Mansoa alliacea.
Family Bignoniaceae.
The Garlic vine is one of the 12 accepted species in the genus.
It is the most frequently cultivated.
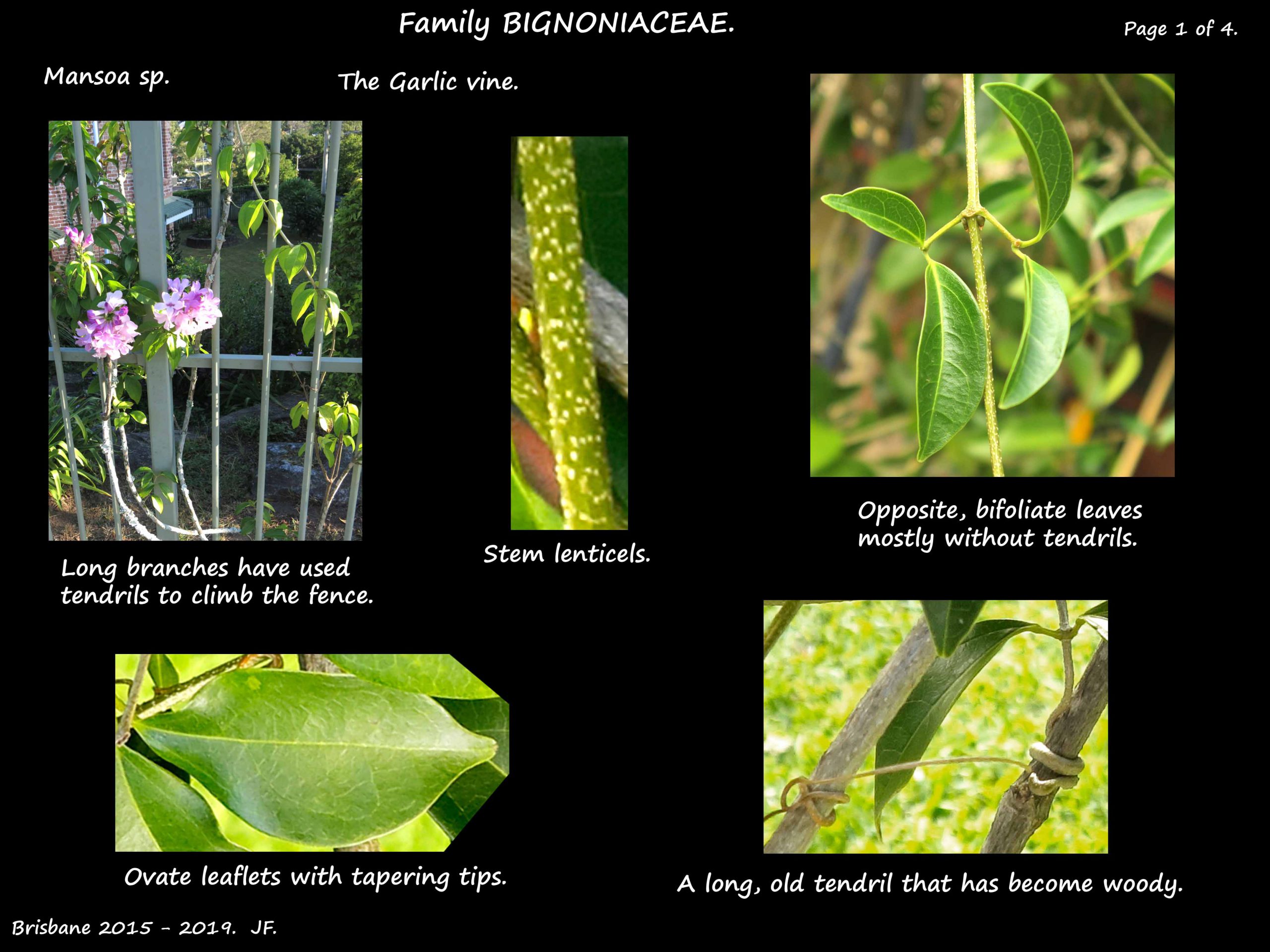
It is an evergreen liana (woody vine) that climbs by tendrils.
Stems are 2 to 3 m long but growth is compact and it can be grown as a shrub.
The leaves, to 15 cm long, are oppositely arranged.
They are bifoliate with 2 ovate leaflets and a sometimes a terminal tendril.
When crushed they smell like garlic.
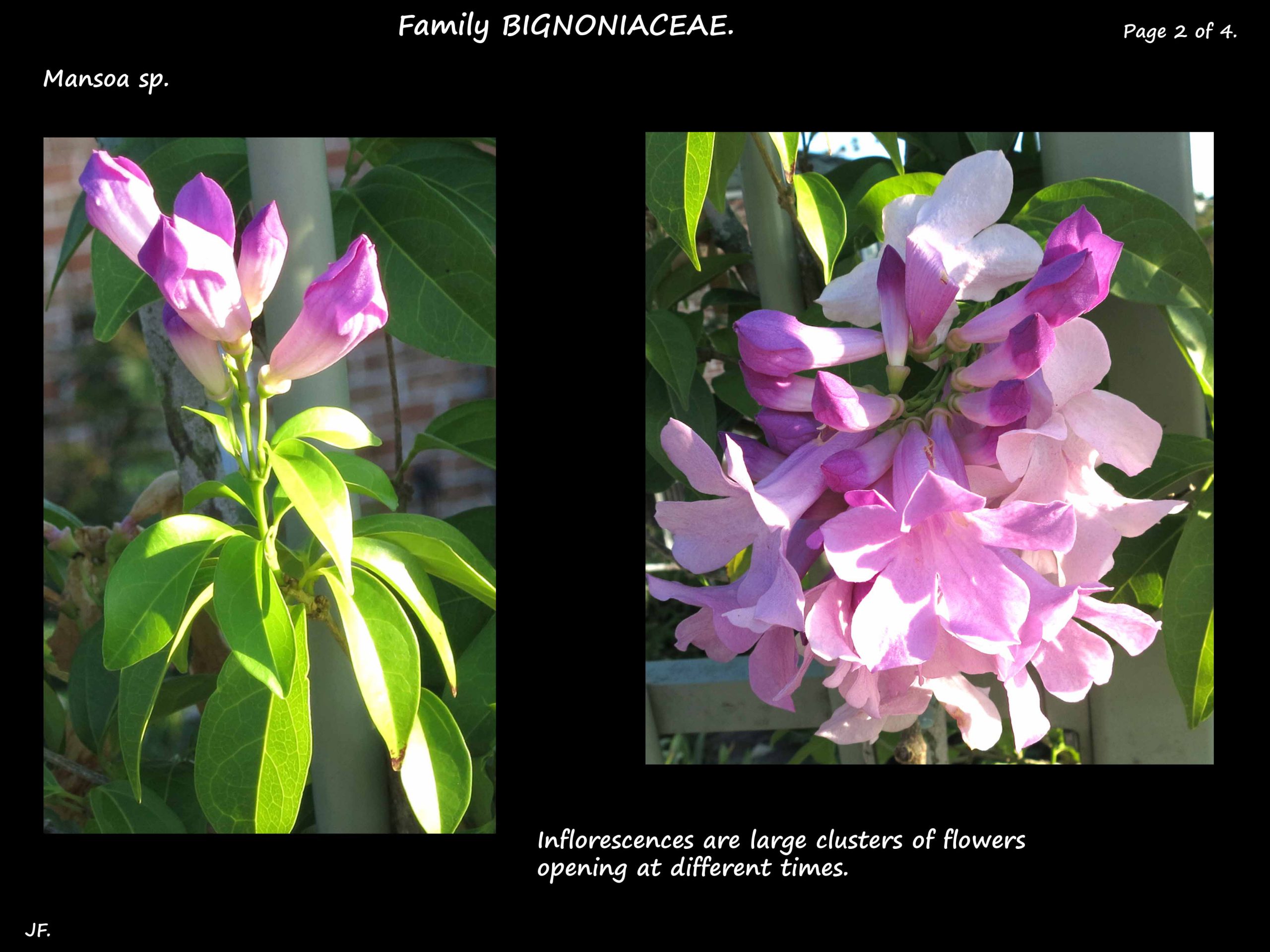
The terminal or axillary inflorescences are large clusters of flowers.
They can flower twice a year but can have a few flowers at any time.
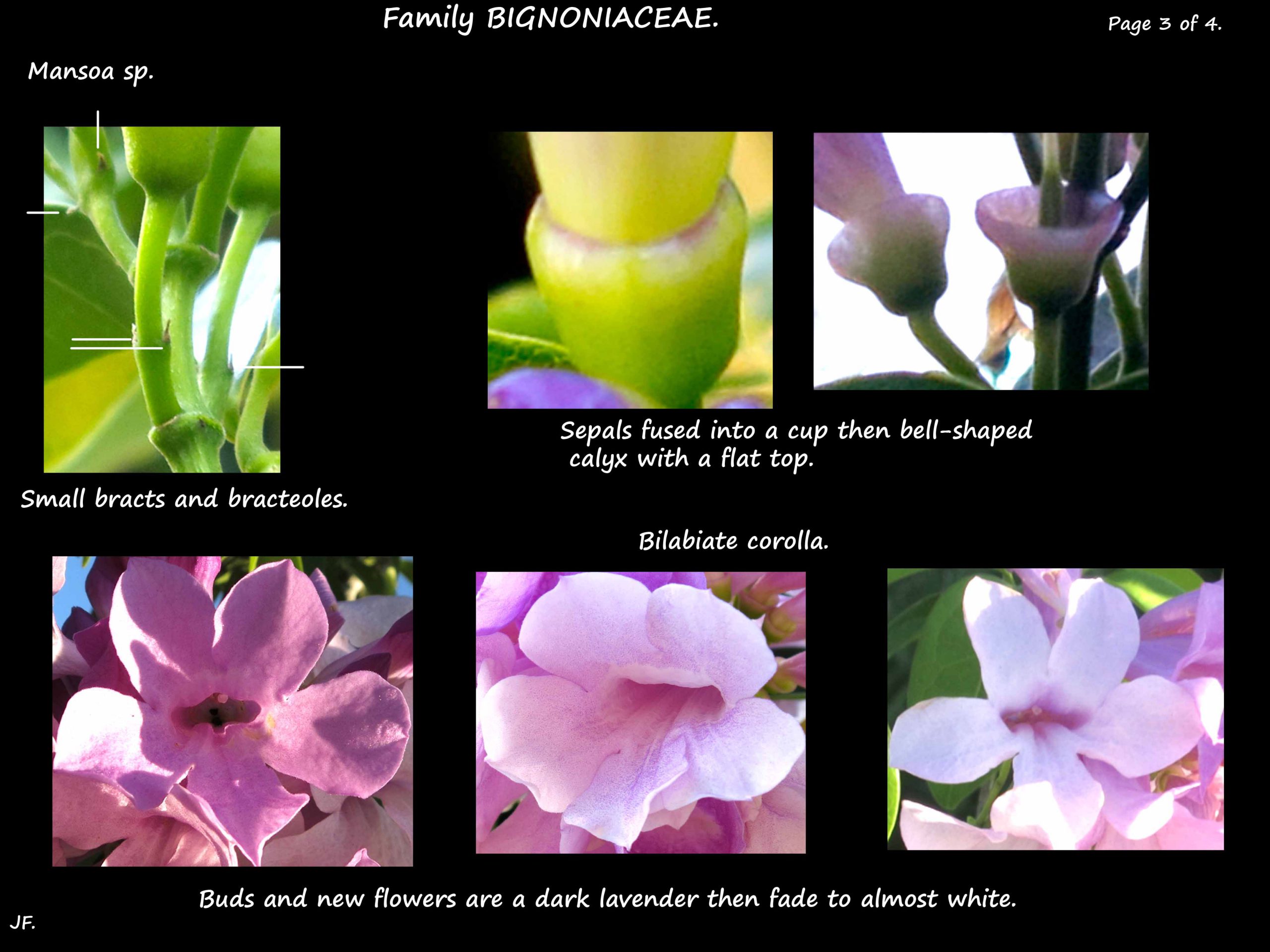
There are small bracts and bracteoles on the inflorescence stalks.
The bell-shaped calyx has a wide, flat top.
The flowers are funnel-shaped.
The narrow tubular part is 3 cm long, slightly flattened and curved.
The 5 rounded, bilabiate, widely spreading terminal lobes are also 3 cm long.
Buds, and newly opened flowers, are a deep lavender with a white throat.
They fade to a pale lavender then almost white.
An inflorescence can have all colours at the same time.
The fruit are brown capsules with winged seeds.
JF.