Syngonium podophyllum.
In Family Araceae its common names include Arrowhead plant or vine.
There are about 36 species and Syngonium podophyllum is the most commonly cultivated one.
It is naturalised in some areas of Queensland where it is a weed.
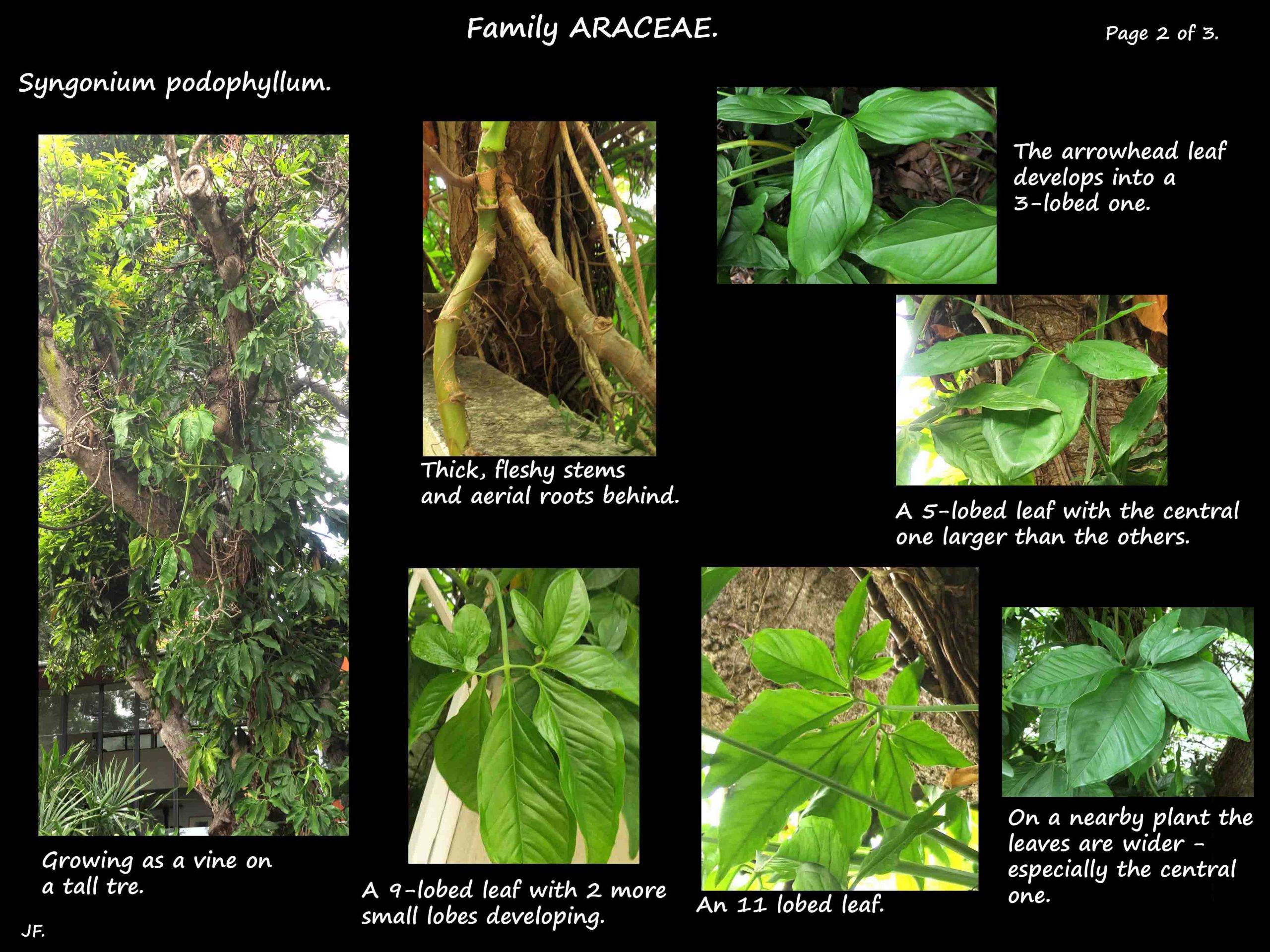
They can remain as a low terrestrial herb or, with support, become a vigorous climber up to 10 m.
Young stems are slightly fleshy while the older brown ones can be slightly woody.
Aerial roots grow from the nodes and help support the plant when growing as a vine.
Leaves vary greatly depending mainly on the age of the plant and their position.
The leaf stalks can be up to 60 cm long with a grooved upper surface and a basal sheath.
Juvenile leaves, most obvious when it is growing as a low herb, are an arrowhead shape.
They are up to 14 cm long, a plain green, green with pale veins or pale centres with a green border.
As the plant grows, especially if it becomes a vine, the leaves are larger and develop lobes near the base.
The plain dark green adult leaves, up to nearly 40 cm long and 15 cm wide can be divided into 3 segments
or into 5 to 11 lobes with the central one being larger.
Up to a dozen inflorescences, on stalks up to 13 cm long, develop in the higher leaf axils.
They consist of a white spadix up to 9 cm long partially protected by a spathe.
The spathe is green outside and cream or pale green inside.
The lower constricted tubular part of the spathe covers the female flowers and the upper expanded blade
partially surrounds the male flowers.
The cream male flowers, a few mms wide, are more numerous than the lower female ones.
There are 4 anthers that are fused to various degrees.
The greenish female flowers are hexagonal in shape and have no petals or sepals consisting only of an
ovary with a stigma at the top.
After pollination the male flowers usually fall off as does the upper part of the spathe.
The lower greenish tubular part of the spathe protects the developing fruit and turns red as the fruit ripens.
The small, fleshy individual fruits merge into a single red then brown fruit up to 7 cm long.
The flowers and fruit are often hidden by the foliage.
Reproduction is almost always by cuttings.
Cultivars are variegated with more cream and white markings and in different patterns.
There are some with almost white leaves and others with yellow or pink ones.
Syngonium neglectum and Syngonium angustatum are very similar to S. podophyllum and flowers are
usually needed to differentiate them.
S. neglectun has inflorescences with hexagonal flowers.
S. augustatum and S. podophyllum have cross-shaped flowers.
S. augustatum has shorter and narrower juvenile leaves that the others.
J.F.