Daphne.
Family Thymelaeaceae > Subfamily Thymelaeoideae.
Most people recognise 70 to 95 species but estimates range from 50 to 100 and there are nearly 50 cultivars.
Many are grown as garden ornamentals and for the scented flowers.
They are compact evergreen or deciduous shrubs nearly 2 m high down to prostrate ground covers from 20 cm high.
Some have hairs on young stems.
The leaves are mostly alternately arranged in a spiral and concentrated near the branch ends.
On a very short or no petiole they are simple, often with a blunt tip and mostly a smooth edge.
Horticulturally they can be divided into large and small leaved varieties.
The blades can be ovate, oblong or lanceolate.
Young leaves may be copper coloured and young and adult leaves may have hairs.
Inflorescences are often terminal on the main or short side branches.
They can also be in the leaf axils or on bare stems at old leaf scars.
They consist of 2 or 3 flowers up to dense clusters of around 20.
The inflorescence may be directly attached to the branch or on a short stalk or peduncle.
Clusters can be a rounded head, a spike or branched.
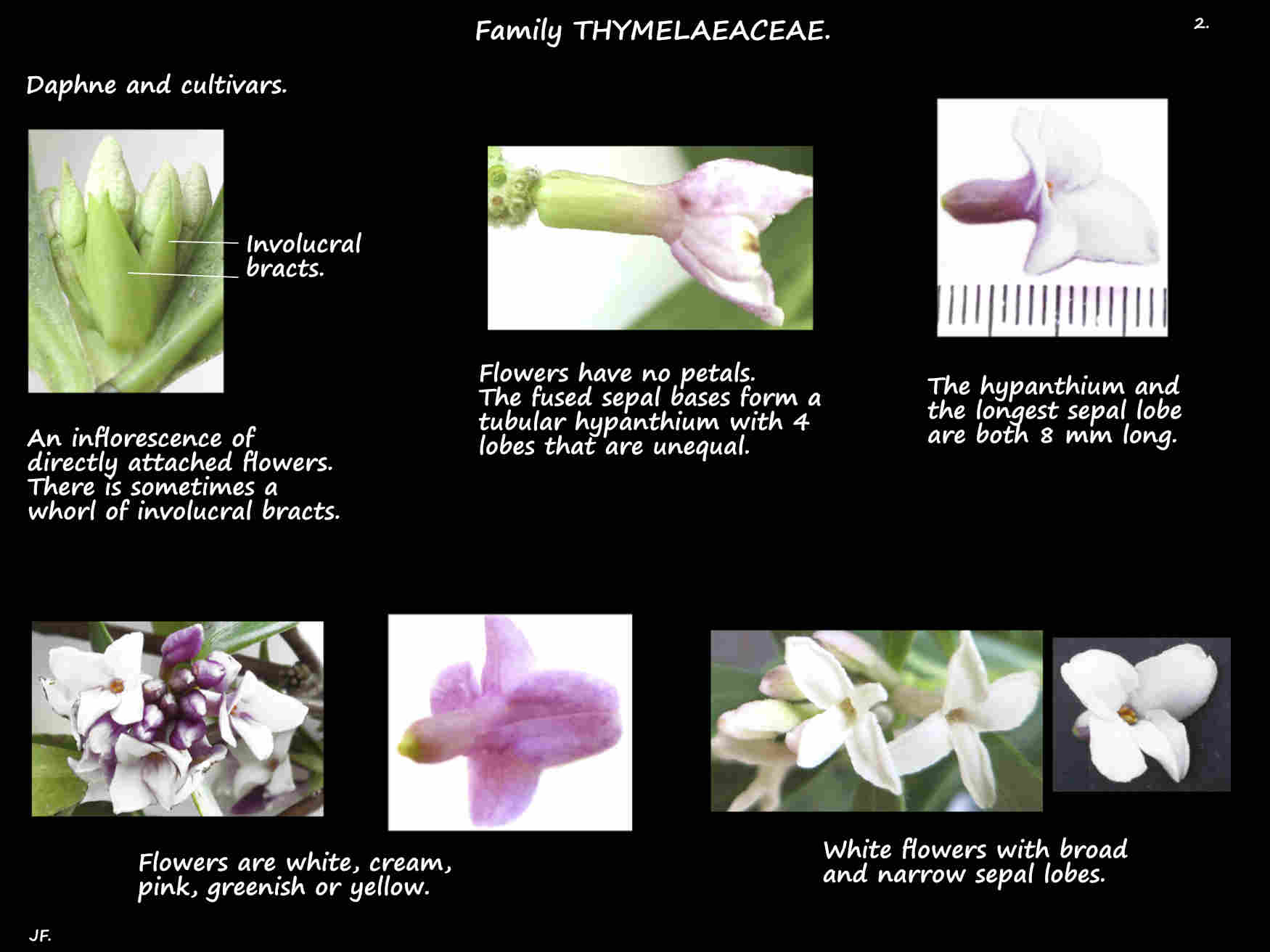
There are no bracts and involucal bracts may be present.
The flowers, on a short or no stalk or pedicel have no petals.
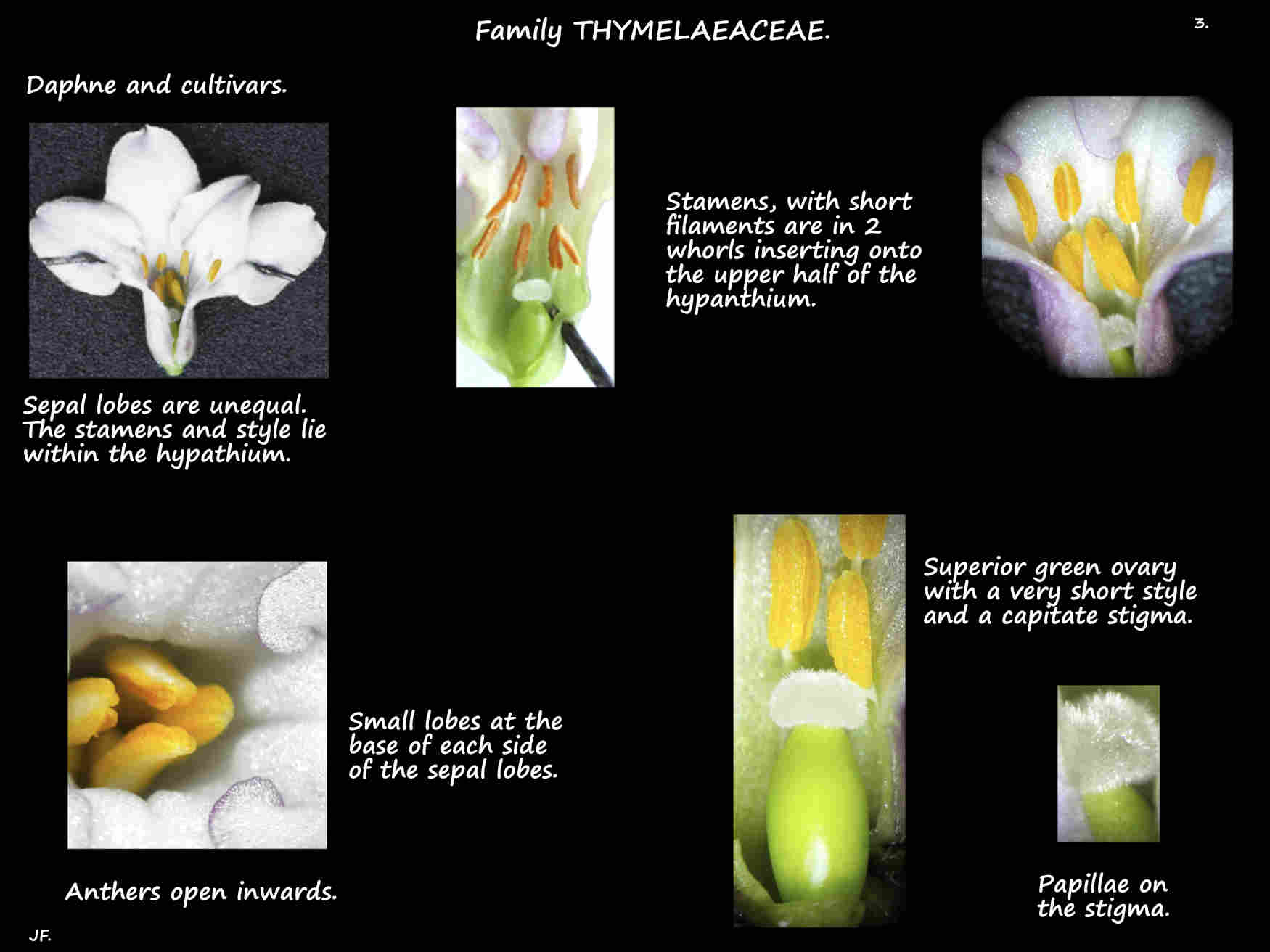
The bases of the sepals are fused into a narrow tubular or funnel-shaped hypanthium with 4 (5) lobes on the rim.
The lobes are erect, spreading or curved back.
There may be hairs on the outer surface.
As well as white they may be cream, yellow, pale green or pink.
The 8 stamens are inserted in 2 whorls in the upper part of the hypanthium.
The anthers, on a short or no filament do not extend past the perianth.
There may be a nectary disc at the base of the hypanthium.
The superior ovary, occasionally on a short stalk or gynophore has 1 locule.
There is a short style with a spherical (capitate) stigma that lies within the hypanthium.
The red, yellow or black fruit, with 1 seed are described as fleshy berries or dry and drupe-like.
J.F.