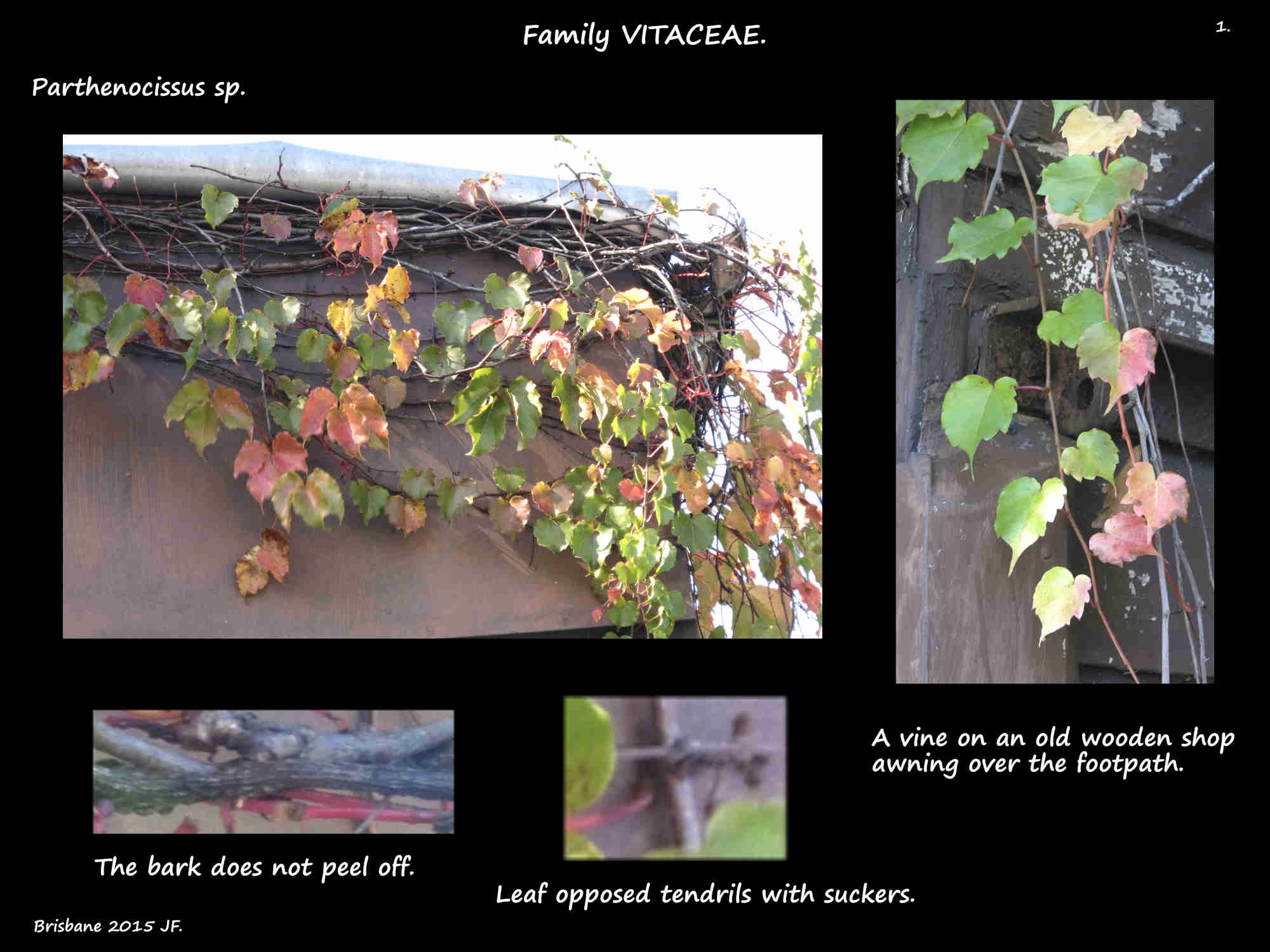
Parthenocissus.
Family Vitaceae > Subfamily Vitoideae.
There are 15 species from Asia and North America.
One species is naturalised in Australia, some are used in gardens and there are many cultivars.
The mostly deciduous woody vines climb using tendrils that are usually branched.
There are lenticels on the branches and the bark does not peel off.
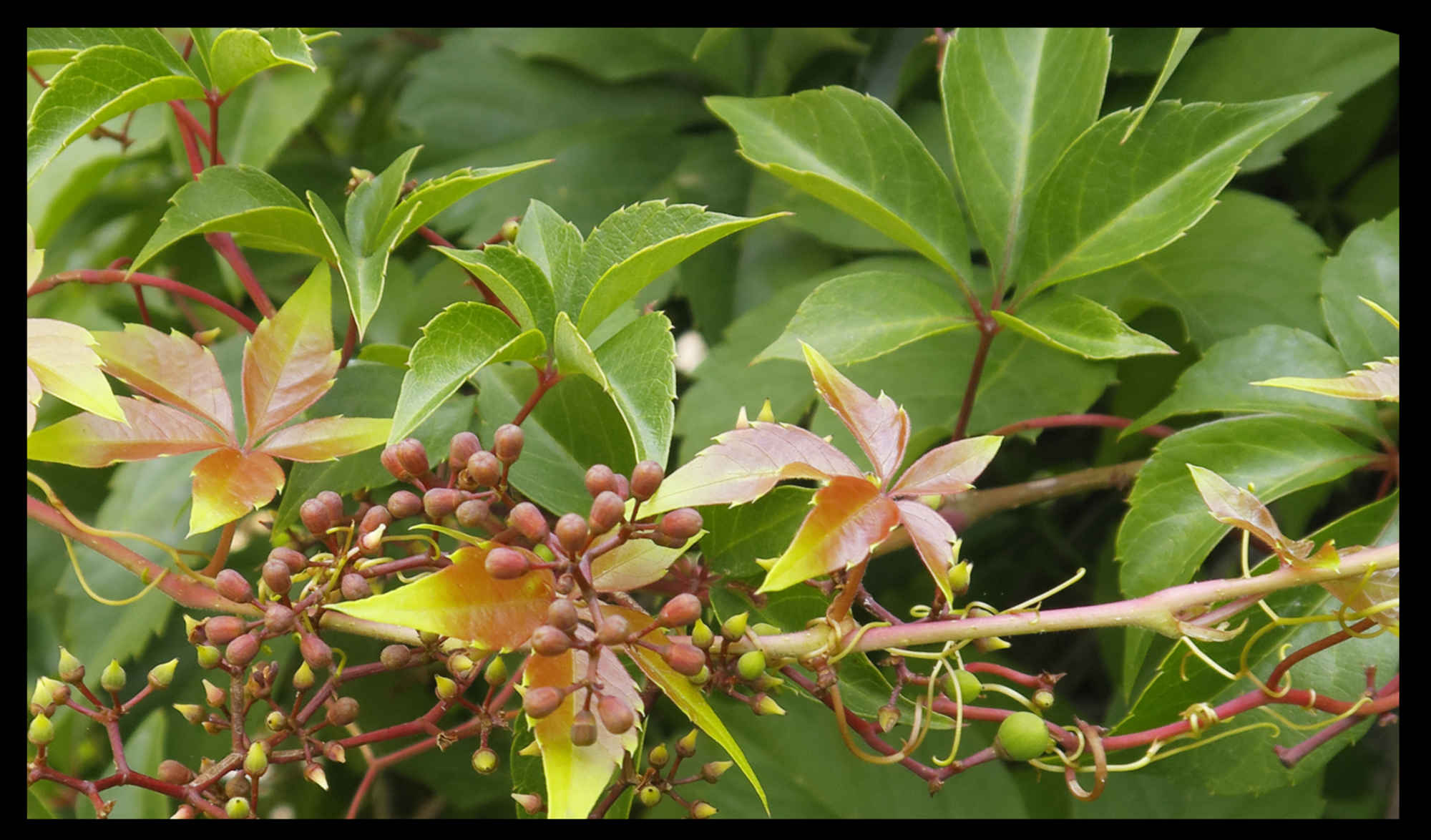
Leaf opposed tendrils can have up to 12 branches.
The slightly swollen tips of the tendrils have suckers.
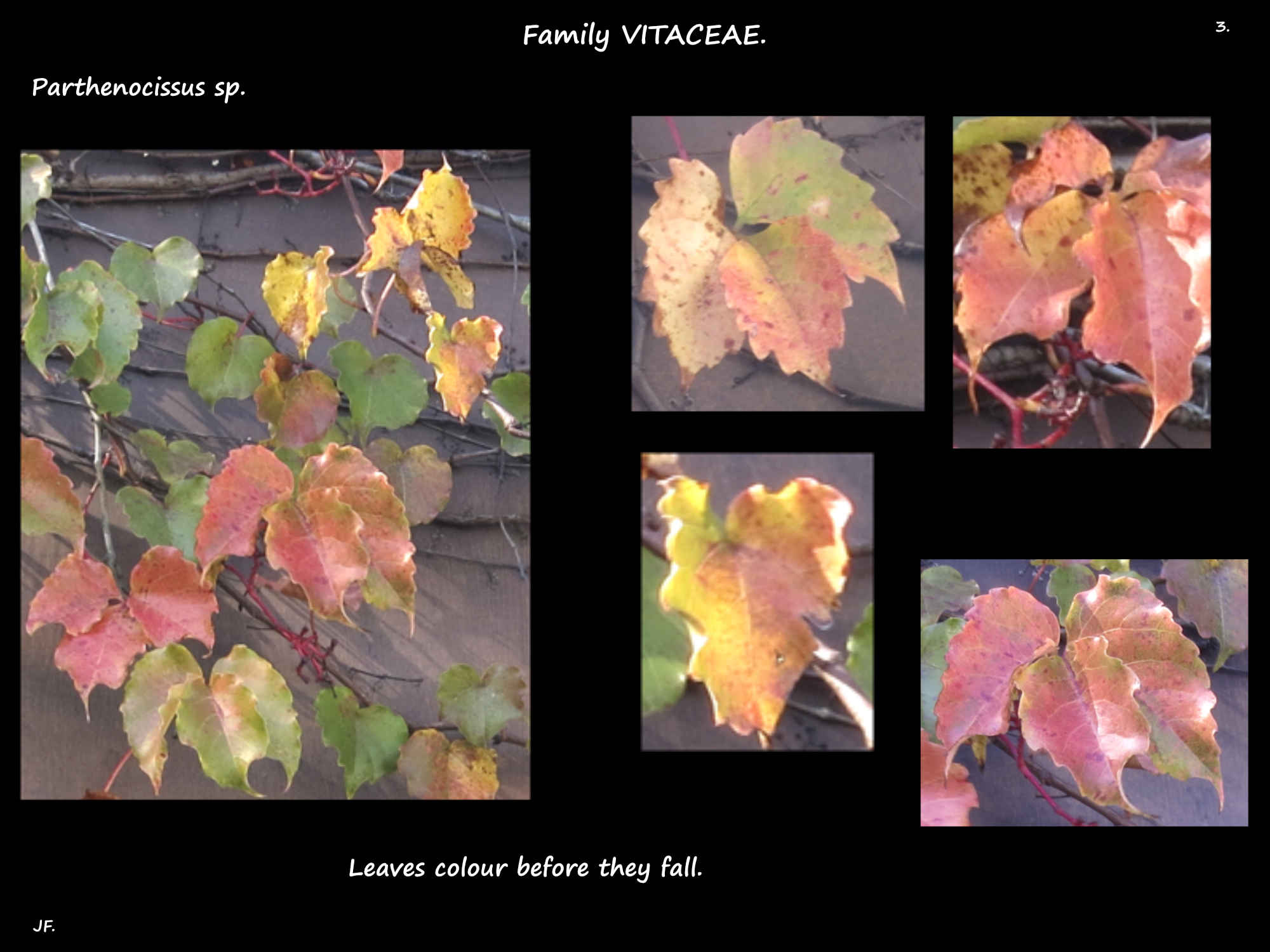
The alternate leaves, on long petioles are usually palmately lobed but some are simple.
Petioles may be grooved on the upper surface.
Leaves can have 3, 5 or 7 leaflets on very short to almost absent petiolules.
Leaflets can be elliptic or obovate and up to 15 cm long.
The edges have teeth with a short, sharp point on the tip.
There may be hairs on the petioles, petiolules and the veins on the lower surface.
There may be 2 green or red stipules, a few mms long.
The leaf opposed or pseudo-terminal inflorescences are branched clusters of flowers.
They can be up to 20 cm long, on a long peduncle and they have bisexual flowers on pedicels.
Bracts and bacteoles may be present and there may be small glandular hairs.
The cup-shaped calyx may have a flat rim or 5 very small teeth or lobes.
The 5 ( 3 to 9) petals may be free or when the tips are joined they can form a hood or calyptra.
There are 5 (6) stamens on filaments under 1 cm long with dorsifixed anthers.
Where there is a beak on the petal tips they lie over the anthers.
The disc may be absent, indistinct or lobular.
The conical superior ovary, a few mms high has 2 locules each with 2 ovules.
There is no obvious style or a short conical one.
The stigma may be slightly lobed.
The fruit are black or dark blue berries around 1 cm across and there may be a short beak.
They often have a white bloom and the flesh is green or purple.
The 1 to 4 seeds have 2 long infolds on the ventral (front) surface and an apical notch.
There is an oval chalaza on the dorsal surface where the ovule/seed was attached to the placenta.
J.F.