Acca sellowiana.
Family Myrtaceae > Subfamily Myrtoideae > Tribe Myrteae.
From South America the Feijoa, Guavasteen or Pineapple guava was known as Feijoa sellowiana until it was moved into the Acca genus.
There are 3 Acca species A. lanuginosa, A. macrostema and A. sellowiana which is the only one commonly cultivated.
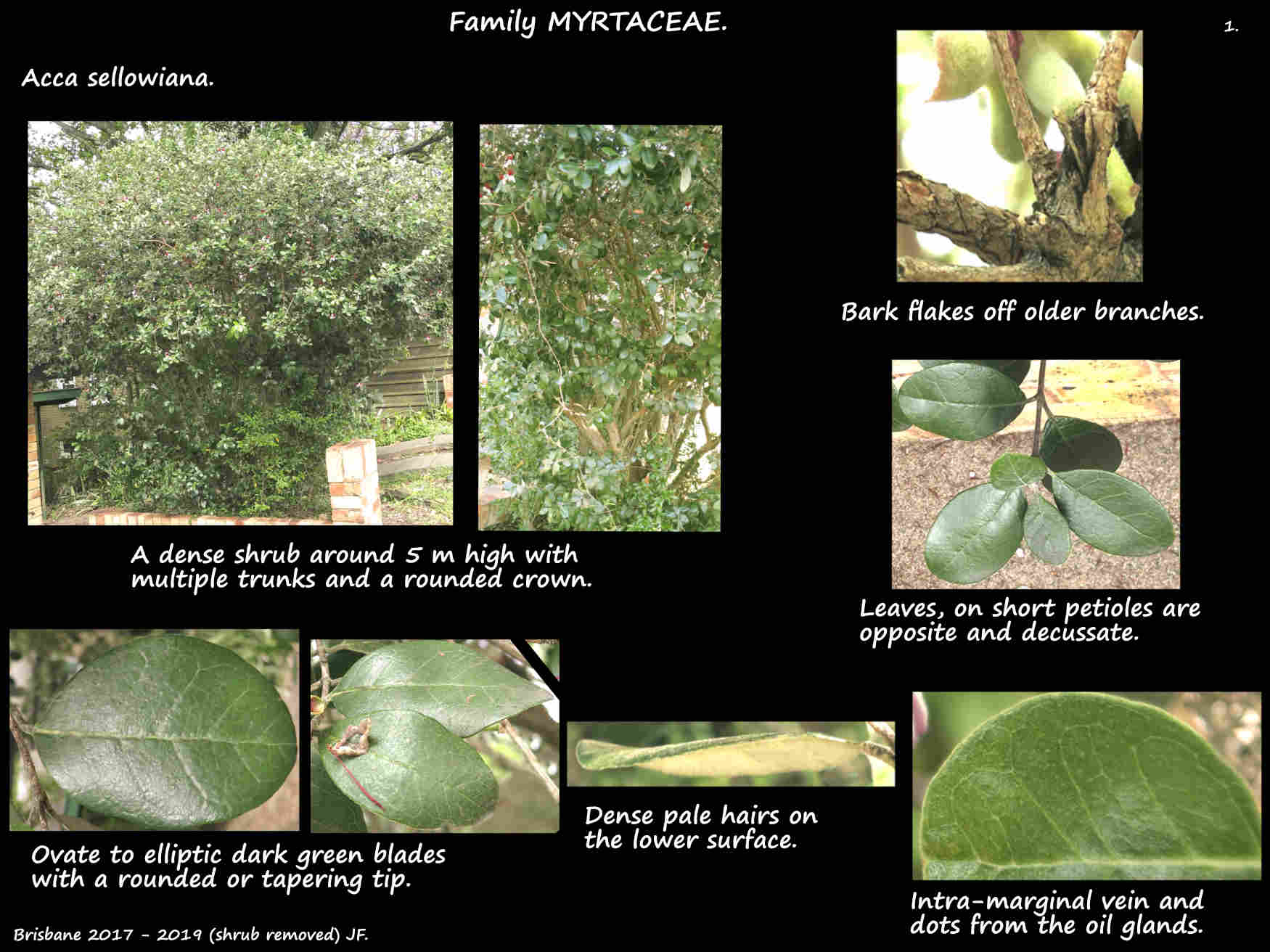
They are usually seen as evergreen shrubs up to 3 m high and wide.
They can grow into small trees up to 6 or 7 m high with a dense crown.
Small green or grey twigs are swollen at the nodes and have simple hairs.
The grey or grey-brown bark on the usually multiple trunks and the larger branches cracks and peels.
The simple leathery leaves, on a short petiole are opposite to sub-opposite.
The ovate to elliptic blades, up to 7 cm long by 4 cm wide have a smooth edge.
The smooth glossy upper surface is dark to grey-green.
The lower surface is white or silver due to a thick layer of pale or brown matted hairs.
There are around 6 main side veins on each side and an intra-marginal vein.
There are oil glands.
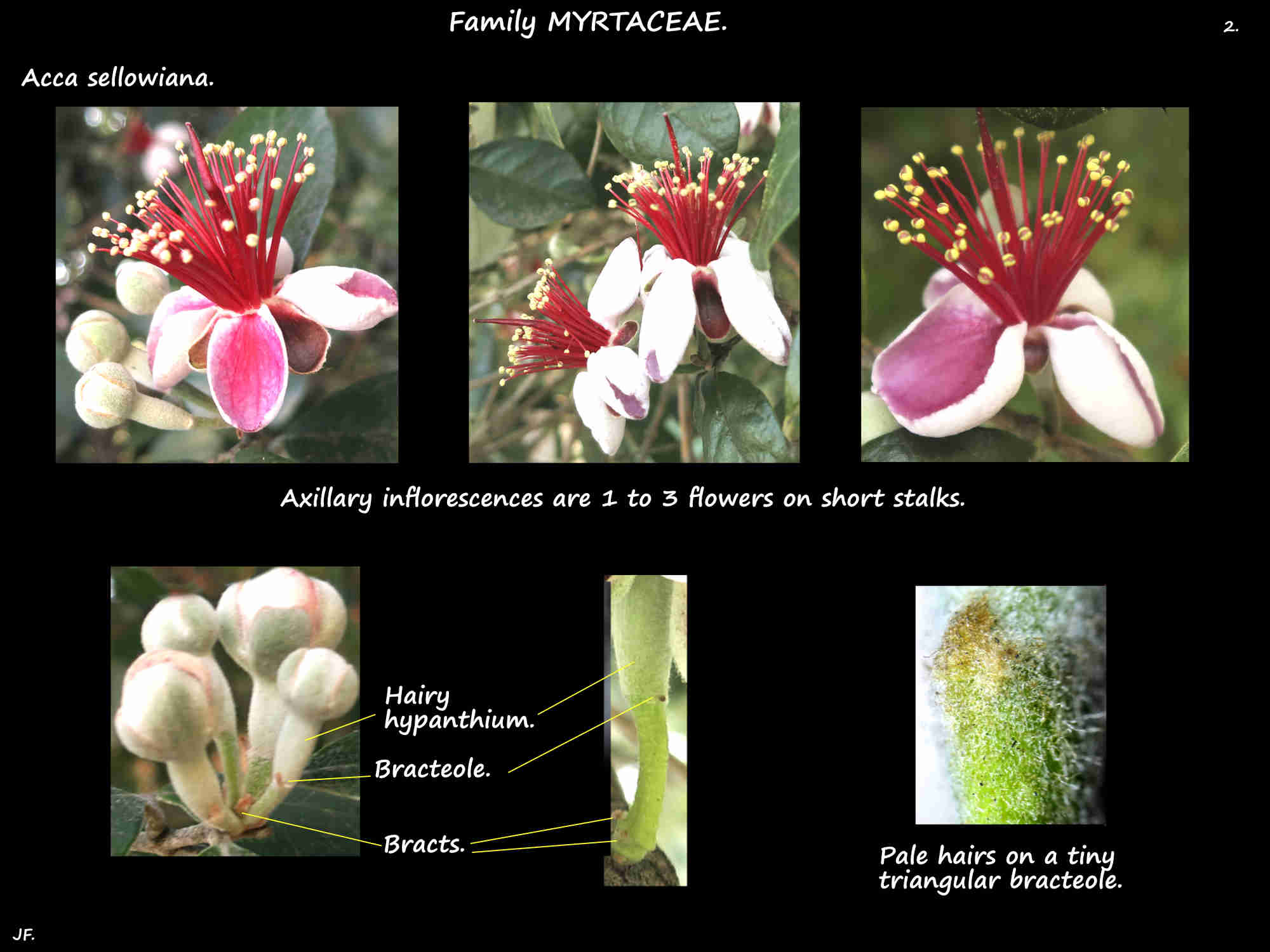
Axillary inflorescences are a solitary flower or a small cluster of 2 or 3 flowers.
The bisexual flowers, on pedicels are around 3 cm across.
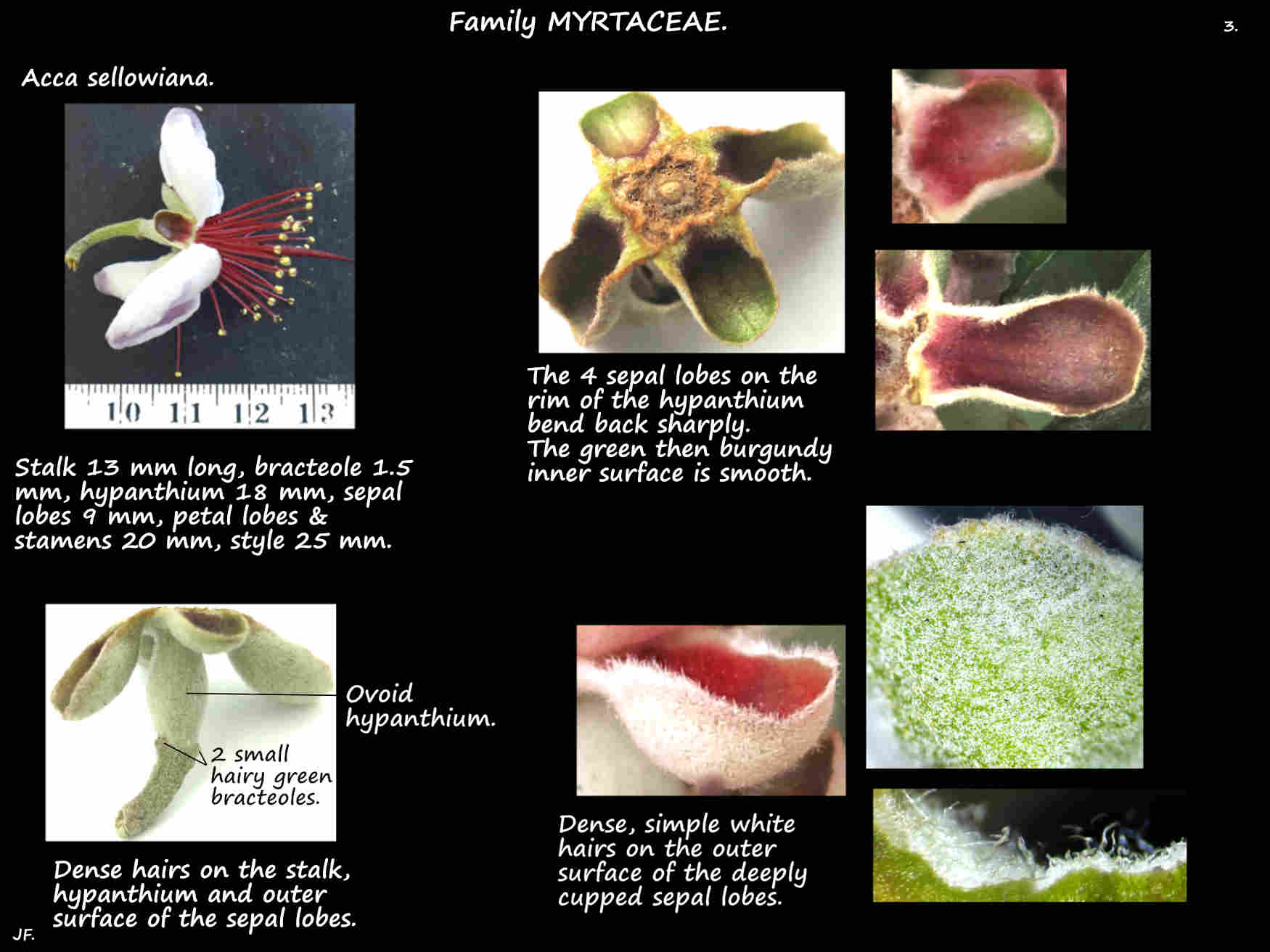
There are bracts at the base of the peduncle and tiny bracteoles on the short pedicel.
There are dense hairs on the peduncle, pedicels, bracts and bracteoles.
The hypanthium, up to 2 cm long is formed from the fused sepal and petal bases.
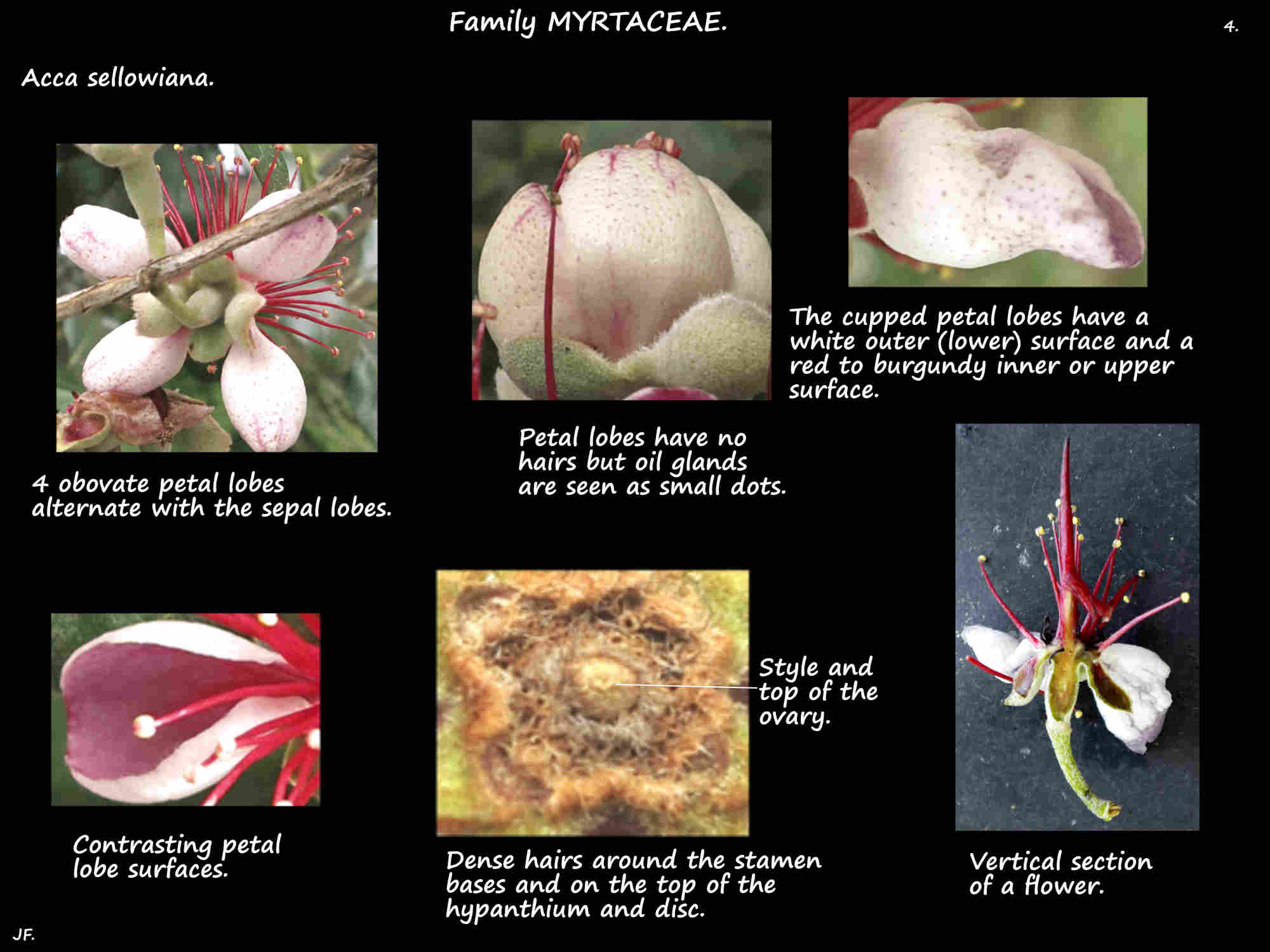
Densely hairy it has the 4 sepal and petal lobes alternating on the rim. (There may be 5 or 6 petal lobes).
The oblong sepal lobes bend back to lie beside the hypanthium.
The margins curve inwards (up) and the smooth inner surface is green then red to burgundy.
The outer green surface looks white due to the dense covering of pale hairs.
The cupped fleshy petal lobes, longer than the sepal lobes also bend backwards.
The inner surface is red to burgundy and the outer is white.
There are no hairs but oil glands are obvious on the outer surface.
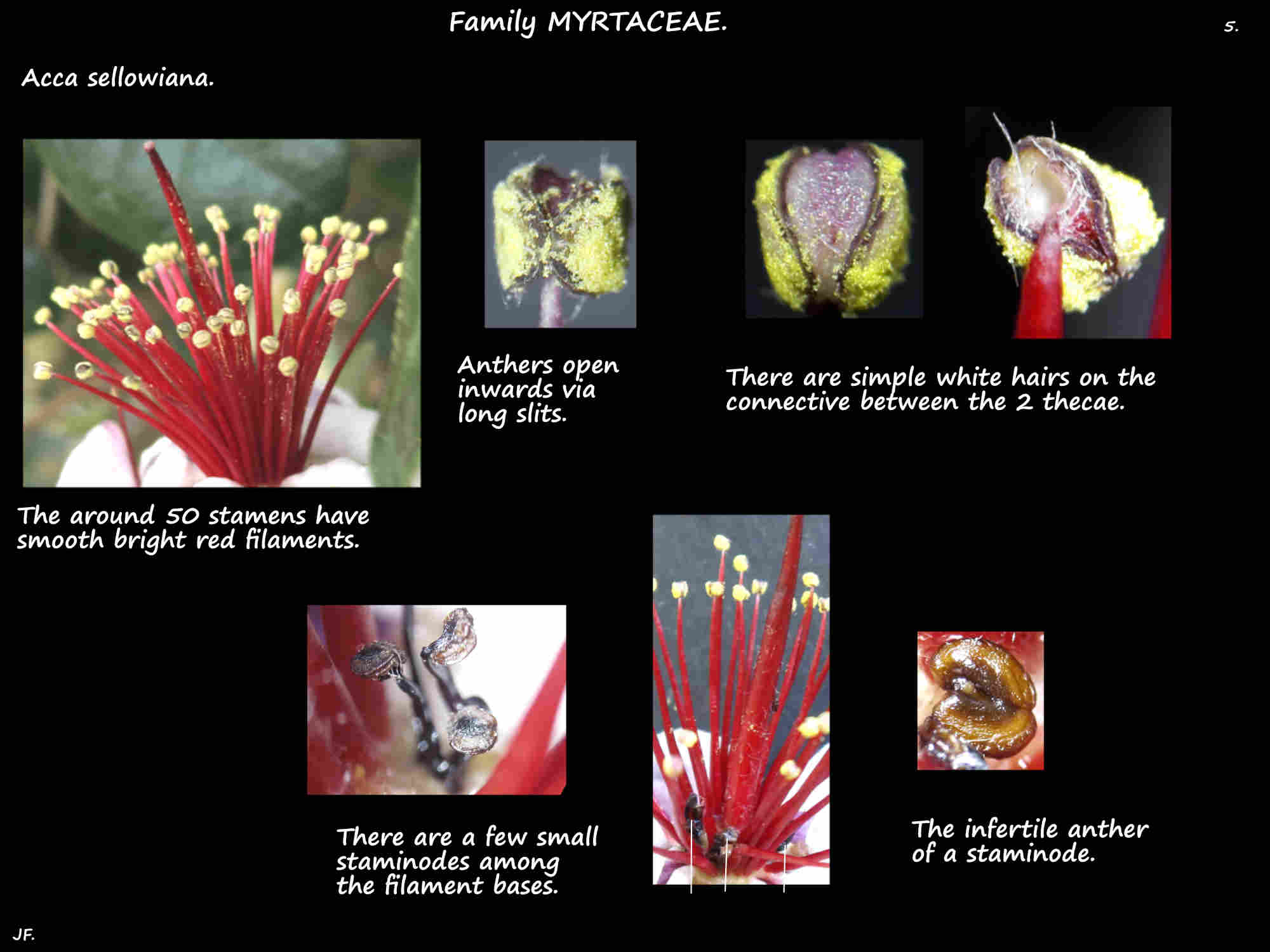
There are around 50 stamens with bright red filaments.
The 2 pollen sacs or thecae release the yellow pollen through longitudinal slits.
There are longish white hairs on the connective between the 2 sacs.
There are a few staminodes and dense short hairs on the disc and around the filament bases.
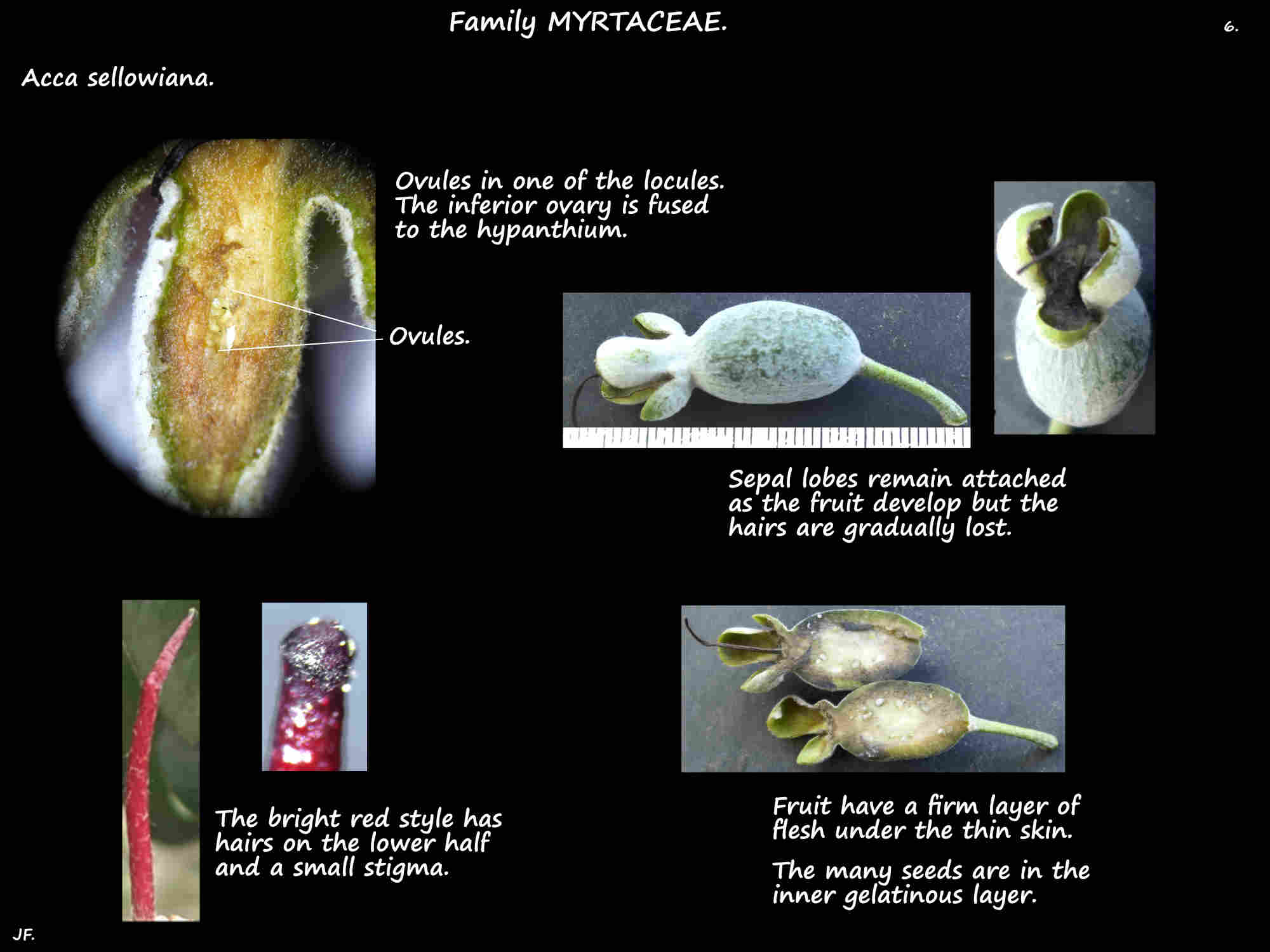
The inferior ovary, with up to 5 locules is fused to the hypanthium.
The single red style, with scattered hairs on the lower half has a small capitate stigma.
The fruit are ovoid, oblong or ellipsoid berries often around 6 cm long and 4 cm wide.
The thin skin matures from green or grey-green to yellow or slightly orange.
The sepal lobes remain, the white hairs are gradually lost and there are oil glands just under the skin.
Firm granular cream or white flesh surrounds a translucent gelatinous inner pulp with the seeds.
There are around 30 (to 100) tiny flat seeds in the inner pulp.
There are several cultivars mainly with variations in the fruit size and surface.
J.F.