Alpinia caerulea.
Common or Native Ginger, in Family Zingiberaceae, is native to Australia.
Often cultivated in gardens it is one of the most commonly seen gingers in Brisbane.
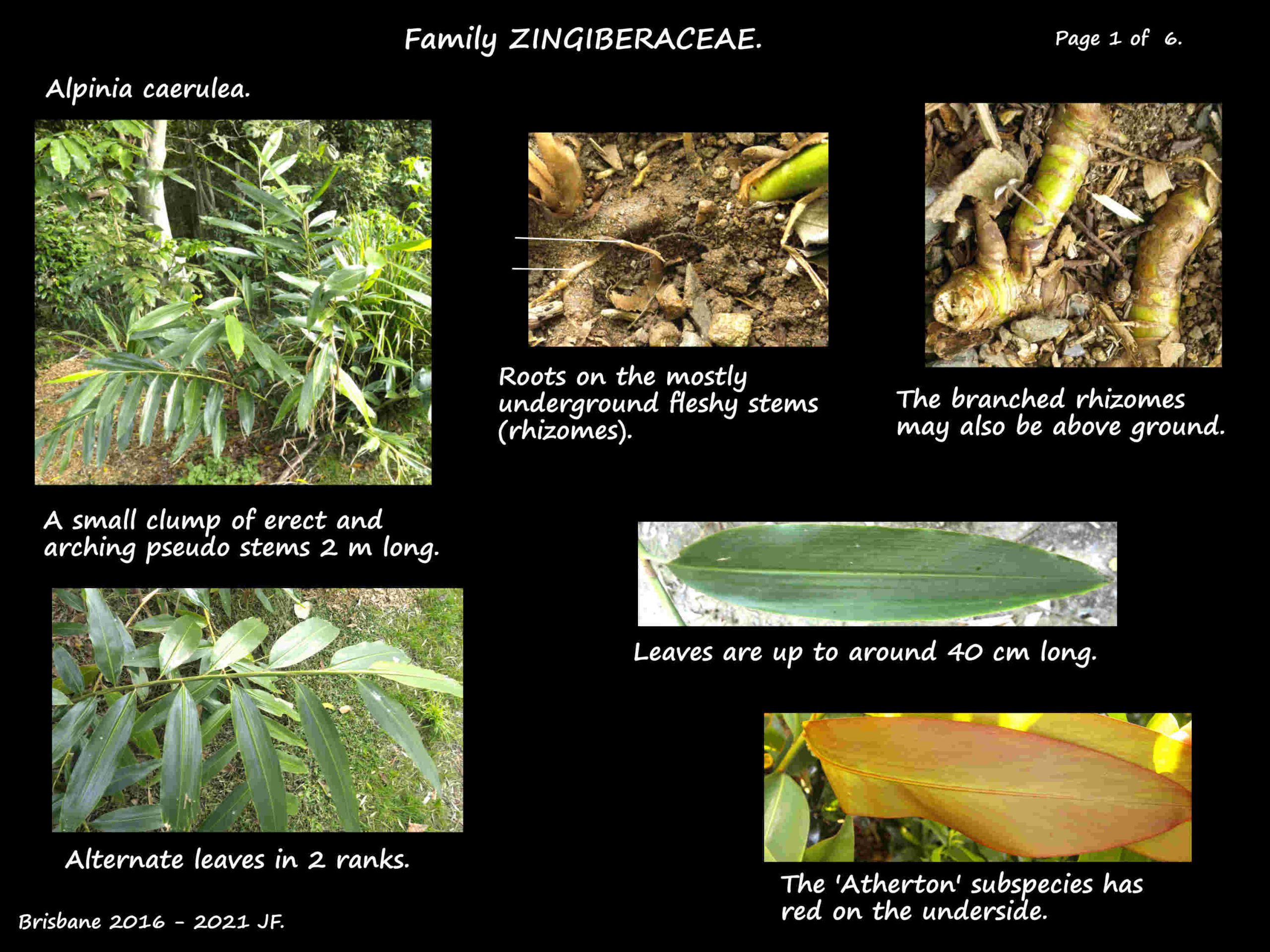
Growing from rhizomes (the underground stem) they form dense clumps.
The above ground canes are pseudo stems formed from the overlapping leaf sheaths.
The erect or arching canes are 1 to 2 m high with alternately arranged leaves in 2 ranks.
The oblong to lanceolate leaves have a very short or no petiole.
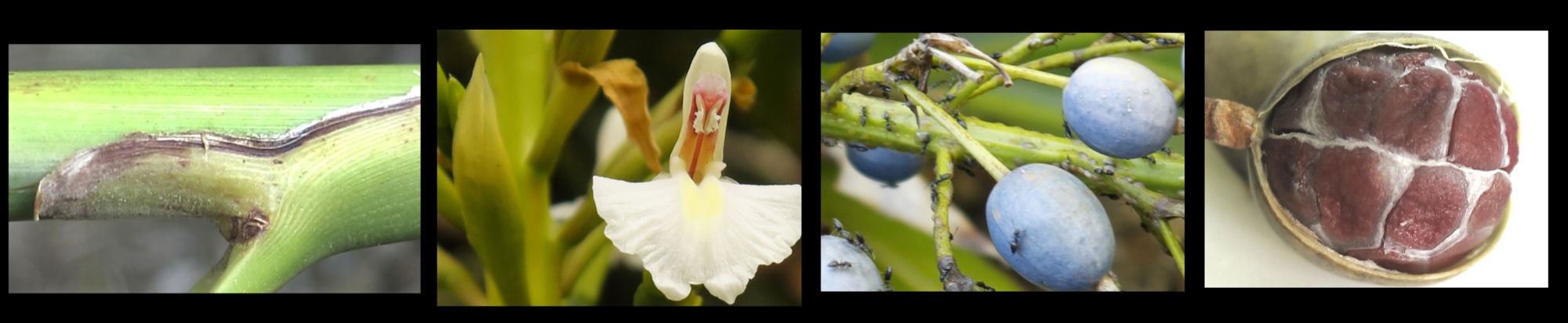
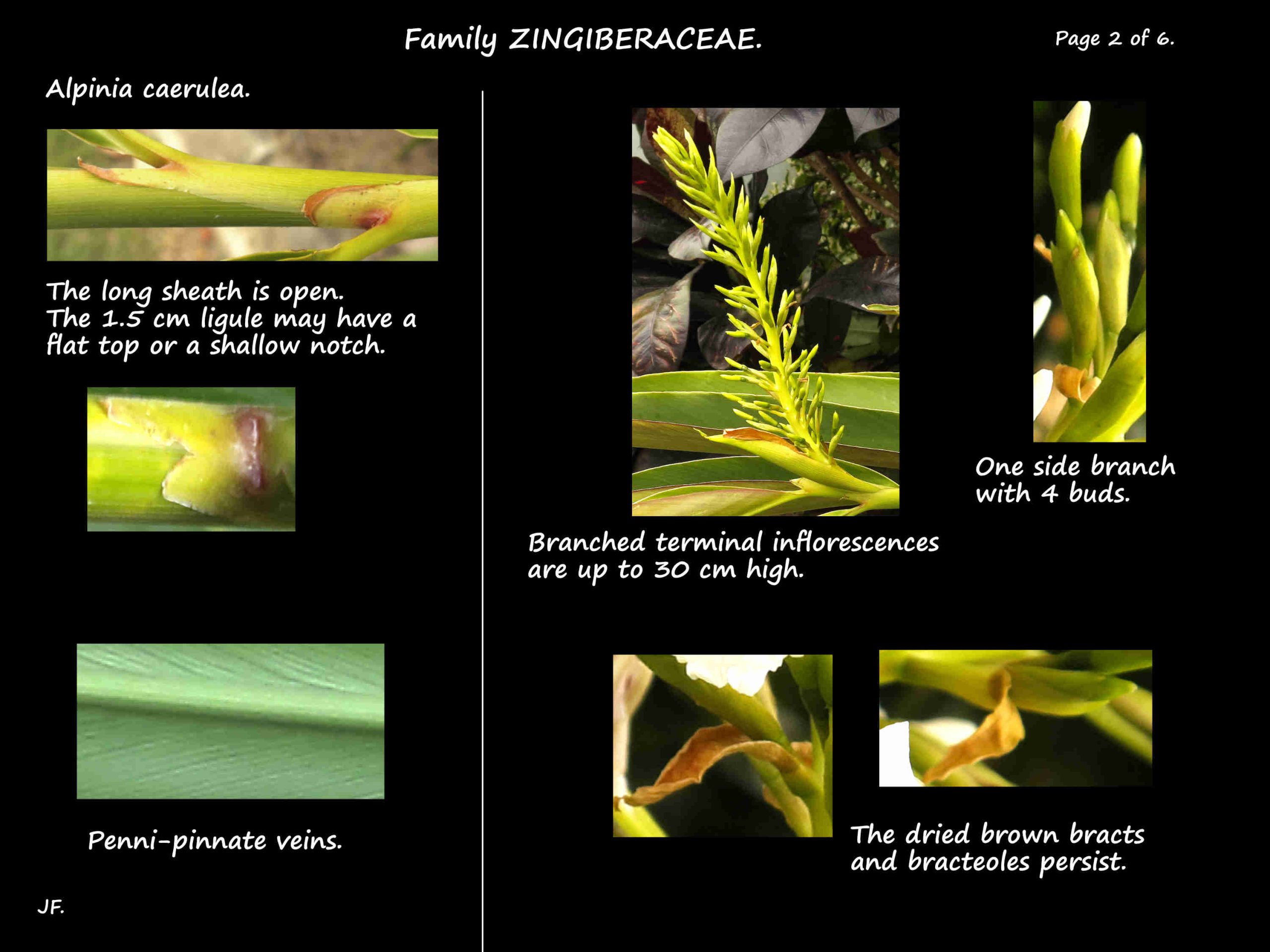
The long sheath down the stem is open (the edges are not fused).
The ligule, up to 1.5 cm long, may have some hairs on the edge.
The top may be flat or have a shallow cleft less than ¼ of the length of the ligule.
The blades are up to 40 cm long and from 3 to 10 cm wide.
The tip is pointed, the base wedge-shaped and the veins penni-pinnate.
Plants in northern Queensland have hairs on the leaves while those in the south tend to have none.
The erect terminal inflorescences are up to 30 cm long on a 1 to 2 cm stalk (peduncle).
They are branched with each side branch having up to 6 flowers.
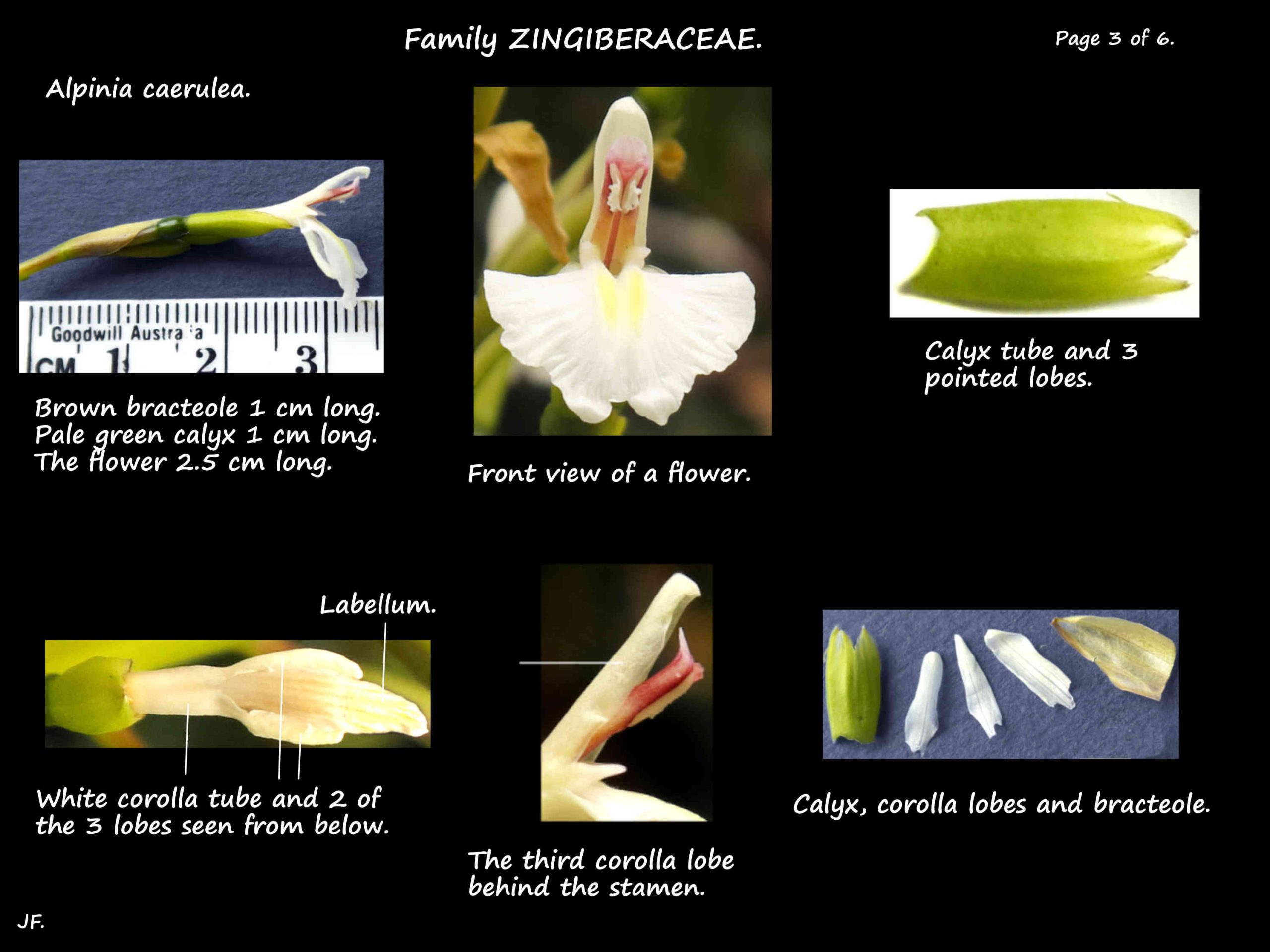
The 2.5 cm long flowers are on stalks (pedicels) around 1.5 cm long.
There are narrow bracts up to 2 cm long at the base of each side branch.
The bracteoles at the base of the flowers are around 1 cm long.
There are usually hairs on the bracts and bracteoles but this is variable.
Flower parts are in threes.
The 1 cm long, green calyx consists of a tube with 3 pointed lobes.
The whitish corolla tube is around 13 mm long with three 6 to 8 mm long lobes.
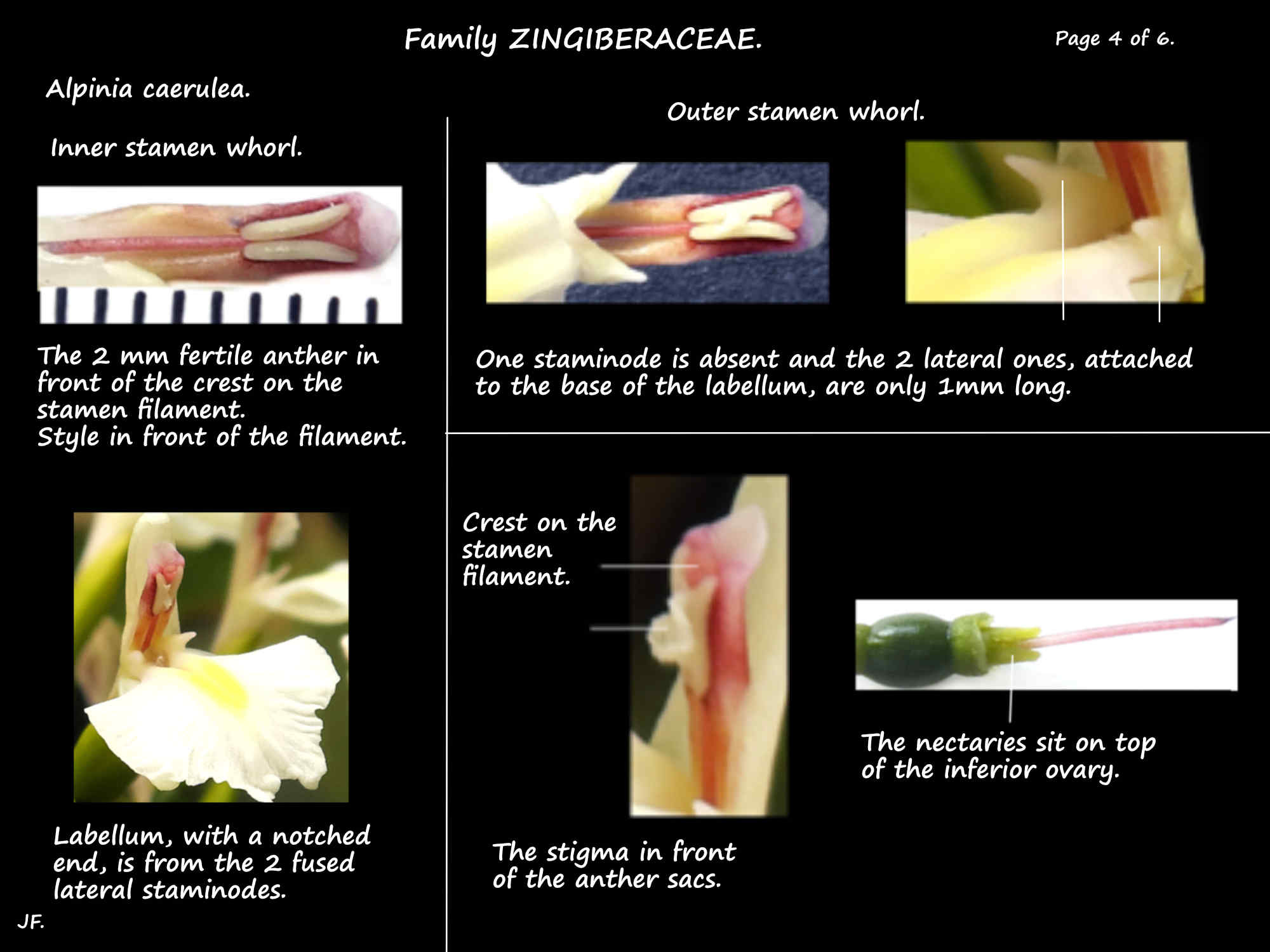
The single fertile stamen, and the staminodes, are in 2 whorls.
In the inner whorl.
i.) The filament and anther of the fertile stamen are both only 2 to 3 mm long.
The filament is wider than the anther and has a crest at the top behind the anther.
ii.) The 2 lateral staminodes are fused into a petal-like labellum.
It has a short narrow base with a circular end about 1 cm across.
It has a short cleft at the tip.
It is white with 2 pale yellow ridges down the centre.
In the outer whorl.
i.) One staminode is missing.
ii.) The 2 lateral are only 1 mm long.
The 6 mm long, green, usually hairy ovary is inferior and has 3 locules.
The 1 cm long style lies in a groove on the stamen filament then between the anther sacs.
The stigma lies between the top of the sacs and in front of the crest.
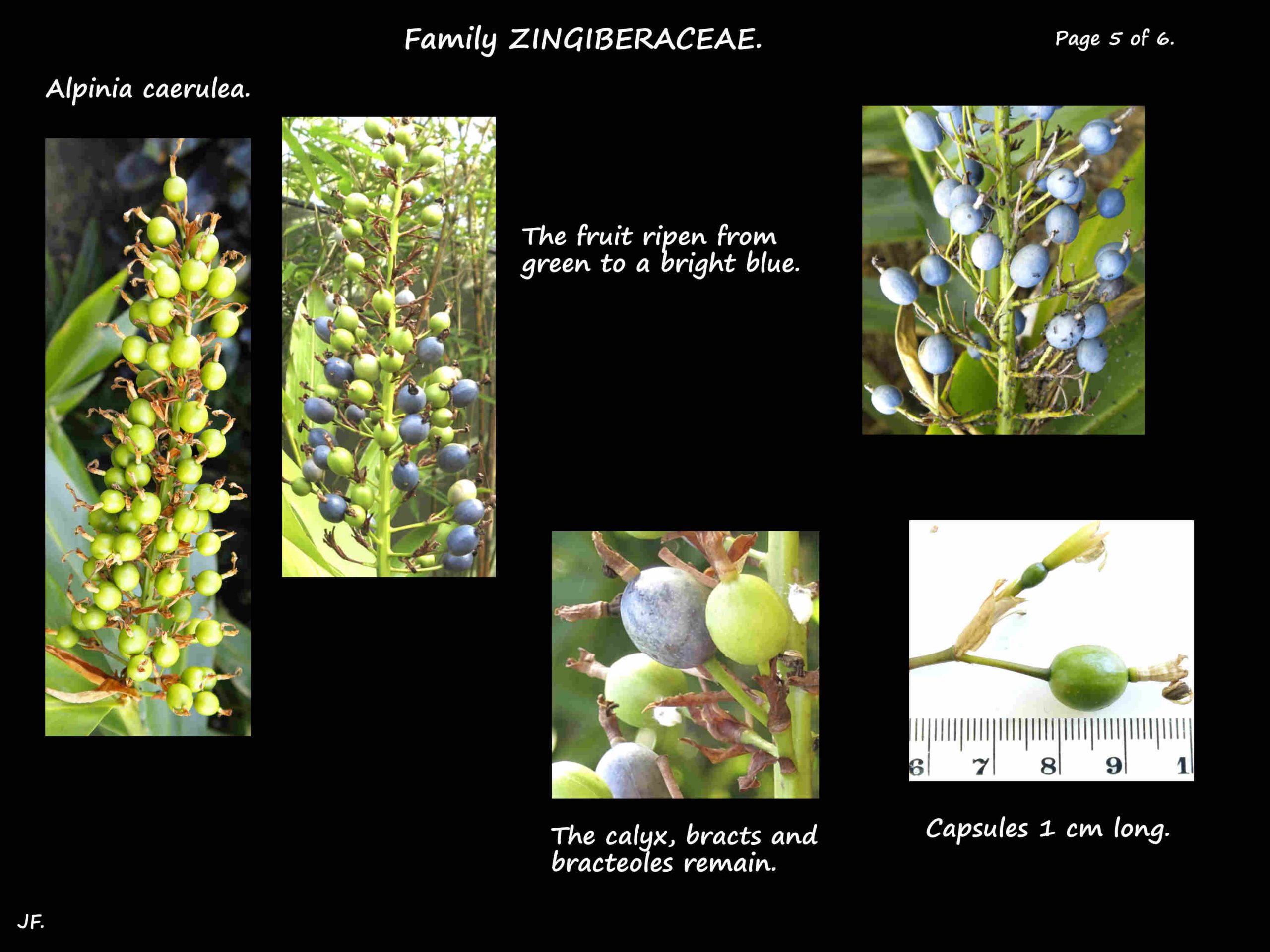
The fruit are spherical capsules about 1 cm long.
They mature from green to blue then become black and papery.
There are numerous black seeds in a white pulp.
There are other species with blue fruit but they are smaller plants with smaller
inflorescences and they lack a bilobed labellum.
Alpinia caerulea ‘Atherton’.
Red back Ginger is a subspecies from near Cairns that is similar to A. caerulea except
that the backs of the leaves are darkish red.
J.F.