Trifolium repens.
Clover, White clover or Shamrock is in Family Fabaceae > Subfamily Faboideae.
A widely cultivated crop it is now naturalised in Australia.
A common weed in lawns it is an environmental weed in some states.
They are herbaceous perennial plants with prostrate stems.
These stems are stolons and they root at the nodes.
They are up to 30 cm long and, with the branching dense mats can form.
Stems have few or no hairs.
The alternately arranged leaves are on a petiole up to 10 to 20 cm long.
The grooved petioles are mainly erect and they have no (or few) hairs.
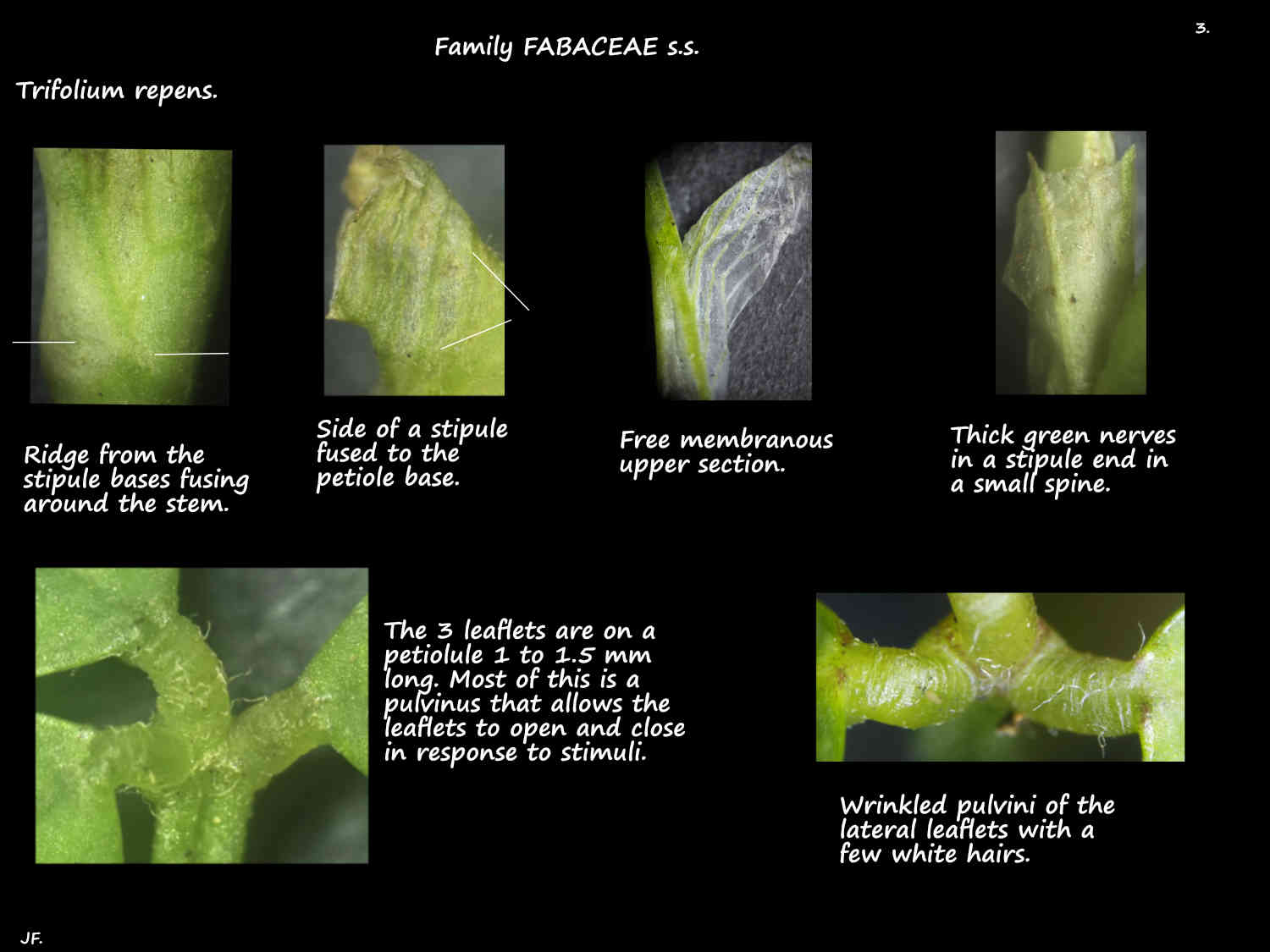
There are 2 stipules on the stem at the base of the petiole.
Around 12 mm long they are thin and membranous with thick green nerves.
Their wide bases meet around the stem making a ridge.
Above the base the edges are fused to the petiole for a few mms.
The free upper sections form a sheath around the stem.
The upper edge has prominent teeth where a vein ends.
The blades are tri-foliate with 3 leaflets off a short midrib.
Some leaves have 4 leaflets giving the plant the common name ‘Shamrock’.
All leaflets have a pulvinus 1-1.5 mm long with a few hairs.
(Called a petiolule but is a wrinkled pulvinus).
The broad ovate to obovate leaflets are up to around 25 mm long and 20 mm wide.
The close roughly parallel veins run from the midrib to the edge where they end in a small tooth.
The leaflet tips are rounded and may have a shallow notch.
The upper surface typically has a pale green or whitish ‘V’ shaped or semi-circular marking (a chevron).
Axillary inflorescences are a roughly spherical head around 2 to 3 cm across.
They are on an erect peduncle that can be over 15 cm high.
At the base are small membranous bracts.
The heads are a raceme with a very short midrib holding up to 30 or more flowers.
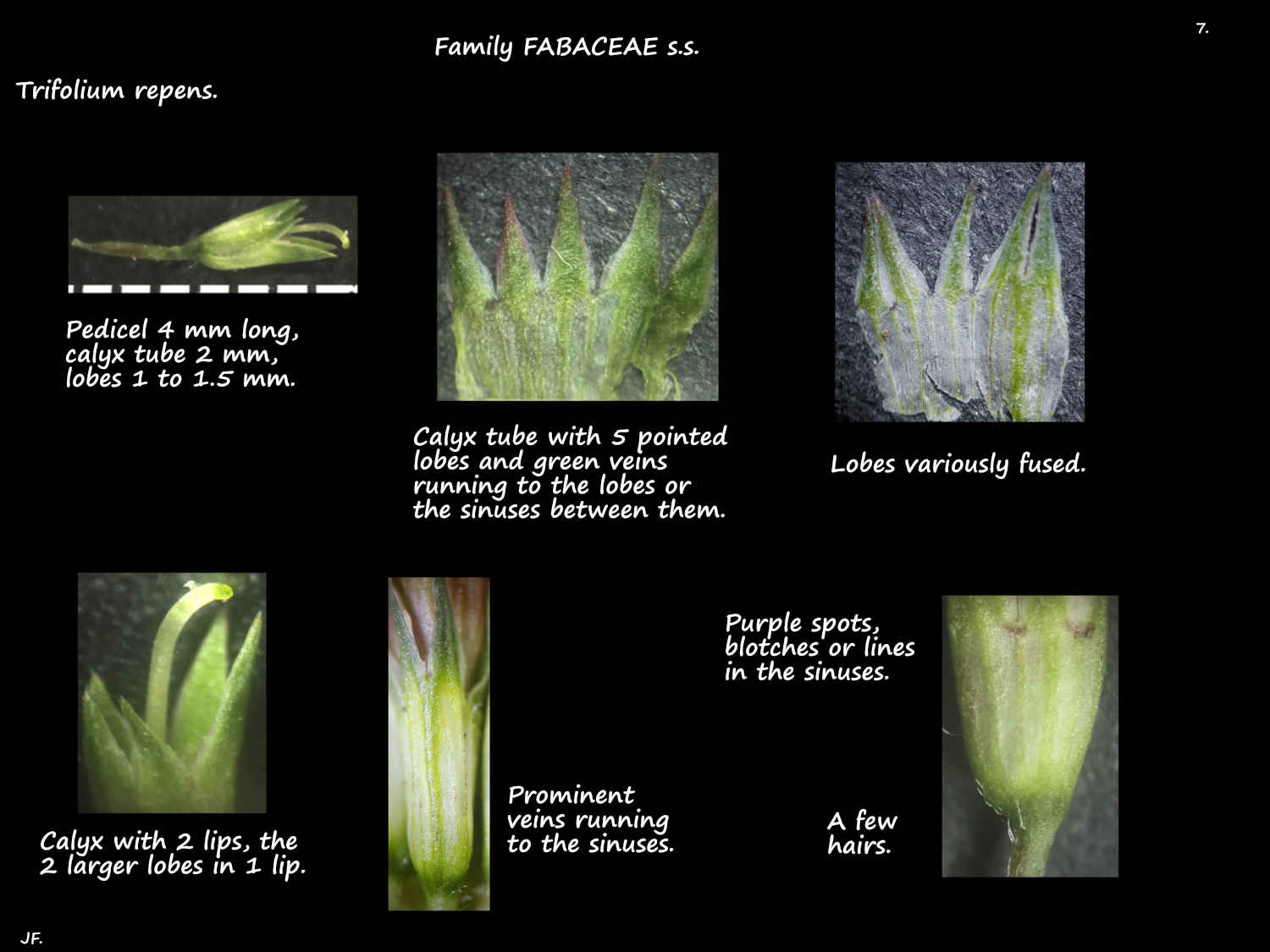
Flowers, on a pedicel around 4 mm long, open from the bottom first.
After pollination the pedicels bend down so the flowers are upside down.
The bell-shaped calyx tube, around 2 mm long has 5 triangular lobes on the rim.
The upper 1 or 2 lobes are much longer than the others.
The 5 (10 or more) prominent green nerves run up the tube to the tips of the lobes or to the sinuses between them.
There is a purple spot under each sinus at the end of a nerve.
The calyx remains on the fruit.
The 5 petals in the corolla, up to around 12 mm long extend well past the calyx.
Petals are white or cream and may have a pink tinge.
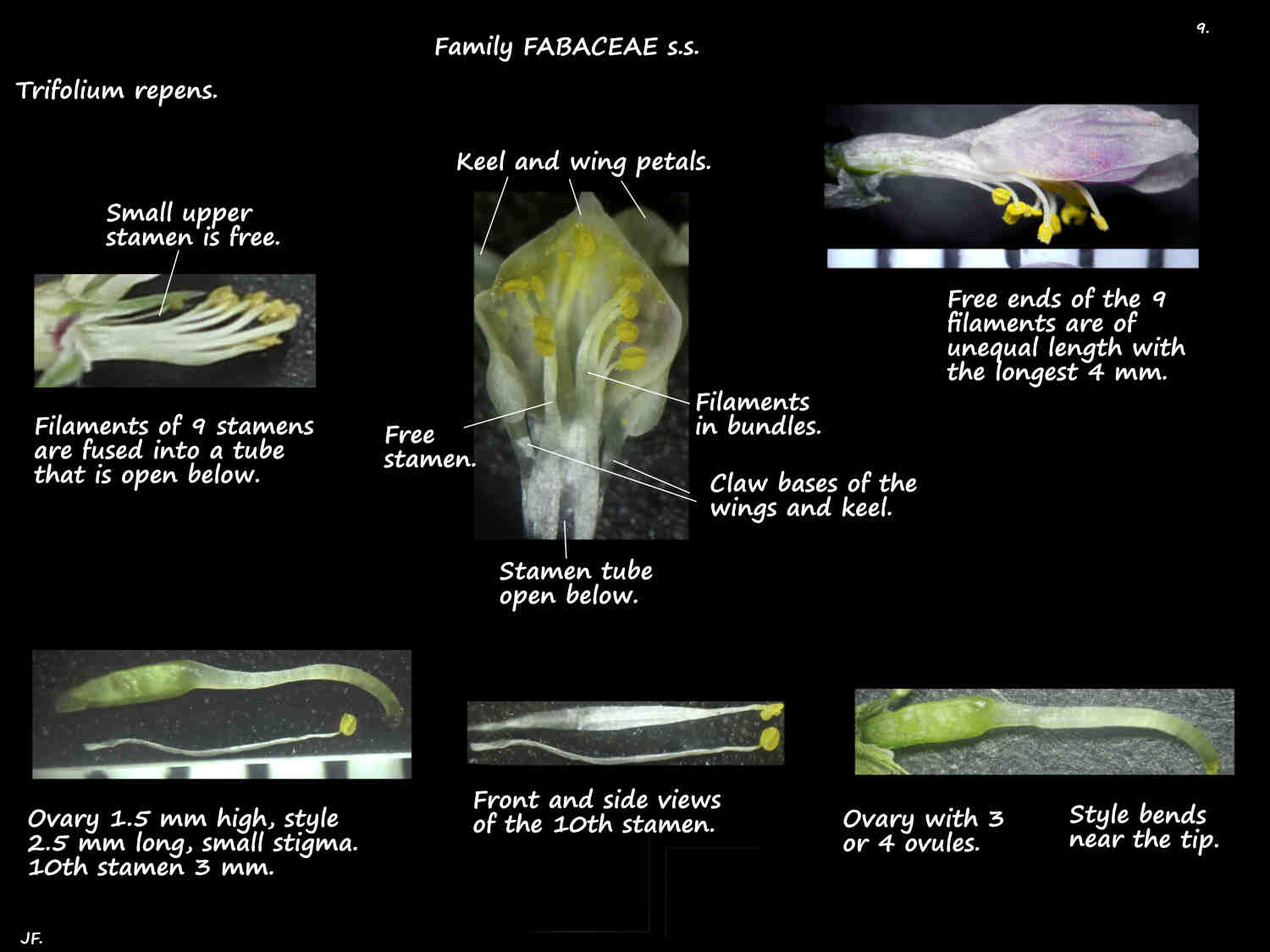
The oblong to elliptic upper or standard petal is the largest.
The sides are folded down around the wings and keel.
The bottom 2 mm of the standard base is fused to a wing petal which is fused to the stamen column.
The 2 side wings have a claw base and an oblong lobe.
At the base of the lobe is a small ear or auricle.
The 2 keel petals are shorter than the wings that enclose them.
The keel petals have a claw base and the oblong lobes are fused along the upper edge and folded down.
The filaments of 9 stamens are fused for up to nearly half their length.
The upper or 10th stamen is free.
The free ends of the 9 fused filaments are of different lengths.
The superior ovary has 3 or 4 ovules and the style is bent.
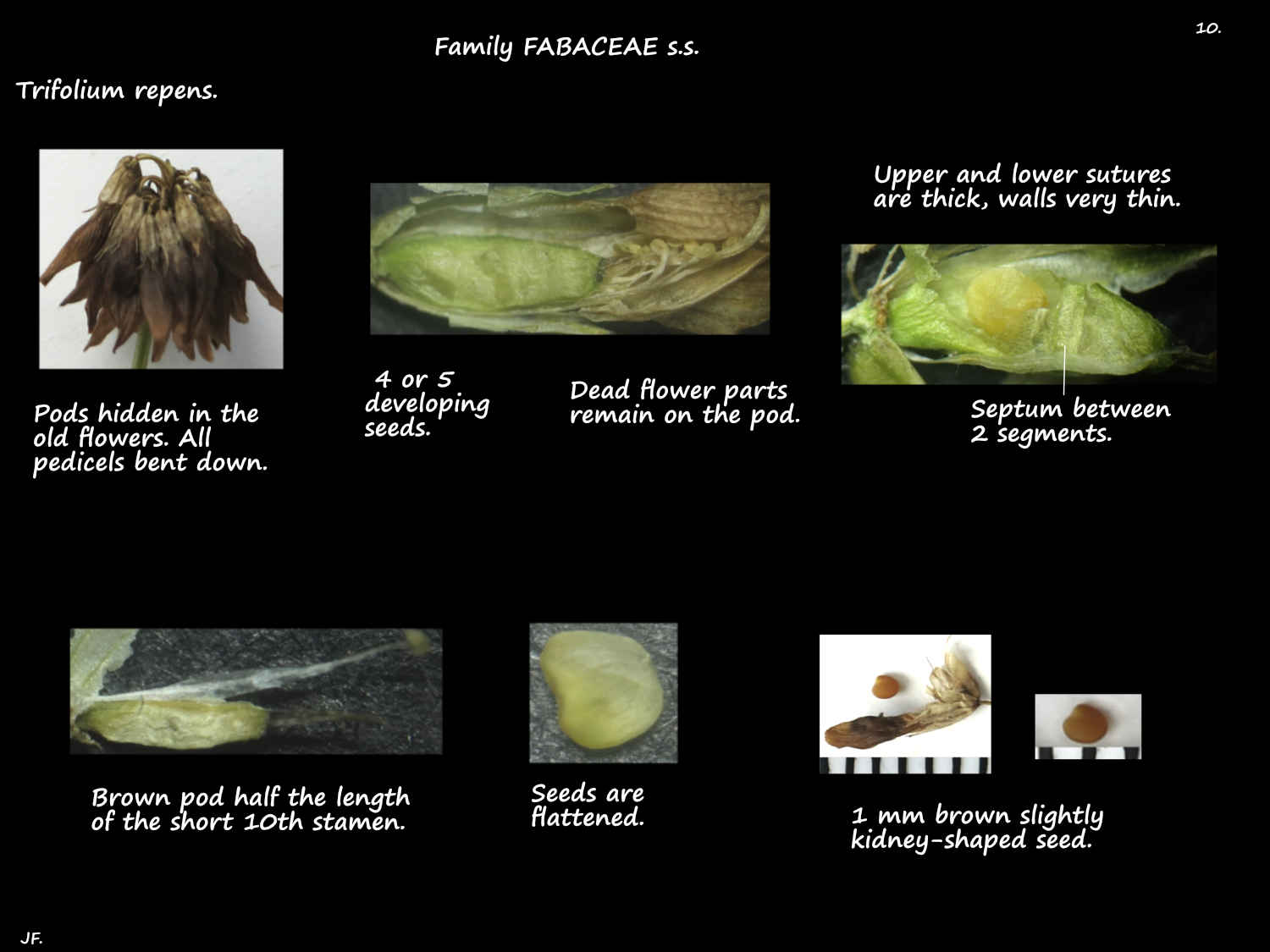
Fruit are a narrow oblong legume or pod compressed between the seeds (strictly a loment).
The enlarged calyx remains on the base of the around 5 mm long pod.
The whole fruit is enclosed by the old dead corolla.
The ovoid or kidney-shaped seeds are a pale brown.
J.F.