Family Dipsacaceae (or Subfamily Dipsacoideae in the loosely defined Caprifoliaceae s.l.).
Pincushion flowers are mostly perennial herbs while a few are shrubs with a woody base.
Some have spreading stems while others are erect and branched.
Stems may have some hairs.
Leaves are in a basal collection and/or on erect stems.
Basal leaves typically have a petiole while leaves up the stems have progressively shorter then no petiole.
Basal blades can be round to lance or spatula-shaped with a lobed or dissected edge.
Stem leaves are opposite and shallowly to very deeply lobed.
A few species have undivided (simple or entire) leaves.
Leaves are up to around 15 cm long and most have some hairs.
Leaves on any one plant are often of 2 different types.
Terminal inflorescences are typically a long leafless peduncle (scape) with a flowerhead of small densely packed florets on the receptacle.
The receptacle (an upward extension of the peduncle) can be conical, hemispherical or cylindrical.
Heads can be up to 8 cm across.
At the base of the head are 1 or 2 (3) rows of bracts forming an involucre that supports the head.
These bracts, longer or shorter than the florets have a wide base, a pointed tip and may have hairs.
There are linear to lance-shaped leaf-like bracts, shorter than the flowers on the receptacle.
These may have some hairs on the edge and outer surface.
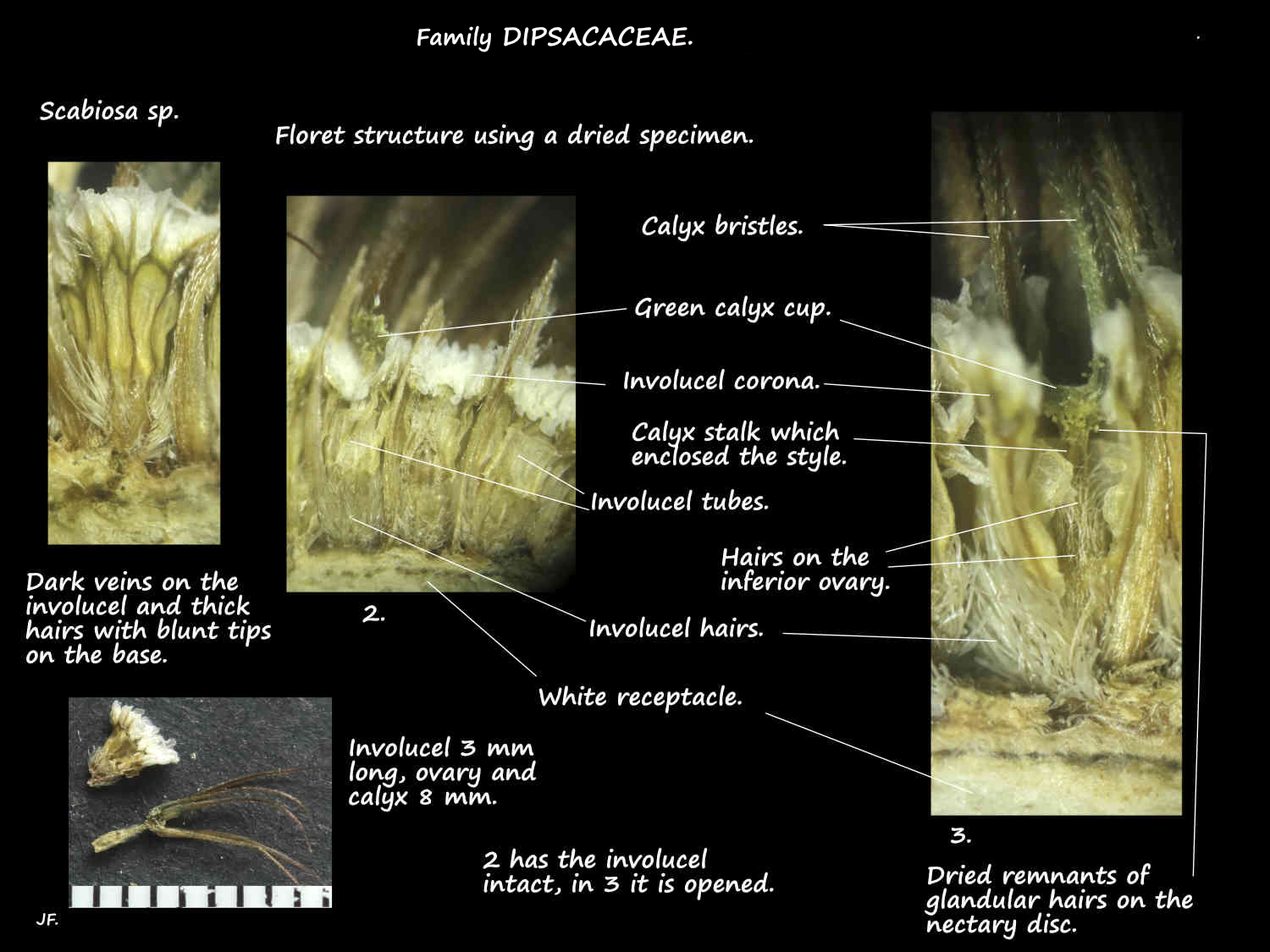
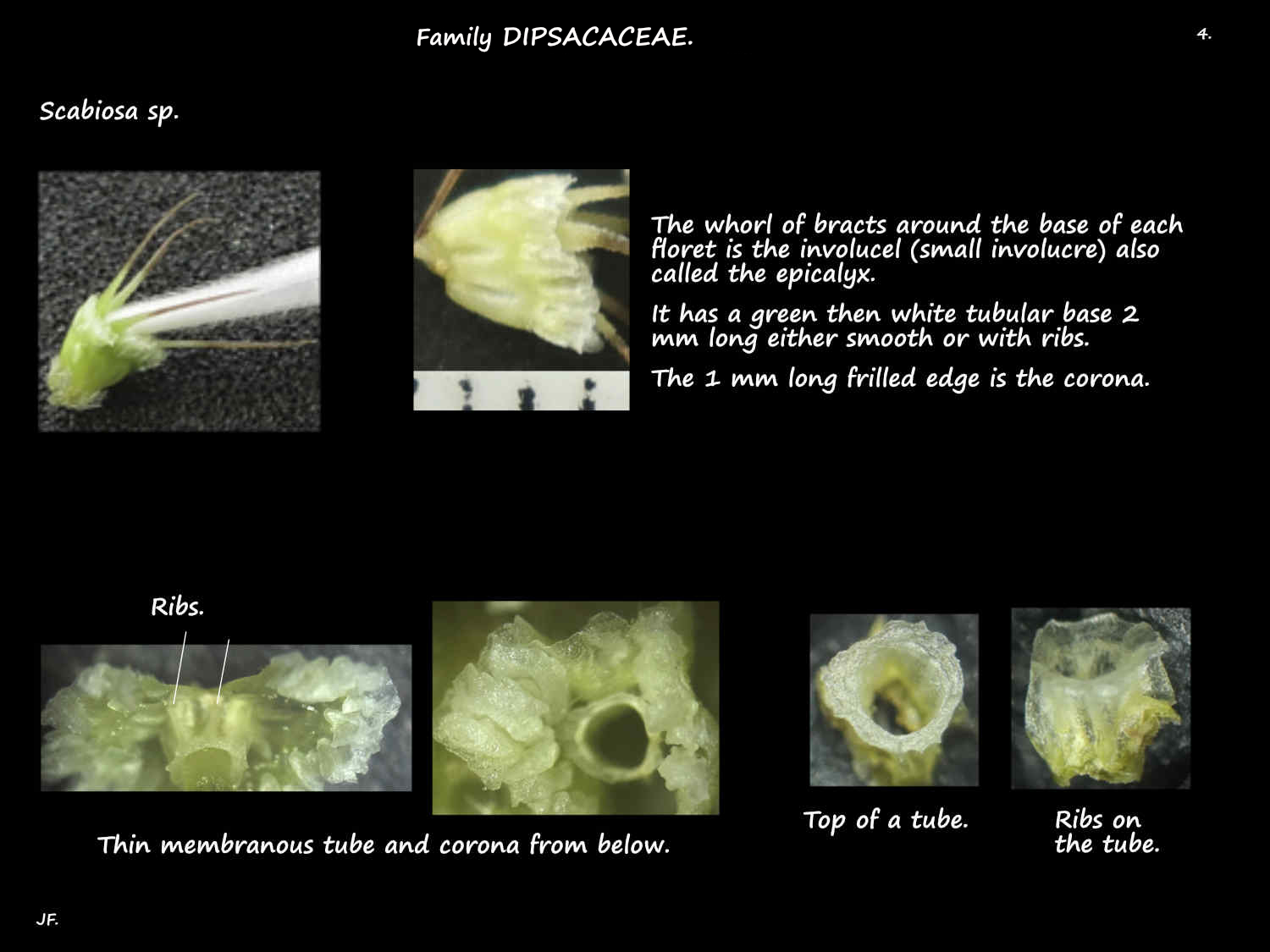
Each individual floret has 1 row of basal bracts collectively called an involucel or epicalyx.
(An involucel is a secondary involucre).
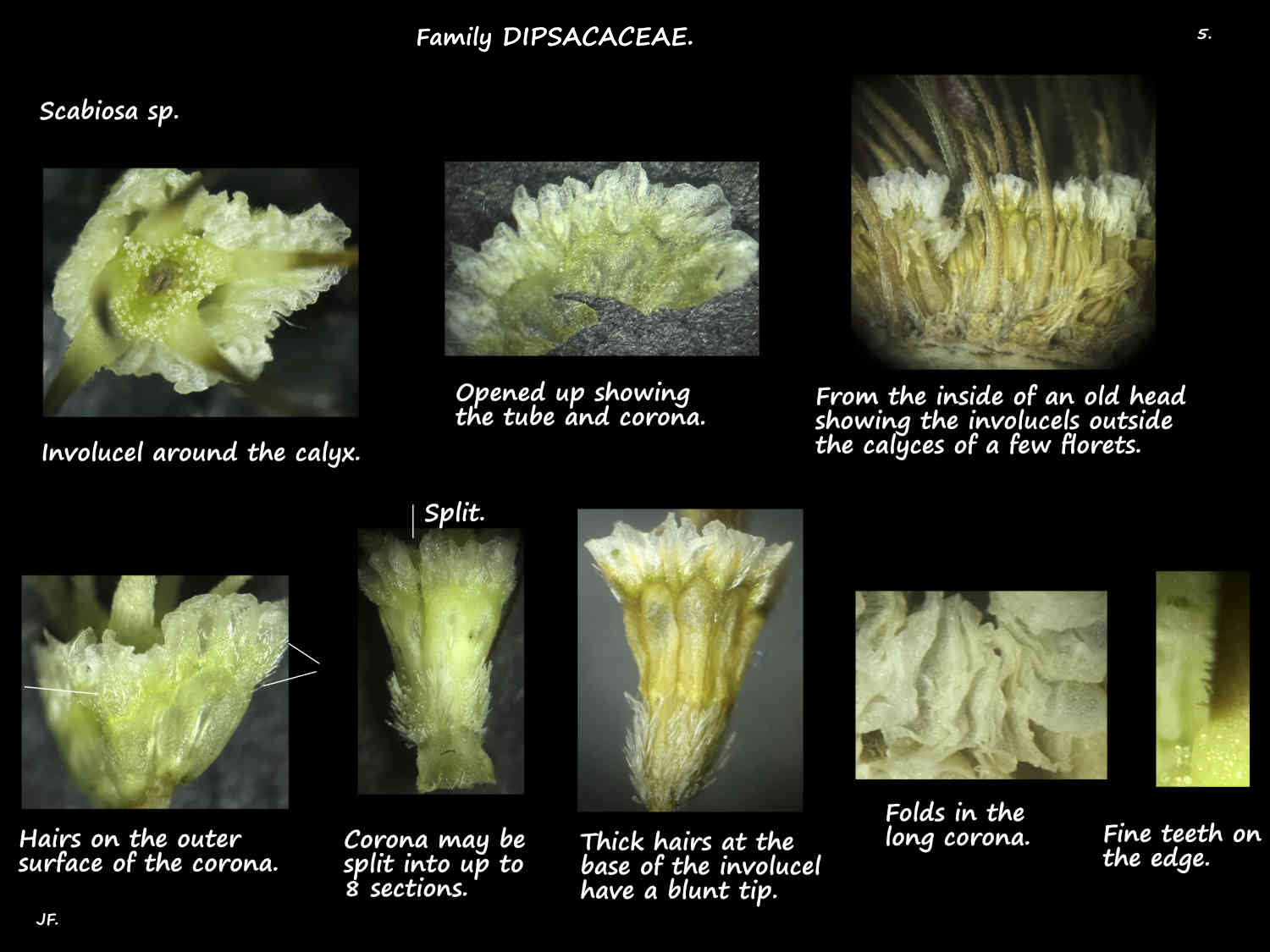
The involucels have a tubular or funnel-shaped base that may be smooth or have 4 or 8 ridges down it.
The ridges may extend the whole length of the tube or be just at the top.
On the rim of the tube is a membranous limb or corona that is erect or spreading.
The corona, with many veins may be cut into up to 8 sections.
The upper edge may be smooth or toothed.
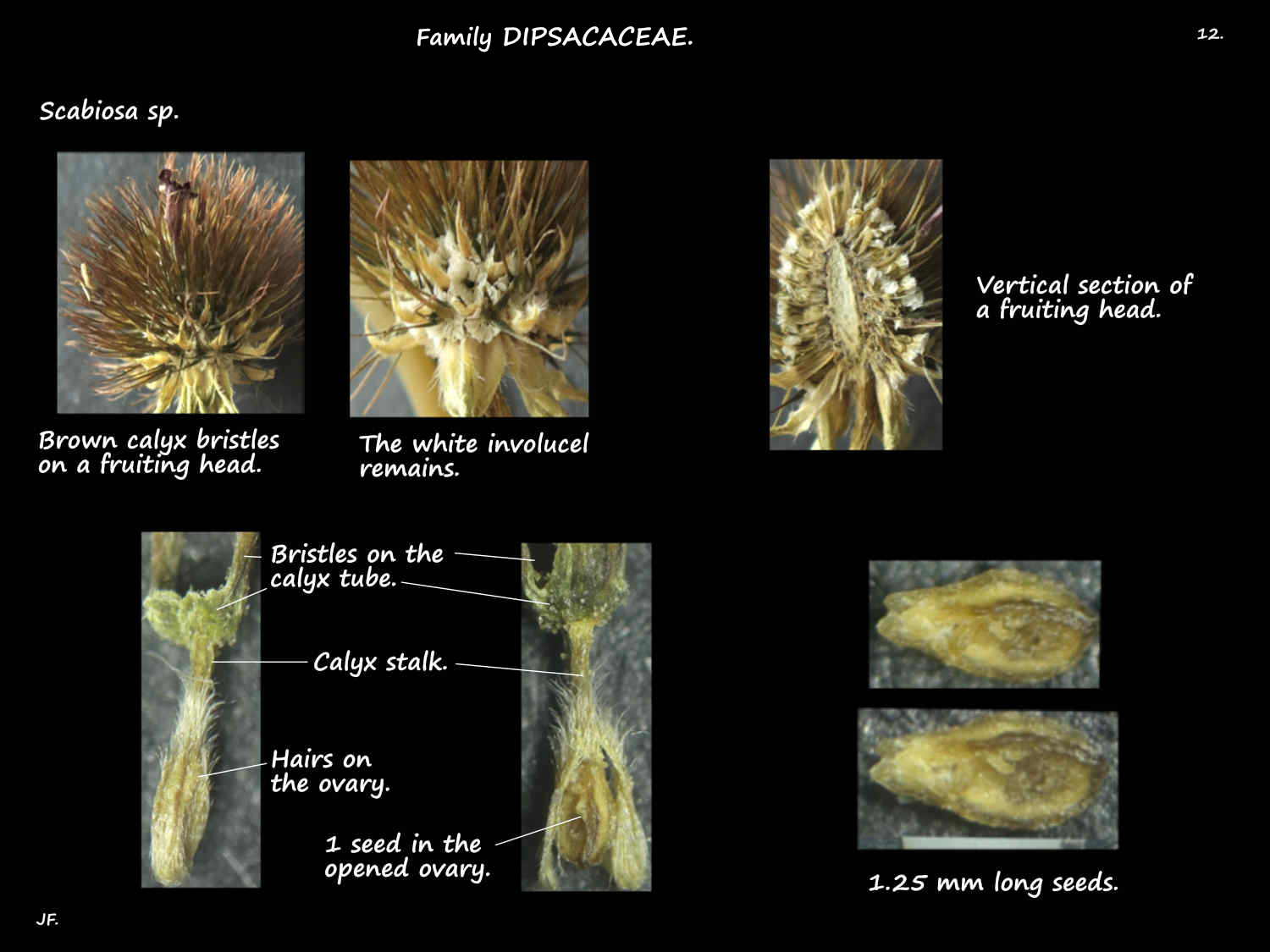
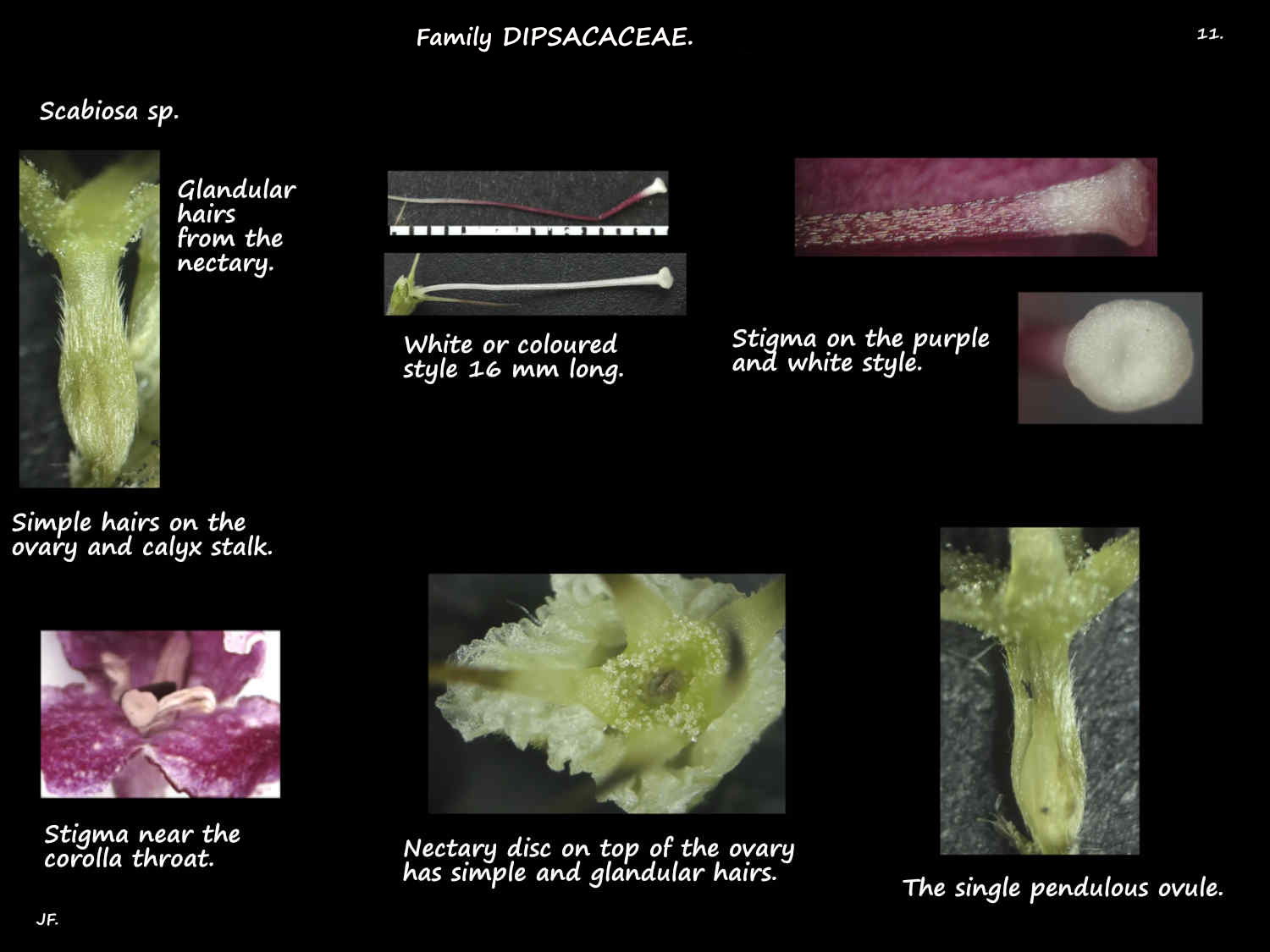
The calyx, on a short or almost no stalk has a small cup-like base.
On the rim are 5 unequal erect then spreading bristles with barbs on the edges.
The calyx also has simple and multicellular glandular hairs on it.
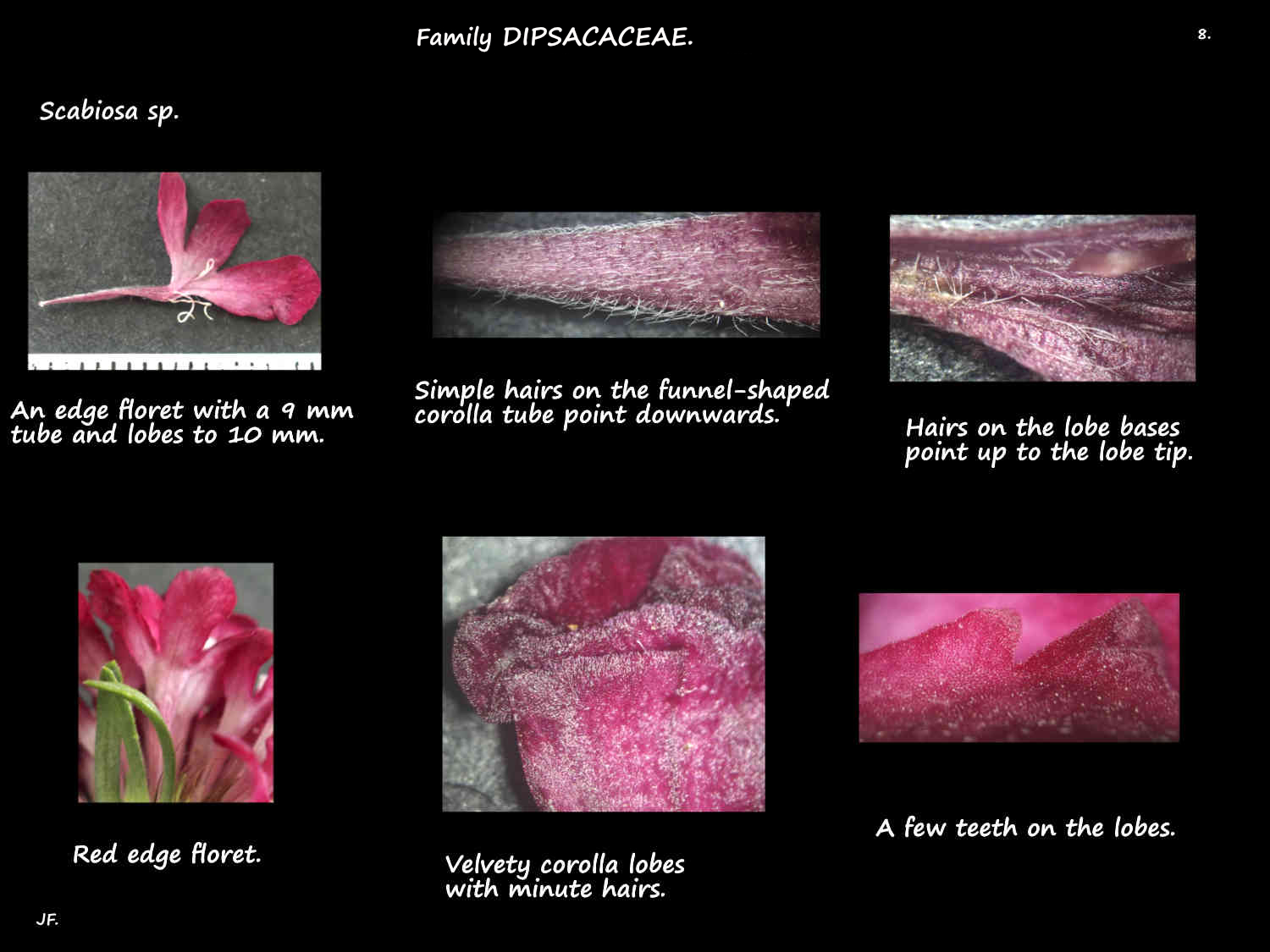
The corolla has a basal tube with 5 (4 to 6) shorter unequal lobes on it.
Flowers on the base of the head are longer and more asymmetric sometimes having 2 lips.
Petals can be white or pale shades of blue, mauve, purple, yellow or pink.
The corolla also has simple and multicellular glandular hairs on it.
The 4 stamens are inserted near the top of the corolla tube.
Filaments hold the anthers past the corolla.
The inferior ovary, of 1 locule with 1 pendulous ovule is surrounded by the involucel.
The style has 2 stigma lobes.
On top of the ovary, around the syle base is a nectary disc.
The ovary and nectary disc have hairs the same as those on the calyx and corolla.
Fruit are called achenes although strictly speaking achenes are from a superior ovary.
They are better called a cypsela which is a dry indehiscent, single seeded fruit with the calyx attached.
The involucel remains attached as do the 5 spreading calyx bristles.
All the bristles on the fruiting head make it prickly like a pincushion.
************************
Species plants include:
Scabiosa atropurpurea or ‘Sweet Scabiosa’ up to 1 m high has 15 cm long deeply lobed leaves.
The 4 to 5 cm flower heads have deep purple, crimson or white flowers. It can become a weed.
Scabiosa caucasia has 8 cm heads with pale blue to mauve flowers.
Scabiosa columbaria, with pink flowers is commonly used in hybridisation.
Scabiosa drakensburgensis has white flowers.
Scabiosa graminifolia has hairy grass-like leaves and lavender flowers.
Cultivars, of various heights can have single or double heads.
As well as white, flowers come in pale pinks, blues or mauves.
They can also be deep blues, pinks, purples or a red that is almost black.
There are yellow flowers or flowers with bronze calyces.
J.F.