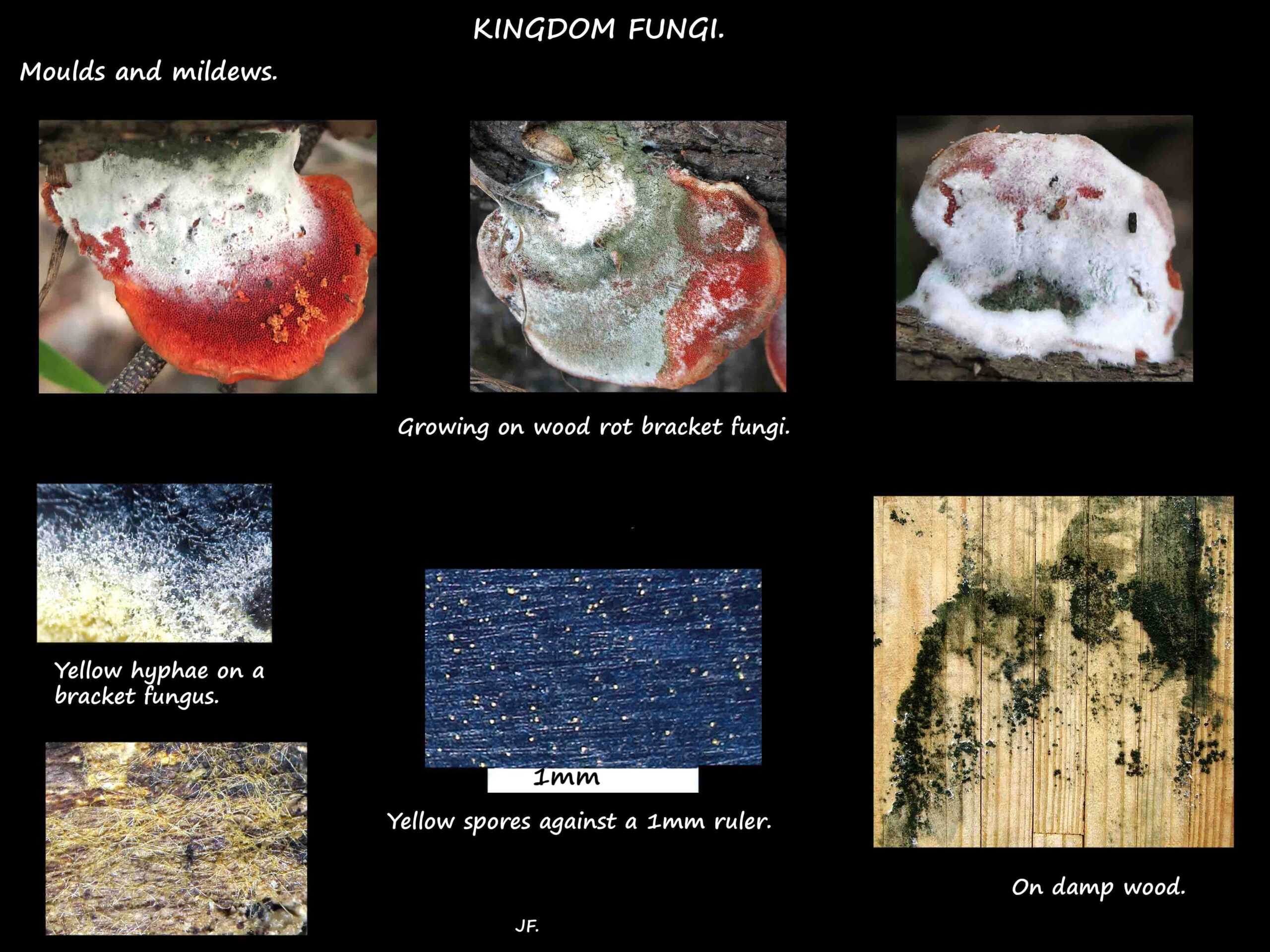
Moulds and mildews.
These are fungi found in the divisions Ascomycota and Zygomycota.
They consist of multicellular filaments or hyphae which when massed form a visible mycelium.
They are often considered together under either name.
Colour is often used to distinguish moulds and mildews but is not always reliable.
Moulds.
Typically form fuzzy raised colonies on decaying organic matter especially food.
They can be black, white, green, yellow, brown, grey, blue or red.
There are thousands of species and all require moisture to grow.
Enzymes are secreted from the tips of the hyphae which digest starch, lignin and cellulose
into simple molecules that can be absorbed.
These enzymes, and myxotoxins, can inhibit the growth of other microorganisms.
Moulds are important in the decomposition of organic matter.
Mildews.
Closely related but tend to form flat colonies and be white rather than coloured.
They may also be grey or yellowish and turn black or brown with age.
Reproduction is by masses of spores formed on the hyphal tips.
Powdery and downy mildews of plants, seen as white spots, are caused by many species.
J.F.