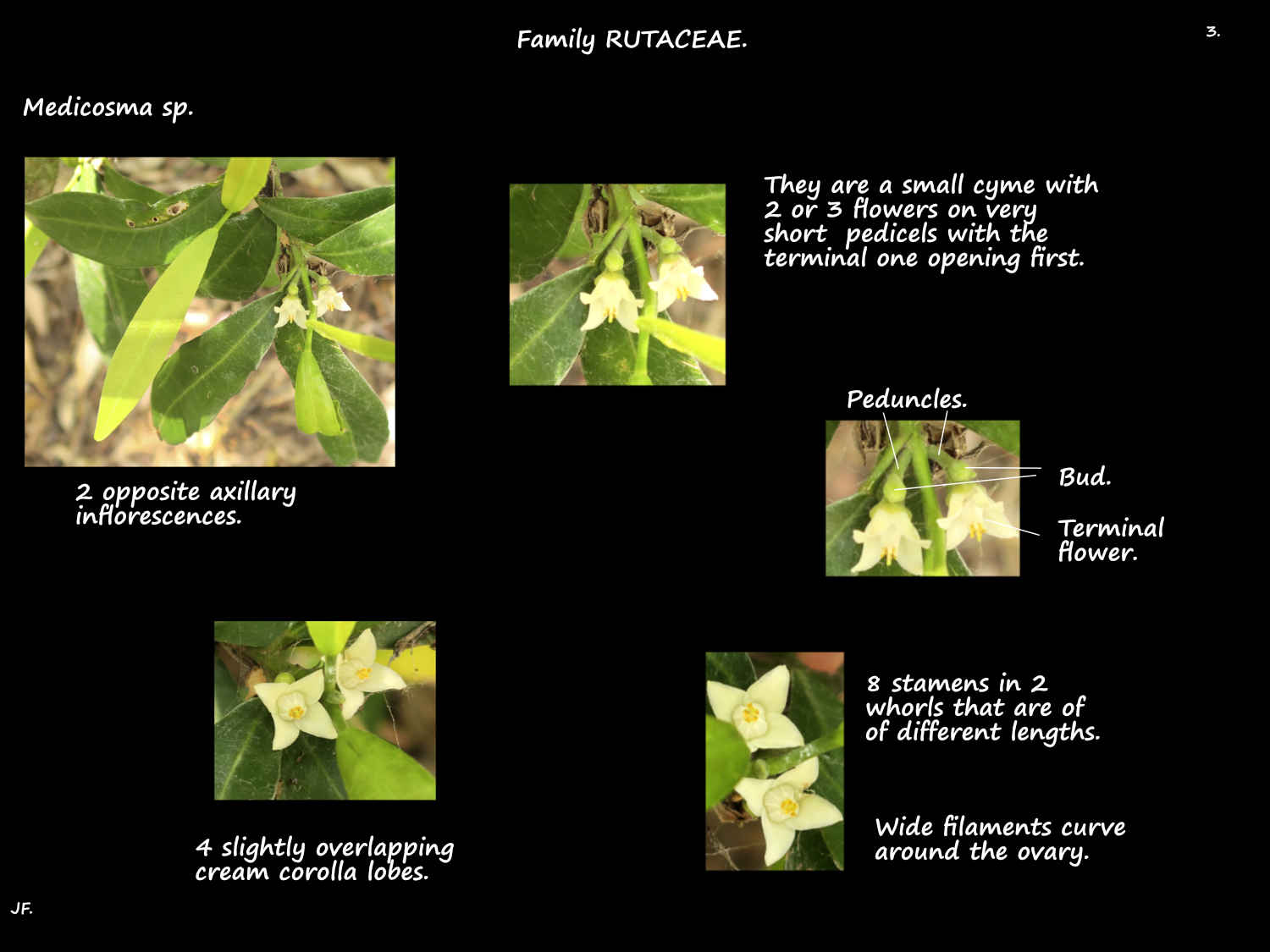
Axillary inflorescences are 1 to a few flowers on a short midrib.
They are cyme-like with flowers opening from the top down.
Flowers have no pedicel or one a few mms long.
The 4 sepals, 2 to 6 mm long have their bases fused and 5 lobes.
There may be hairs on the outer surface and the calyx persists on the fruit.
The 4 usually overlapping petals are free or fused at the base.
Petals persist on the fruit and may increase in size as the fruit grows.
The white (or cream) petals are from 4 to 20 (40) mm long.
They may have dense hairs on the outer surface.
Filaments of the 8 (4) stamens may be fused just at the base to most of their length.
The 4 long and 4 short filaments may be straight or curve around the ovary.
Filaments may have small glands, hairs or villi.
The nectary around the ovary base can be continuous or divided into 8 lobes.
Most species have bisexual flowers but some are male with an undeveloped ovary.
The superior ovary has 4 carpels that may be free, joined just at the base or at the top by the styles.
Each carpel has 2 ovules and the fused styles may have hairs at the base.
The stigma can be capitate (head-like) or 4-lobed.
Each of the 4 carpels can develop into a follicle that opens along one side.
The up to 4 follicles are joined at the base.
The other flower parts may remain on the ovate to elliptic follicles.
The around 4 to 6 mm long follicles (cocci) may have hairs.
Each has 1 or 2 black or brown seeds.
J.F.