Lepidium virginicum.
Virginian peppercress, from North America is a common weed in S. E. Queensland.
The herbs, lasting 1 or 2 years can be 50 to 70 cm high.
The much branched stems and the leaves can be smooth or have a few simple hairs.
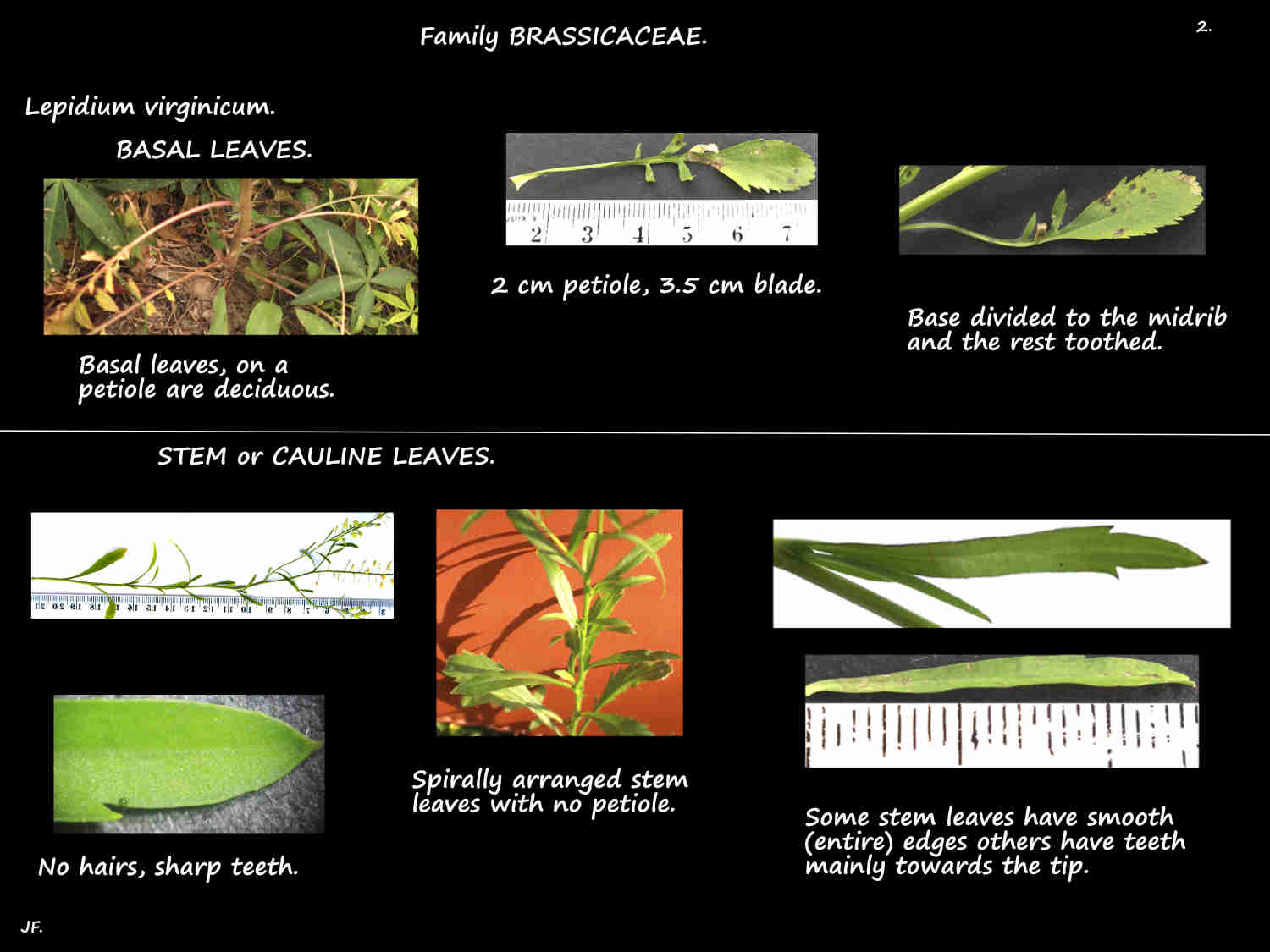
The basal leaves are on a petiole up to 3.5 cm long.
The obovate or oblanceolate (widest part above the centre) blades are up to 15 cm long.
Part or all of the blade is deeply divided down to the midrib (pinnatifid).
Any undivided part is toothed.
Basal and lower stem leaves fall off.
Stem leaves, up to 4 cm long at the base get smaller towards the top.
They have no petiole and the blade is narrowly elliptic to linear.
The tips are pointed and the edges are smooth or toothed.
Inflorescences are terminal racemes up to 10 cm long with the flowers spirally arranged along the midrib.
Each flower is on a stalk or pedicel up to 6 mm long.
Flowers are at the tip of the midrib which keeps growing.
There are 4 free green sepals alternating with 4 free white petals.
The ovate sepals are around 1 mm long.
The spoon-shaped petals are 1 to 2 mm long and 0.5 to 1 mm wide.
Petals remain fairly erect so flowers are only 1 to 2 mm across when fully open.
There are usually only 2 stamens but occasionally (1) 4.
On a filament 0.5 to around 1 mm long they have a basifixed anther 0.2 mm long.
Anthers open through longitudinal slits.
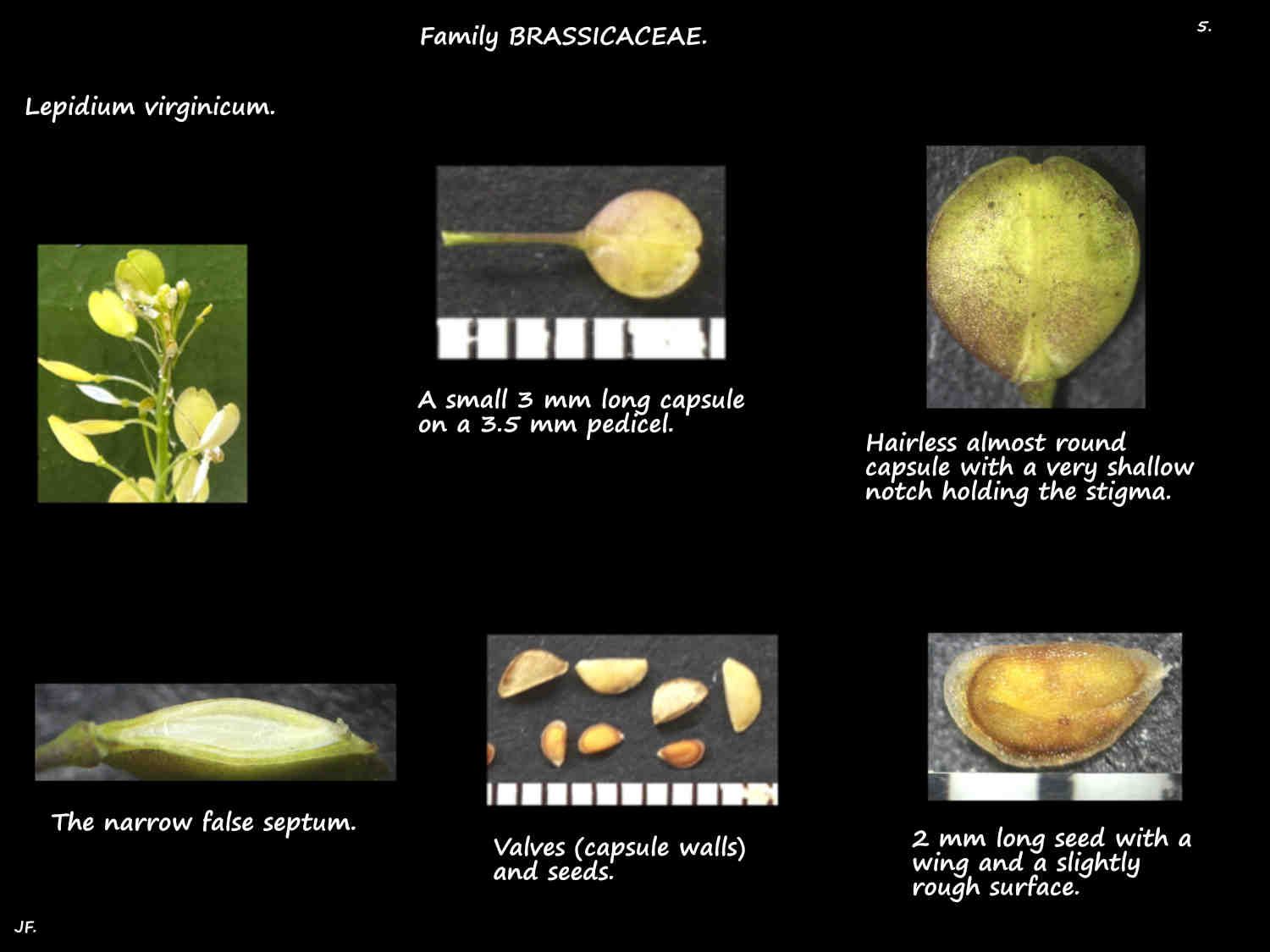
The superior ovary, of 2 fused carpels has 1 locule divided into 2 chambers by a false septum.
The single ovule in each chamber has parietal placentation.
The stigma is attached to the ovary or on a style under 1 mm long.
The fruit are a flattened capsule (siliqua) and the 2 seeds are released when the chamber walls (valves) fall off.
The roughly circular fruit are on a pedicel around 4 mm long.
Up to 4 mm long and 3.5 mm wide the capsules have a narrow wing on the upper part.
There are no hairs but the surface may be finely granular.
J.F.