Psidium guineense.
The Brazilian guava is naturalised in Queensland where it is an environmental weed.
They can grow as a shrub around 3 m high or a tree up to 6 or 7 m.
They can sucker from the base forming thickets.
There are hairs on the round or slightly angular young branches.
The trunk and older branches have greyish bark.
The leaves are opposite or sub-opposite and on petioles up to 1.5 cm long.
Leaves are up to 12 or 14 cm long and 8 cm wide.
The stiff green or greyish-green blades can be ovate, obovate, oblong or elliptic.
The edge is typically smooth but occasionally it has fine teeth.
The lower surface has rust-coloured or pale hairs while the upper surface may have a few.
There are up to 10 lateral veins and the translucent oil glands are obvious on the lower surface.
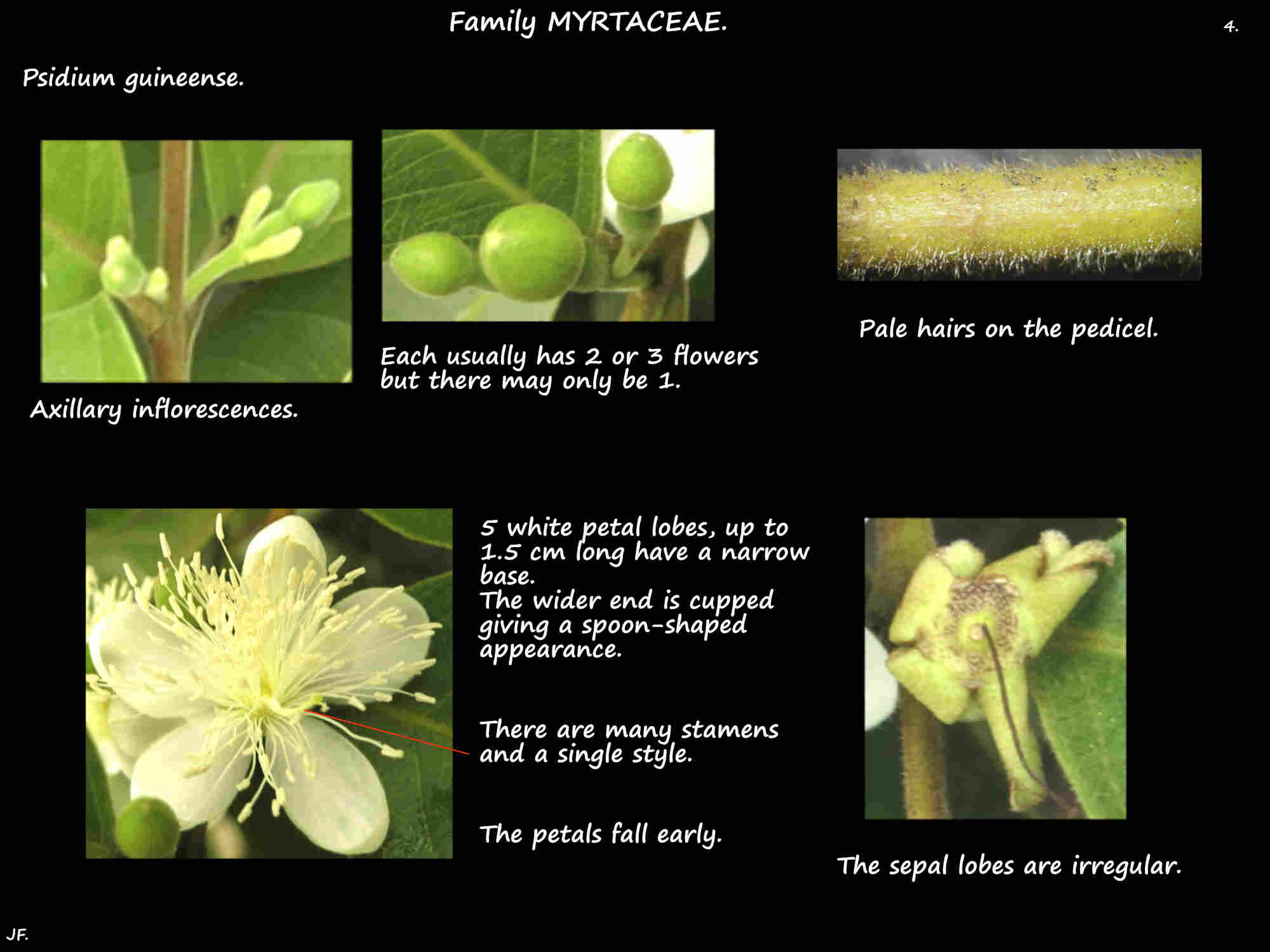
Axillary inflorescences can be single flowers but mostly there are 2 or 3.
Flowers, on thin stalks are around 2.5 cm across.
The sepal and petal bases are fused into a hypanthium which has hairs on it.
The up to 5 often unequal green sepal lobes have hairs on the outer surface.
The 5 white petal lobes are spoon-shaped up to 1.5 cm long and slightly narrower.
The petals fall off early.
There are up to 200 stamens on white filaments around 1 cm long.
The anthers open inwards through longitudinal slits.
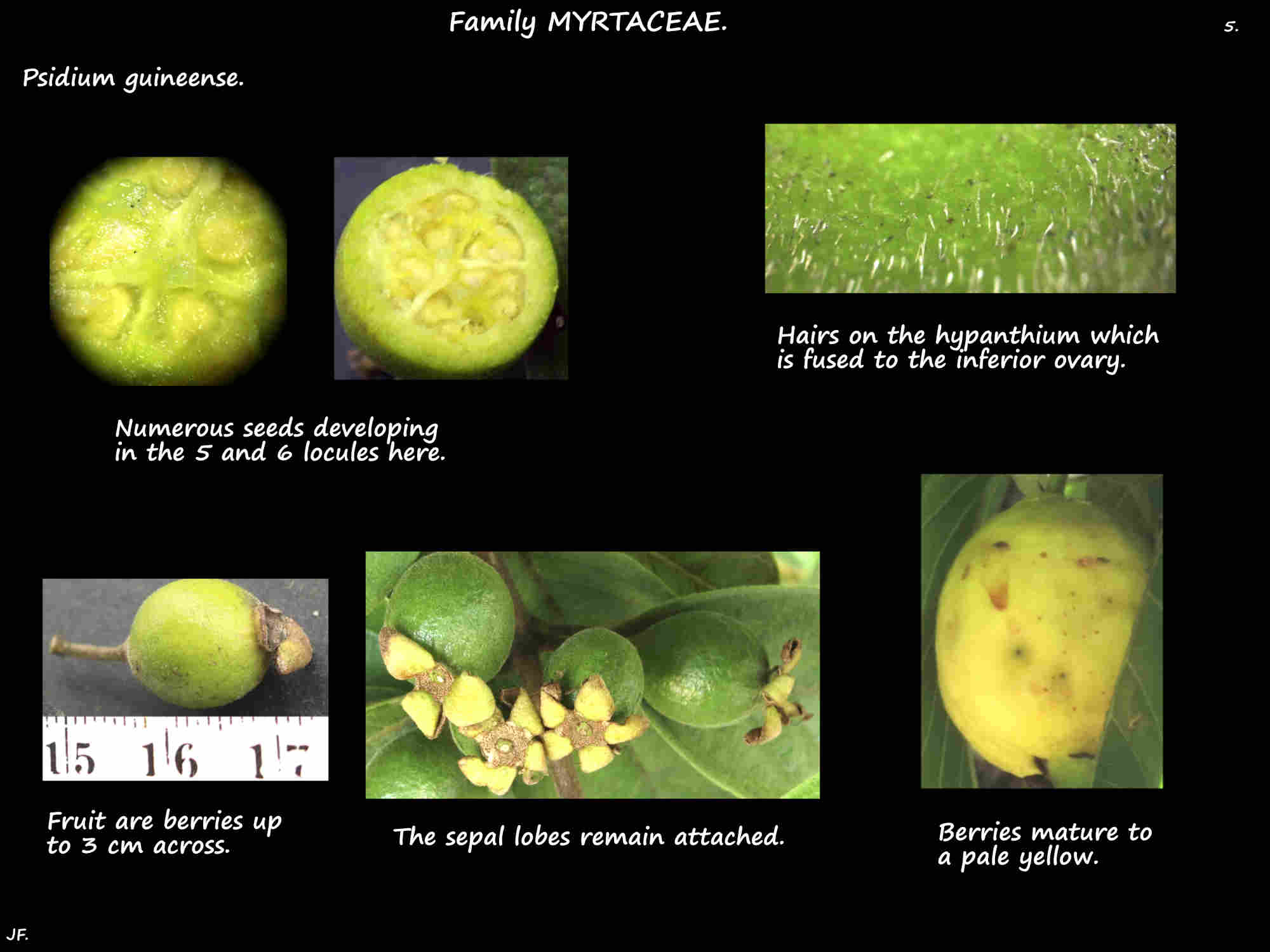
The inferior ovary is fused to the hypanthium.
Each of its many locules have numerous ovules.
There is a single style just over 1 cm long with a white stigma.
The fruit are round or slightly pear-shaped berries up to 3 cm across.
They mature from green to yellow and retain the short hairs.
The flesh under the skin is pale yellow while that around the many hard seeds is white.
There are a number of varieties and a hybrid with Psidium guajava.
J.F.