Asparagus officinalis.
Family Asparagaceae s.l.
Garden asparagus, and numerous cultivars, are grown commercially.
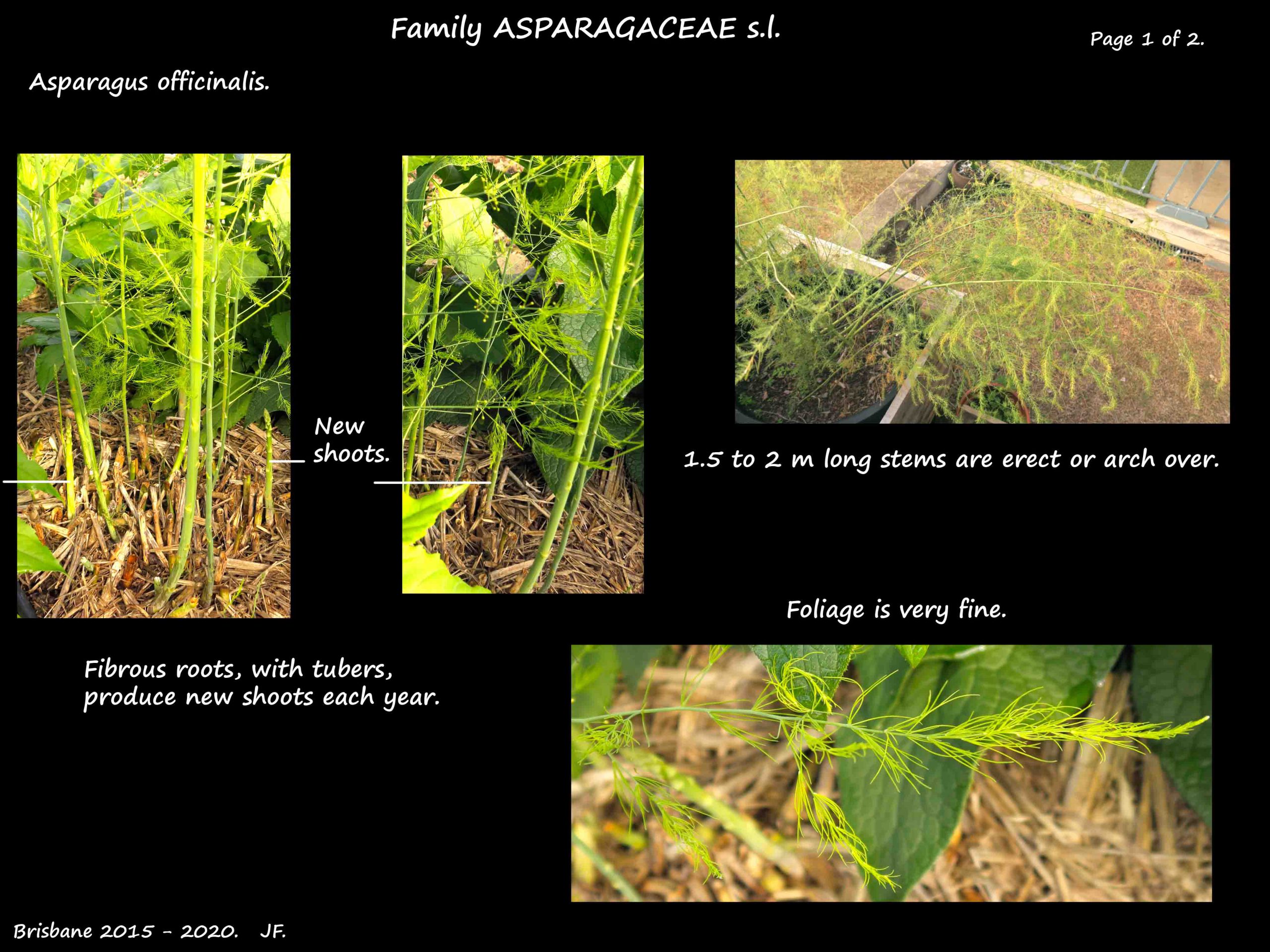
A perennial plant with a compact base or crown of fibrous roots and tubers.
New, erect stems grow from the crown each year.
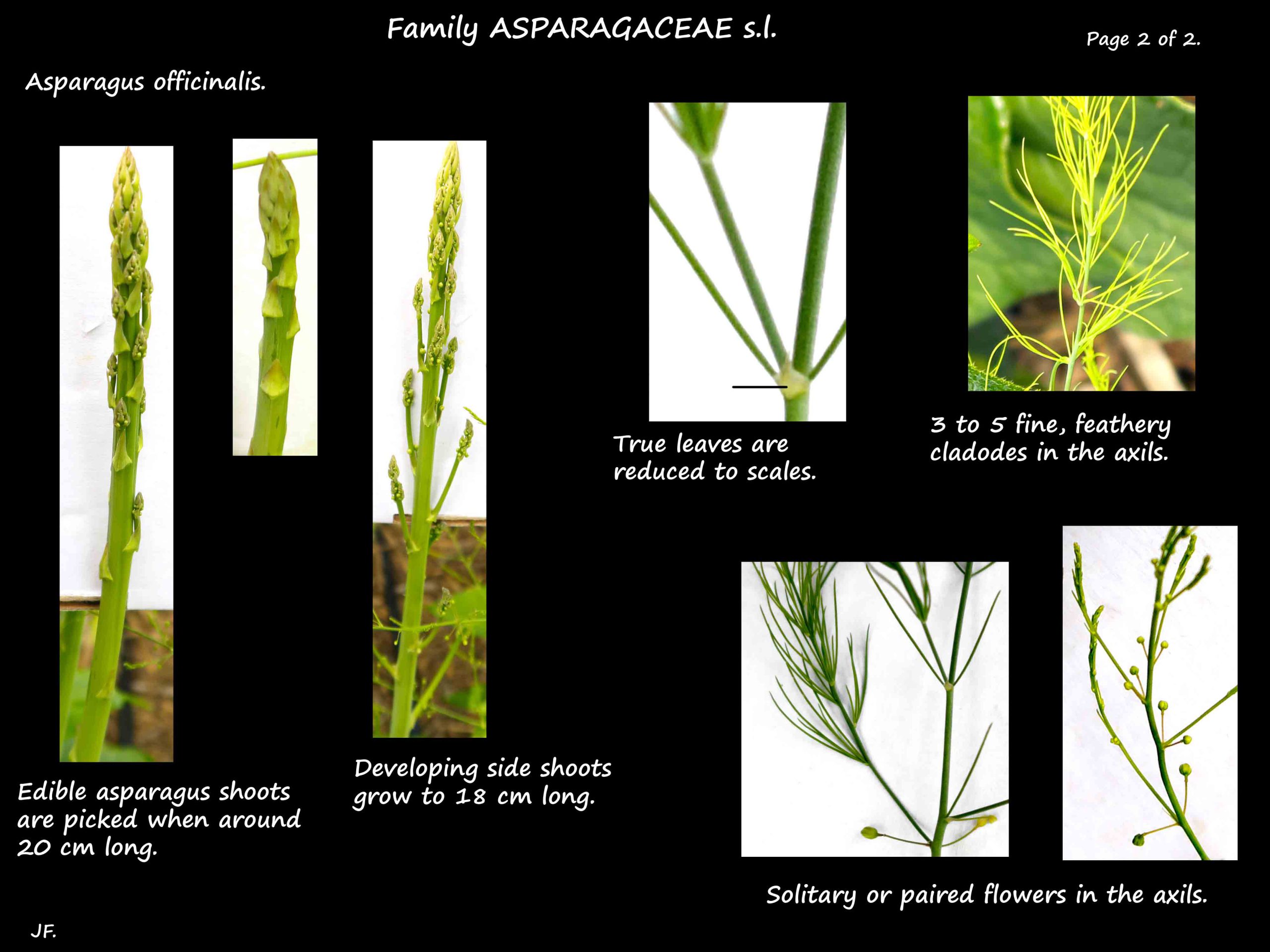
At 15 to 25 cm high each stem has multiple buds ready to form side branches.
At this stage they can be harvested.
If left, the stems grow up to 1.5 or 2 m high with side branches up to 18 cm long.
The true leaves are reduced to 3 to 4 mm long scales with an extension or spur at the base.
There are 3 to 5 (1 – 10) very fine cladodes in each leaf axil but no spines.
The flattened green cladodes are up to 25 or 30 mm long and 0.5 to 1 mm wide.
The branches have a very fine, feathery appearance.
Inflorescences are 1 or 2 drooping flowers in each axil.
Typically male and female flowers are on separate plants but, especially in cultivars,
there may be some bisexual flowers.
The jointed flower stalks or pedicels are 1 to 2 cm long.
The flowers, with 6 tepals, are a slender bell shape and around 5 mm long.
In 2 whorls of 3 they are white to cream with greenish to brown markings.
The 6 stamens are 1.5 to 3 mm long, with anthers that open inwards.
The superior ovary with 3 locules, is 2 to 3 mm long and has one style with 3 branches.
The red berries, nearly 1 cm across, are red and have up to 6 black seeds.
J.F.