Ficus rubiginosa f. glabrescens.
The Rusty or Port Jackson fig is native to the east coast areas of Queensland and N.S.W.
These non-strangling trees are seen in large parks and gardens.
Trees may start as an epiphyte on another tree or in cracks in rocks, walls, pavements etc.
Reaching the ground their aerial roots can develop into multiple trunks that are fused to various degrees.
Germinating in the ground they typically have a single trunk.
Most trees seen are around 10 m high but they can reach 25 or 30 m.
They have a dense rounded canopy and may be wider than tall.
The trunk bark can be pale grey or yellow-brown and aerial roots are few or absent.
The buttress roots increase in size and spread as the tree grows.
Small twigs are green while older ones are brown.
Twigs and petioles may have no hairs or have white/translucent ones sometimes mixed with very small rust-coloured hairs.
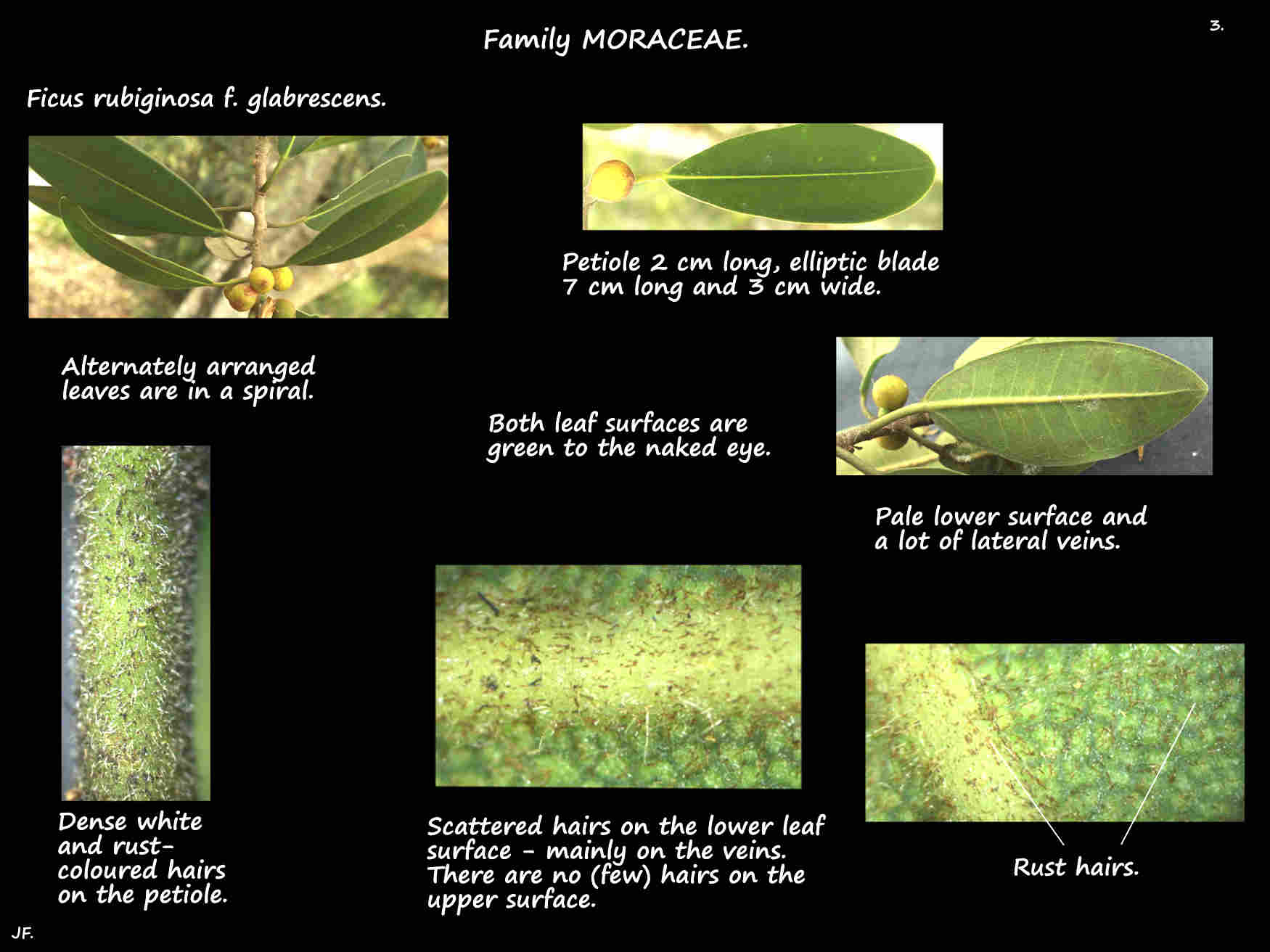
The simple alternately arranged leaves, on petioles 2 to 4 cm long are in a spiral.
Leaf buds are covered by stipules 3 to 7 cm long that may be smooth but usually have hairs like the twigs and petioles.
The stipules fall off early leaving a scar on the branch.
The medium to dark green leaf blades are mostly ovate, elliptic or widely elliptic.
Young leaves have a few rust-coloured hairs on the lower surface and sometimes on both.
Adult leaves usually have no hairs on the upper surface but the lower surface may have a few.
There are many close lateral veins with the basal pair being the most prominent.
Inflorescences are paired syconia in the axils of leaves or the leaf scars on a bare branch.
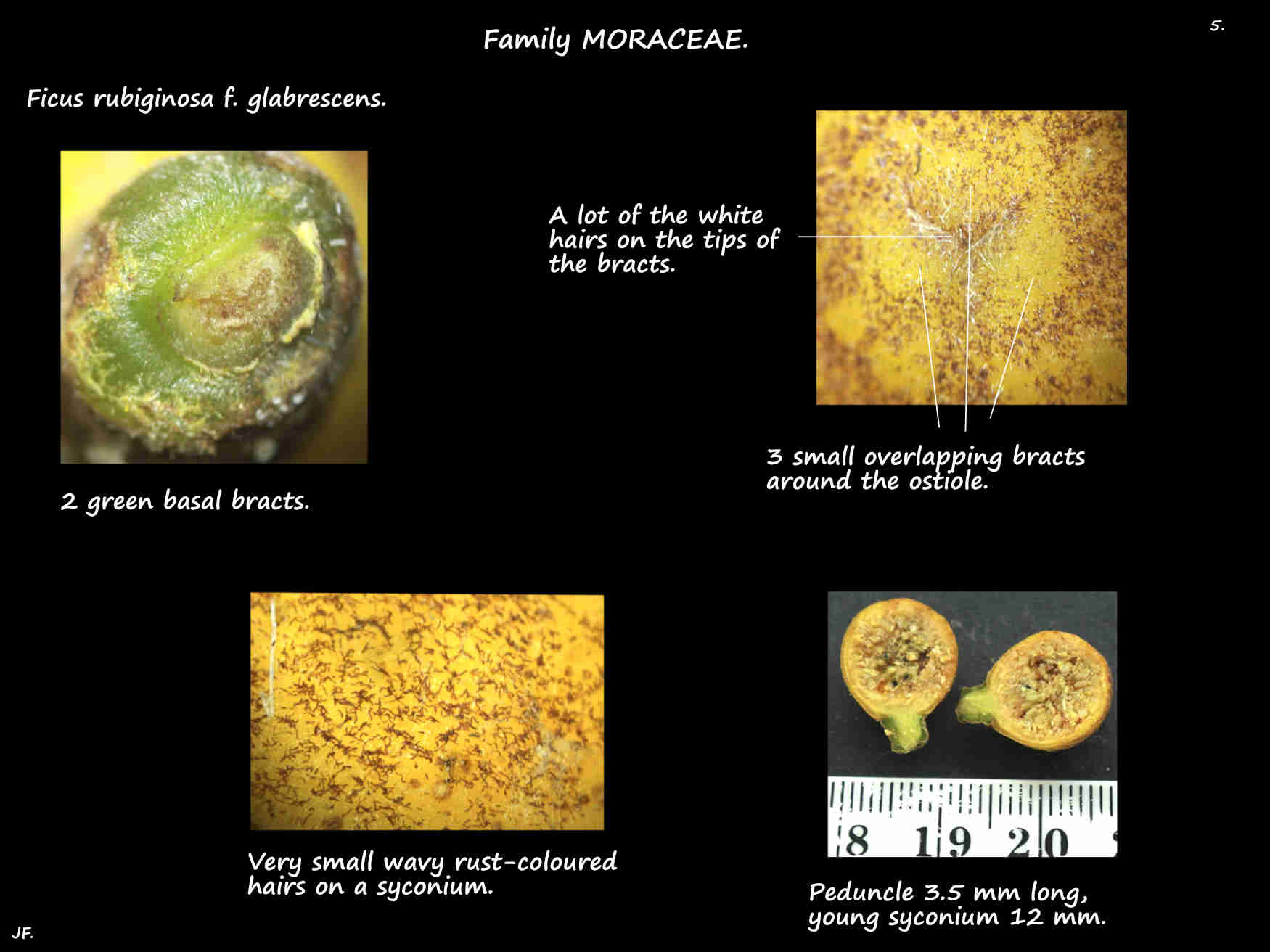
The 1 cm, roughly spherical yellow syconia are on a stalk or peduncle up to 5 mm long.
At the top of the peduncle are 2 (3) basal bracts that fall off.
There are 3 or 4 small bracts around the small opening or ostiole at the other end.
Young syconia have rust-coloured hairs but mature ones may have none.
The surface has small pale nodules or warts.
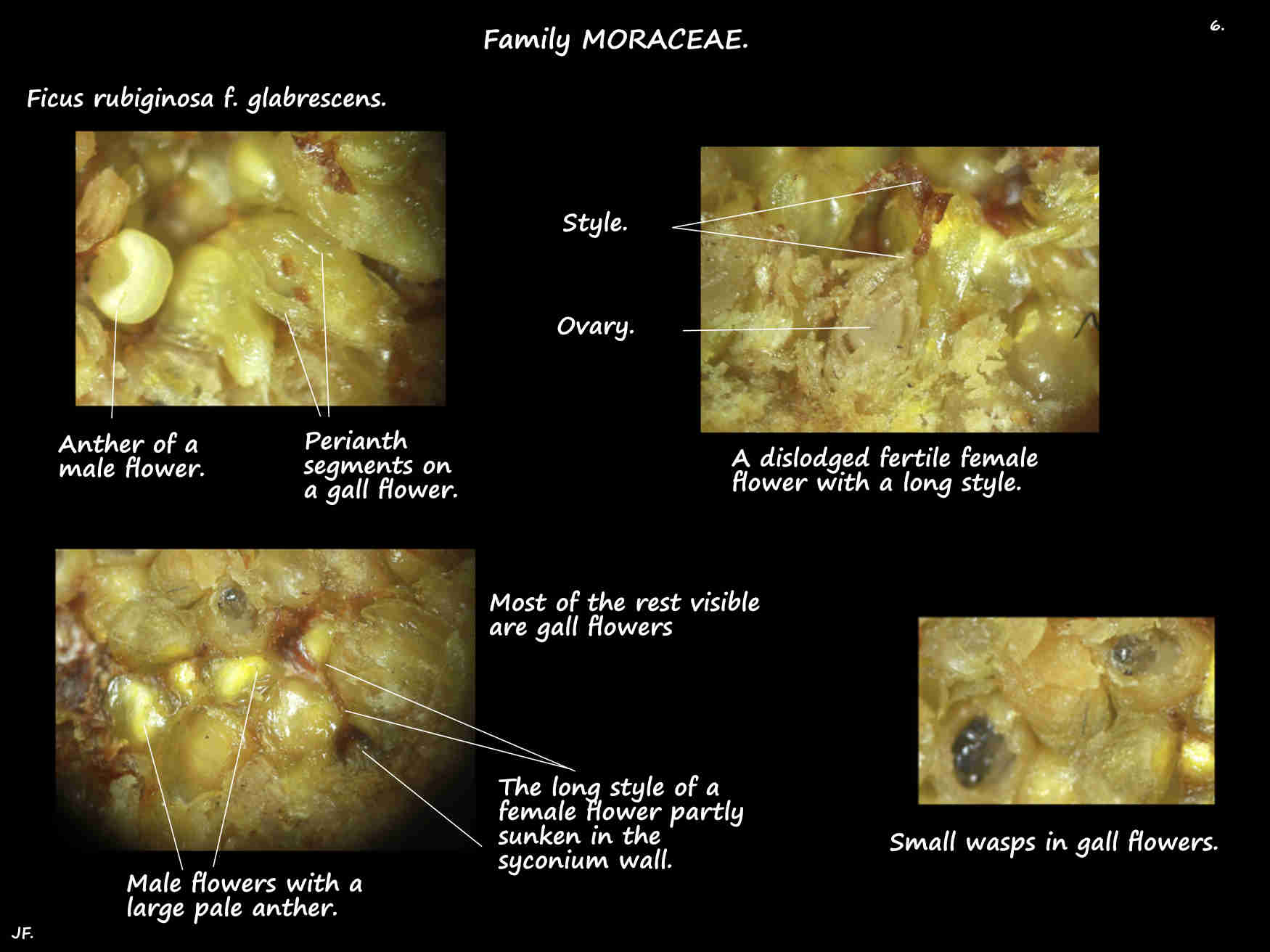
Lining the inner wall of the fleshy syconium are male, female and gall flowers.
They are all mixed together and separated by translucent or whitish bracts.
All have 3 to 5 translucent perianth segments or calyx lobes.
Male flowers, on a short pedicel have 1 prominent white anther.
The female flowers, with a long style are partly sunken into the wall.
The gall or sterile female flowers are taller than the female ones and have a short style.
A female wasp lays her eggs in the gall flower ovaries as she cannot reach the fertile flowers.
Mature fruit are figs up to 2 cm wide on a short stalk.
Initially yellow with small raised greenish spots they become orange then sometimes red.
Trees usually have some fruit on them all year.
Ficus rubiginosa is a variable species and the two forms described may be found in the same area.
Ficus rubiginosa f. glabrescens has no hairs on the upper leaf surface and only scattered rust-coloured ones
on the lower surface together with the longer whitish ones.
Ficus rubiginosa f. rubiginosa has more hairs on the lower leaf surface giving it an obvious rust colour.
J.F.